Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T06421
(Former ID: TTDS00492)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Interferon alpha/beta receptor 2 (IFNAR2)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Type I interferon receptor 2; Type I interferon receptor; Interferon alpha/beta receptor; Interferon alpha binding protein; IFNARB; IFNABR; IFN-alpha/beta receptor 2; IFN-alpha-REC; IFN-alpha binding protein; IFN-R-2; IFN-R
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
IFNAR2
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Successful target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 6 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Hepatitis virus infection [ICD-11: 1E50-1E51] | |||||
| 2 | Lupus erythematosus [ICD-11: 4A40] | |||||
| 3 | Mature B-cell leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A82] | |||||
| 4 | Multiple sclerosis [ICD-11: 8A40] | |||||
| 5 | Myeloproliferative neoplasm [ICD-11: 2A20] | |||||
| 6 | Renal cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C90] | |||||
| Function |
Receptor for interferons alpha and beta. Involved in IFN-mediated STAT1, STAT2 and STAT3 activation. Isoform 1 and isoform 2 are directly involved in signal transduction due to their association with the TYR kinase, JAK1. Isoform 3 is a potent inhibitor of type I IFN receptor activity. Associates with IFNAR1 to form the type I interferon receptor.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Cytokine receptor
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| Sequence |
MLLSQNAFIFRSLNLVLMVYISLVFGISYDSPDYTDESCTFKISLRNFRSILSWELKNHS
IVPTHYTLLYTIMSKPEDLKVVKNCANTTRSFCDLTDEWRSTHEAYVTVLEGFSGNTTLF SCSHNFWLAIDMSFEPPEFEIVGFTNHINVMVKFPSIVEEELQFDLSLVIEEQSEGIVKK HKPEIKGNMSGNFTYIIDKLIPNTNYCVSVYLEHSDEQAVIKSPLKCTLLPPGQESESAE SAKIGGIITVFLIALVLTSTIVTLKWIGYICLRNSLPKVLNFHNFLAWPFPNLPPLEAMD MVEVIYINRKKKVWDYNYDDESDSDTEAAPRTSGGGYTMHGLTVRPLGQASATSTESQLI DPESEEEPDLPEVDVELPTMPKDSPQQLELLSGPCERRKSPLQDPFPEEDYSSTEGSGGR ITFNVDLNSVFLRVLDDEDSDDLEAPLMLSSHLEEMVDPEDPDNVQSNHLLASGEGTQPT FPSPSSEGLWSEDAPSDQSDTSESDVDLGDGYIMR Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T99S78 | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approved Drug(s) | [+] 6 Approved Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Anifrolumab | Drug Info | Approved | Systemic lupus erythematosus | [2] | |
| 2 | Interferon Alfa-2b, Recombinant | Drug Info | Approved | Hairy cell leukaemia | [3] | |
| 3 | Interferon alfa-n1 | Drug Info | Approved | Chronic myelogenous leukaemia | [3], [4] | |
| 4 | Interferon alfacon-1 | Drug Info | Approved | Hepatitis C | [3], [4] | |
| 5 | Interferon beta-1b | Drug Info | Approved | Multiple sclerosis | [3] | |
| 6 | Sifalimumab | Drug Info | Approved | Renal cell carcinoma | [5], [6] | |
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 1 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Alfa-interferon | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Endometriosis | [7] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 3 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Antagonist | [+] 1 Antagonist drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Anifrolumab | Drug Info | [2] | |||
| Binder | [+] 4 Binder drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Interferon Alfa-2b, Recombinant | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 2 | Interferon alfa-n1 | Drug Info | [9], [10], [11] | |||
| 3 | Interferon alfacon-1 | Drug Info | [12] | |||
| 4 | Interferon beta-1b | Drug Info | [13] | |||
| Stimulator | [+] 1 Stimulator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Alfa-interferon | Drug Info | [15] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
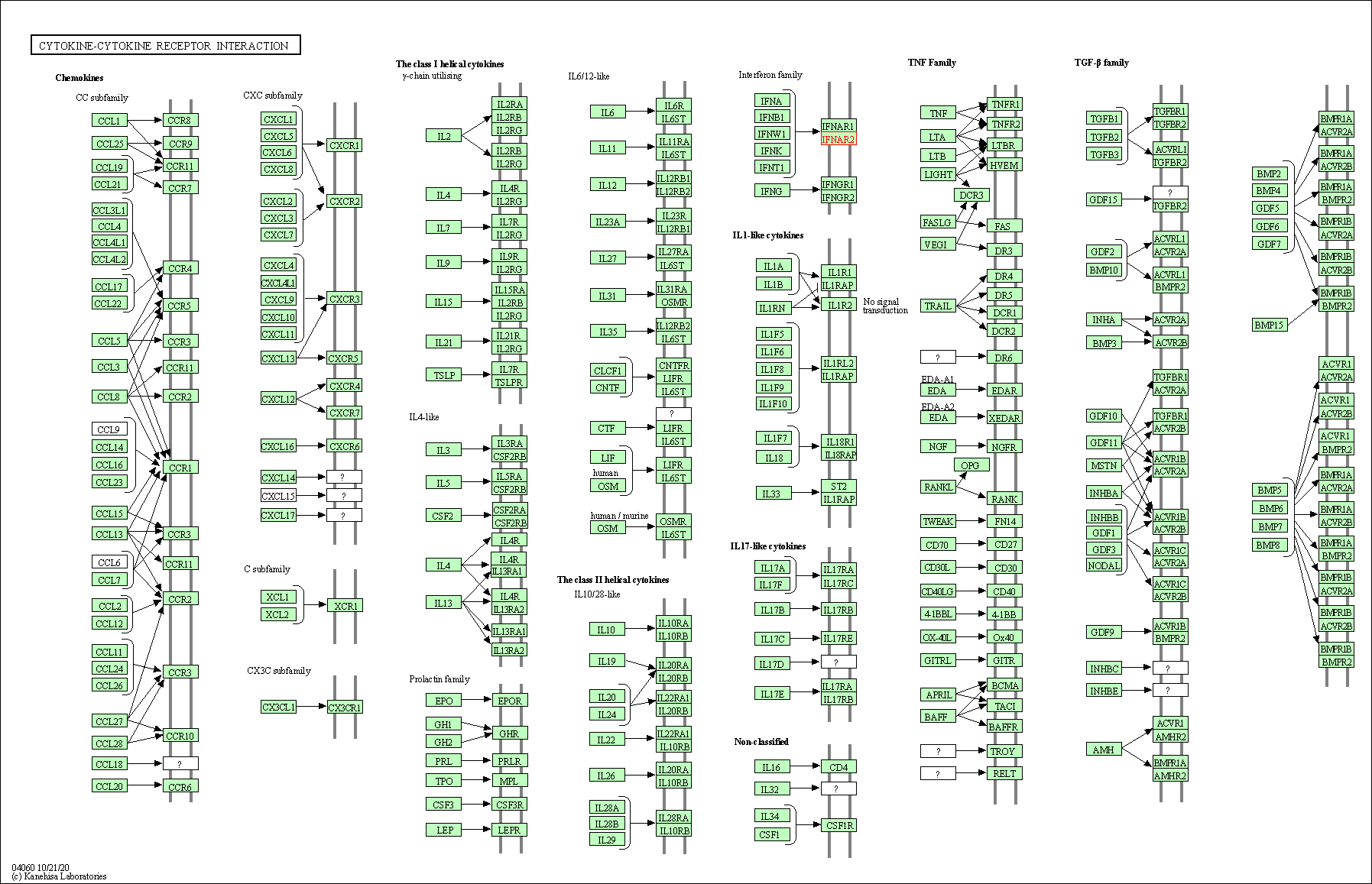
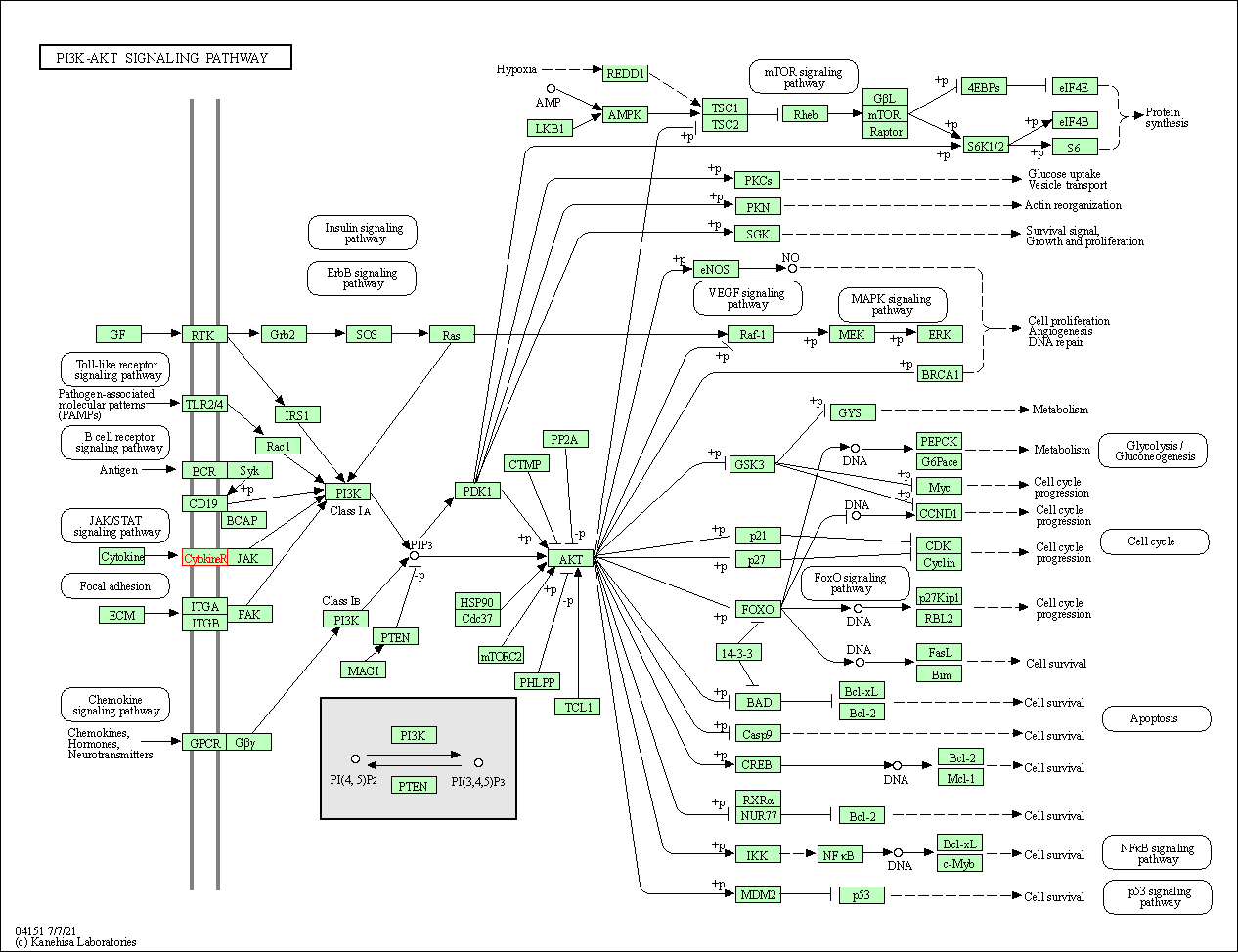
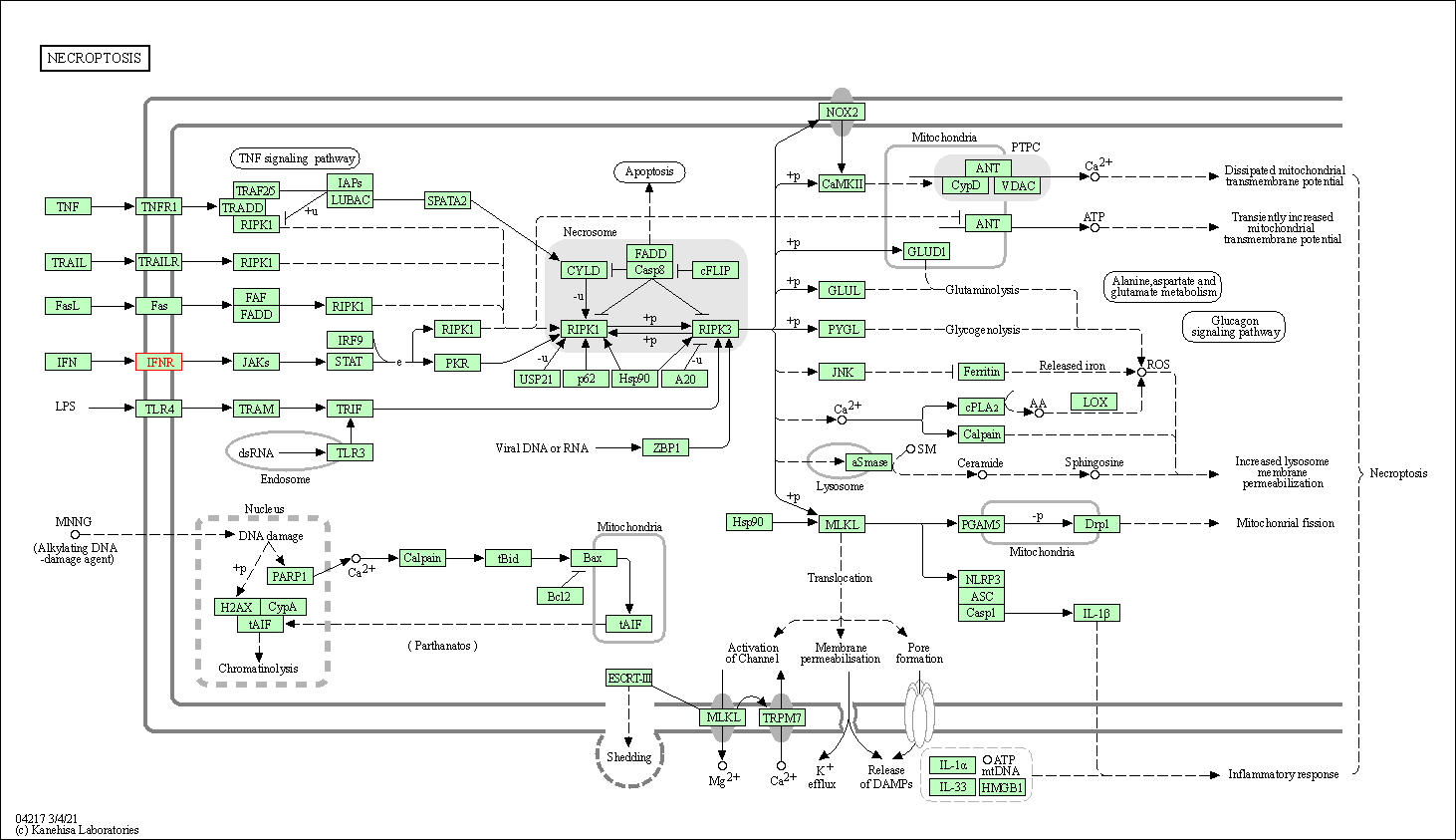
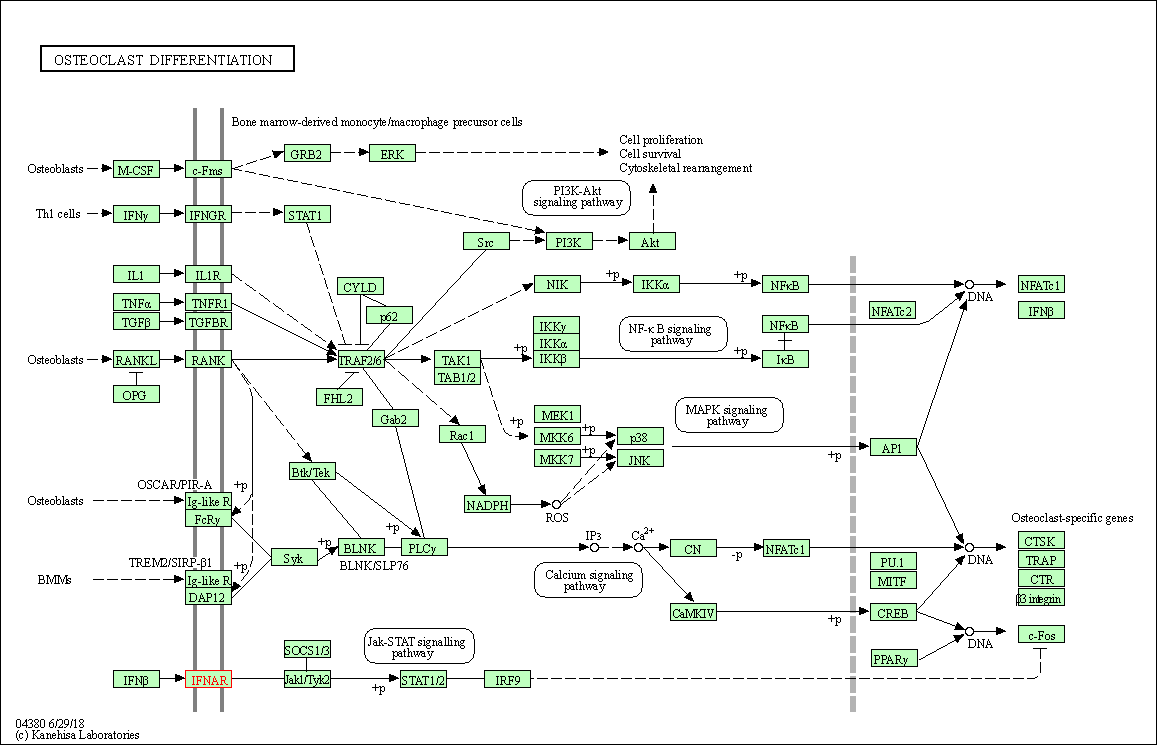

| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction | hsa04060 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signaling molecules and interaction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Necroptosis | hsa04217 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Osteoclast differentiation | hsa04380 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Development and regeneration | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
