Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T04831
(Former ID: TTDNR00694)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Tyrosine-protein kinase EIF2AK2 (p68)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
p68 kinase; Proteinkinase RNA-activated; Interferon-inducible RNA-dependent protein kinase p68; Interferon-induced, double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase p68
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
EIF2AK2
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Patented-recorded target
|
[1] | ||||
| Function |
Exerts its antiviral activity on a wide range of DNA and RNA viruses including hepatitis C virus (HCV), hepatitis B virus (HBV), measles virus (MV) and herpes simplex virus 1 (HHV-1). Inhibits viral replication via phosphorylation of the alpha subunit of eukaryotic initiation factor 2 (EIF2S1), this phosphorylation impairs the recycling of EIF2S1 between successive rounds of initiation leading to inhibition of translation which eventually results in shutdown of cellular and viral protein synthesis. Also phosphorylates other substrates including p53/TP53, PPP2R5A, DHX9, ILF3, IRS1 and the HHV-1 viral protein US11. In addition to serine/threonine-protein kinase activity, also has tyrosine-protein kinase activity and phosphorylates CDK1 at 'Tyr-4' upon DNA damage, facilitating its ubiquitination and proteosomal degradation. Either as an adapter protein and/or via its kinase activity, can regulate various signaling pathways (p38 MAP kinase, NF-kappa-B and insulin signaling pathways) and transcription factors (JUN, STAT1, STAT3, IRF1, ATF3) involved in the expression of genes encoding proinflammatory cytokines and IFNs. Activates the NF-kappa-B pathway via interaction with IKBKB and TRAF family of proteins and activates the p38 MAP kinase pathway via interaction with MAP2K6. Can act as both a positive and negative regulator of the insulin signaling pathway (ISP). Negatively regulates ISP by inducing the inhibitory phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS1) at 'Ser-312' and positively regulates ISP via phosphorylation of PPP2R5A which activates FOXO1, which in turn up-regulates the expression of insulin receptor substrate 2 (IRS2). Can regulate NLRP3 inflammasome assembly and the activation of NLRP3, NLRP1, AIM2 and NLRC4 inflammasomes. Can trigger apoptosis via FADD-mediated activation of CASP8. Plays a role in the regulation of the cytoskeleton by binding to gelsolin (GSN), sequestering the protein in an inactive conformation away from actin. IFN-induced dsRNA-dependent serine/threonine-protein kinase which plays a key role in the innate immune response to viral infection and is also involved in the regulation of signal transduction, apoptosis, cell proliferation and differentiation.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Kinase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 2.7.11.1