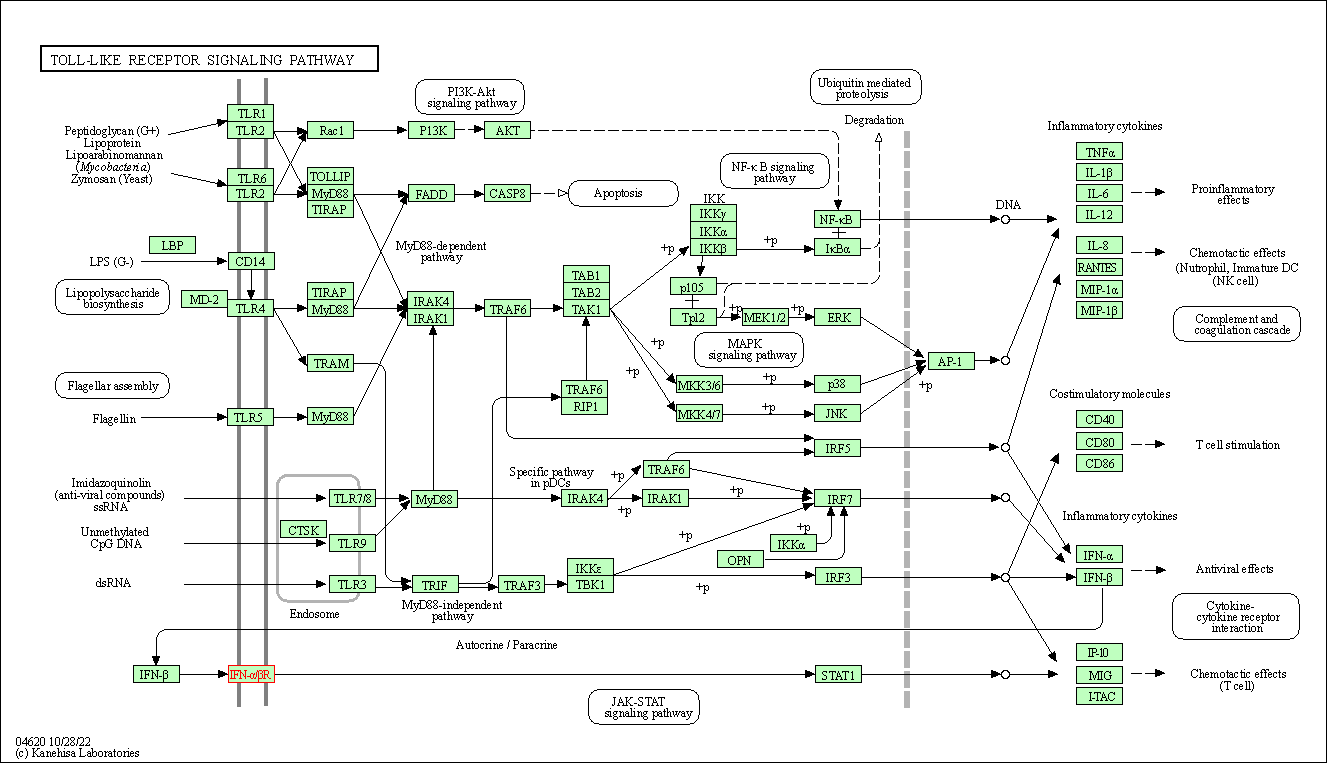
| Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | hsa04620 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
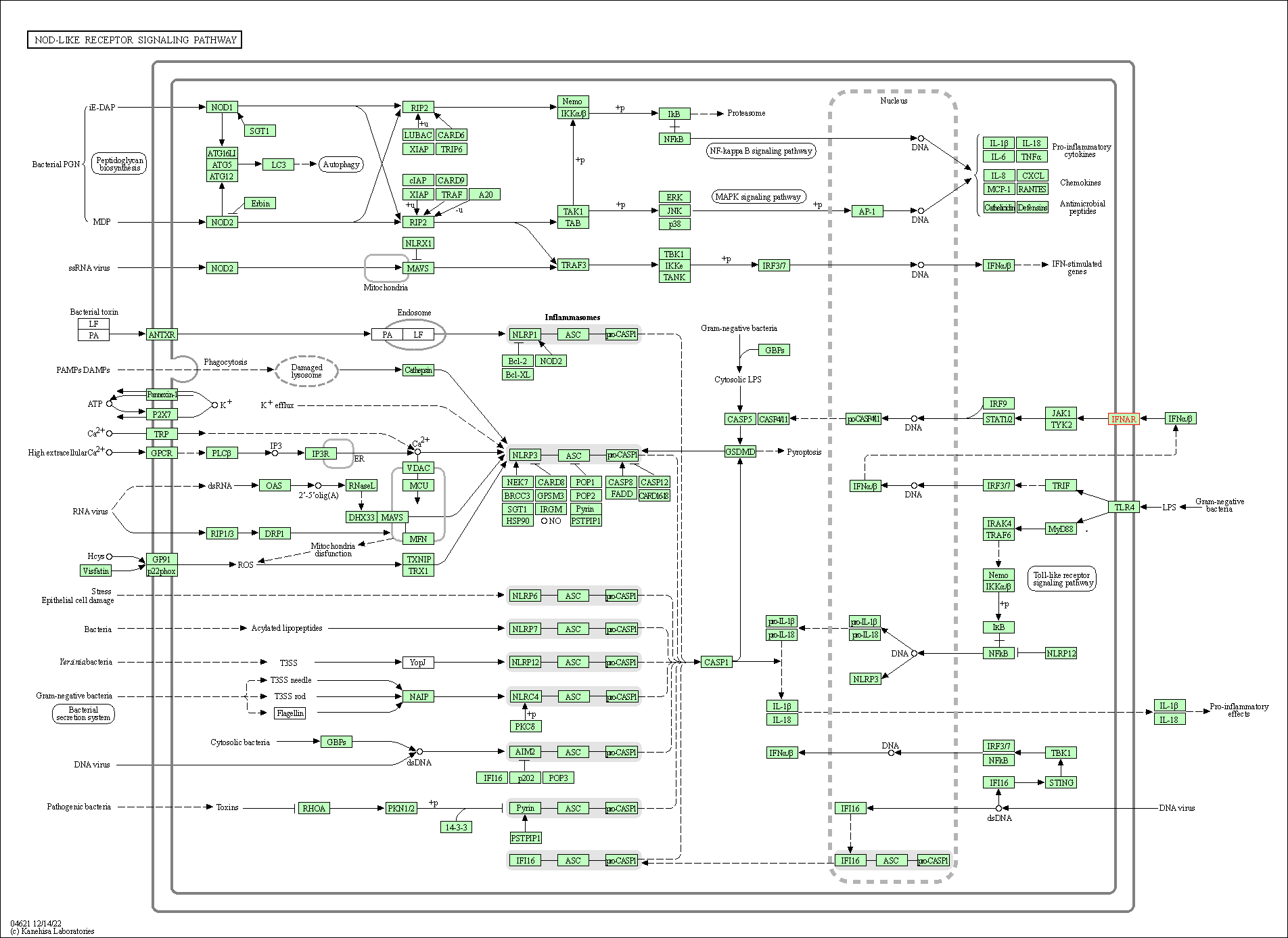
| NOD-like receptor signaling pathway | hsa04621 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| JAK-STAT signaling pathway | hsa04630 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
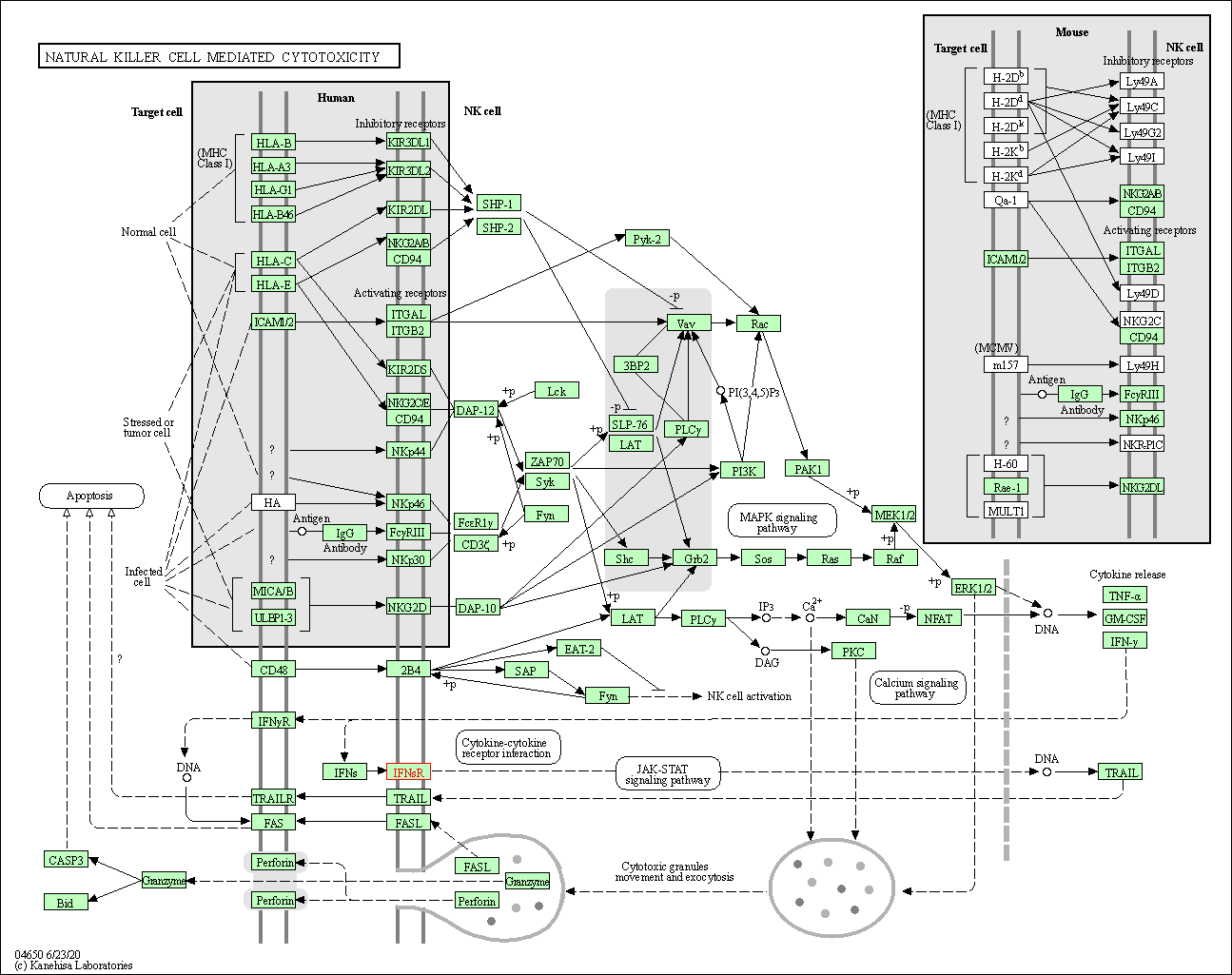
| Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity | hsa04650 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 14 | Degree centrality | 1.50E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 2.86E-04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.21E-01 | Radiality | 1.39E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 3.52E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 3.13E+01 | Topological coefficient | 1.17E-01 | Eccentricity | 12 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Expression Profile (TEP) |
||||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KEGG Pathway | [+] 11 KEGG Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction | |||||
| 2 | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | |||||
| 3 | Osteoclast differentiation | |||||
| 4 | Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | |||||
| 5 | Jak-STAT signaling pathway | |||||
| 6 | Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity | |||||
| 7 | Hepatitis C | |||||
| 8 | Hepatitis B | |||||
| 9 | Measles | |||||
| 10 | Influenza A | |||||
| 11 | Herpes simplex infection | |||||
| Reactome | [+] 2 Reactome Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Interferon alpha/beta signaling | |||||
| 2 | Regulation of IFNA signaling | |||||
| WikiPathways | [+] 5 WikiPathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | |||||
| 2 | Interferon type I signaling pathways | |||||
| 3 | Interferon alpha/beta signaling | |||||
| 4 | Regulation of toll-like receptor signaling pathway | |||||
| 5 | Osteoclast Signaling | |||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of AstraZeneca (2009). | |||||
| REF 2 | FDA Approved Drug Products from FDA Official Website. 2021. Application Number: 761123. | |||||
| REF 3 | Natural products as sources of new drugs over the last 25 years. J Nat Prod. 2007 Mar;70(3):461-77. | |||||
| REF 4 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. 2015 | |||||
| REF 5 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 8257). | |||||
| REF 6 | 2007 FDA drug approvals: a year of flux. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2008 Feb;7(2):107-9. | |||||
| REF 7 | A phase I trial of alpha-interferon in combination with pentostatin in hematologic malignancies. Med Pediatr Oncol. 1991;19(4):276-82. | |||||
| REF 8 | Successful treatment of relapsed Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia with T315I mutation after haplo-identical hematopoie... Leuk Res. 2009 Aug;33(8):e111-3. | |||||
| REF 9 | Lymphoblastoid interferon alfa-n1 improves the long-term response to a 6-month course of treatment in chronic hepatitis C compared with recombinant interferon alfa-2b: results of an international randomized controlled trial. Clinical Advisory Group for the Hepatitis C Comparative Study. Hepatology. 1998 Apr;27(4):1121-7. | |||||
| REF 10 | Therapy of hepatitis C: interferon alfa-n1 trials. Hepatology. 1997 Sep;26(3 Suppl 1):96S-100S. | |||||
| REF 11 | The clinical application of the interferons: a review. NSW Therapeutic Assessment Group. Med J Aust. 1992 Jun 15;156(12):869-72. | |||||
| REF 12 | Retreating chronic hepatitis C with daily interferon alfacon-1/ribavirin after nonresponse to pegylated interferon/ribavirin: DIRECT results. Hepatology. 2009 Jun;49(6):1838-46. | |||||
| REF 13 | Interferon-beta(1b) Treatment in Neuromyelitis Optica. Eur Neurol. 2009 Jul 7;62(3):167-170. | |||||
| REF 14 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of MedImmune (2011). | |||||
| REF 15 | New drugs in development for the treatment of endometriosis. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2008 Aug;17(8):1187-202. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