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MAGDLSAGFFMEELNTYRQKQGVVLKYQELPNSGPPHDRRFTFQVIIDGREFPEGEGRSK
KEAKNAAAKLAVEILNKEKKAVSPLLLTTTNSSEGLSMGNYIGLINRIAQKKRLTVNYEQ CASGVHGPEGFHYKCKMGQKEYSIGTGSTKQEAKQLAAKLAYLQILSEETSVKSDYLSSG SFATTCESQSNSLVTSTLASESSSEGDFSADTSEINSNSDSLNSSSLLMNGLRNNQRKAK RSLAPRFDLPDMKETKYTVDKRFGMDFKEIELIGSGGFGQVFKAKHRIDGKTYVIKRVKY NNEKAEREVKALAKLDHVNIVHYNGCWDGFDYDPETSDDSLESSDYDPENSKNSSRSKTK CLFIQMEFCDKGTLEQWIEKRRGEKLDKVLALELFEQITKGVDYIHSKKLIHRDLKPSNI FLVDTKQVKIGDFGLVTSLKNDGKRTRSKGTLRYMSPEQISSQDYGKEVDLYALGLILAE LLHVCDTAFETSKFFTDLRDGIISDIFDKKEKTLLQKLLSKKPEDRPNTSEILRTLTVWK KSPEKNERHTC Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T13WH4 | |||||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: adenosine diphosphate | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal structure of unphosphorylated human PKR kinase domain in complex with ADP | PDB:6D3K | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.60 Å | Mutation | No | [4] |
| PDB Sequence |
TKYTVDKRFG
264 MDFKEIELIG274 SGGFGQVFKA284 KHRIDGKTYV294 IKRVKYNNEK304 AEREVKALAK 314 LDHVNIVHYN324 GCWDGFDYDR356 SKTKCLFIQM366 EFCDKGTLEQ376 WIEKRRGEKL 386 DKVLALELFE396 QITKGVDYIH406 SKKLIHRDLK416 PSNIFLVDTK426 QVKIGDFGLV 436 TSLTLRYMSP457 EQISSQDYGK467 EVDLYALGLI477 LAELLHVCDT487 AFETSKFFTD 497 LRDGIISDIF507 DKKEKTLLQK517 LLSKKPEDRP527 NTSEILRTLT537 VWKK |
|||||
|
|
ILE273
3.939
GLY274
3.988
SER275
4.910
GLY276
4.752
PHE278
3.986
GLY279
3.179
VAL281
3.501
VAL294
3.751
LYS296
2.900
VAL321
3.960
|
|||||
| Ligand Name: AMP-PNP | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | PKR kinase domain- eIF2alpha- AMP-PNP complex. | PDB:2A19 | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.50 Å | Mutation | Yes | [5] |
| PDB Sequence |
AHTVDKRFGM
265 DFKEIELIGS275 GGFGQVFKAK285 HRIDGKTYVI295 KRVKYNNEKA305 EREVKALAKL 315 DHVNIVHYNG325 CWDGFDYDRS357 KTKCLFIQME367 FCDKGTLEQW377 IEKRRGEKLD 387 KVLALELFEQ397 ITKGVDYIHS407 KKLINRDLKP417 SNIFLVDTKQ427 VKIGDFGLVT 437 SLKNDGKRRS448 KGTLRYMSPE458 QISSQDYGKE468 VDLYALGLIL478 AELLHVCDTA 488 FETSKFFTDL498 RDGIISDIFD508 KKEKTLLQKL518 LSKKPEDRPN528 TSEILRTLTV 538 WKK
|
|||||
|
|
ILE273
4.489
GLY274
4.339
SER275
4.765
GLY277
4.918
PHE278
4.758
GLY279
3.678
VAL281
3.516
VAL294
3.427
LYS296
2.779
VAL321
4.738
|
|||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
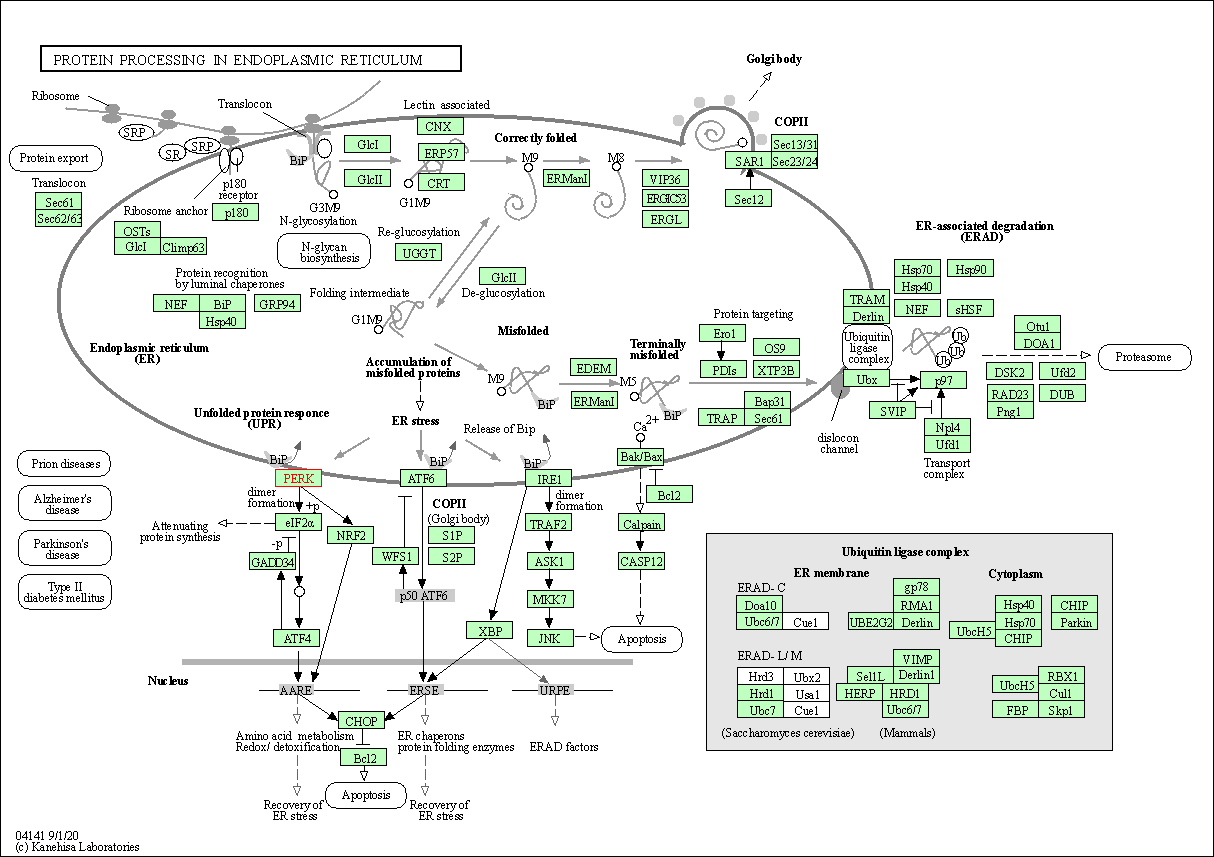
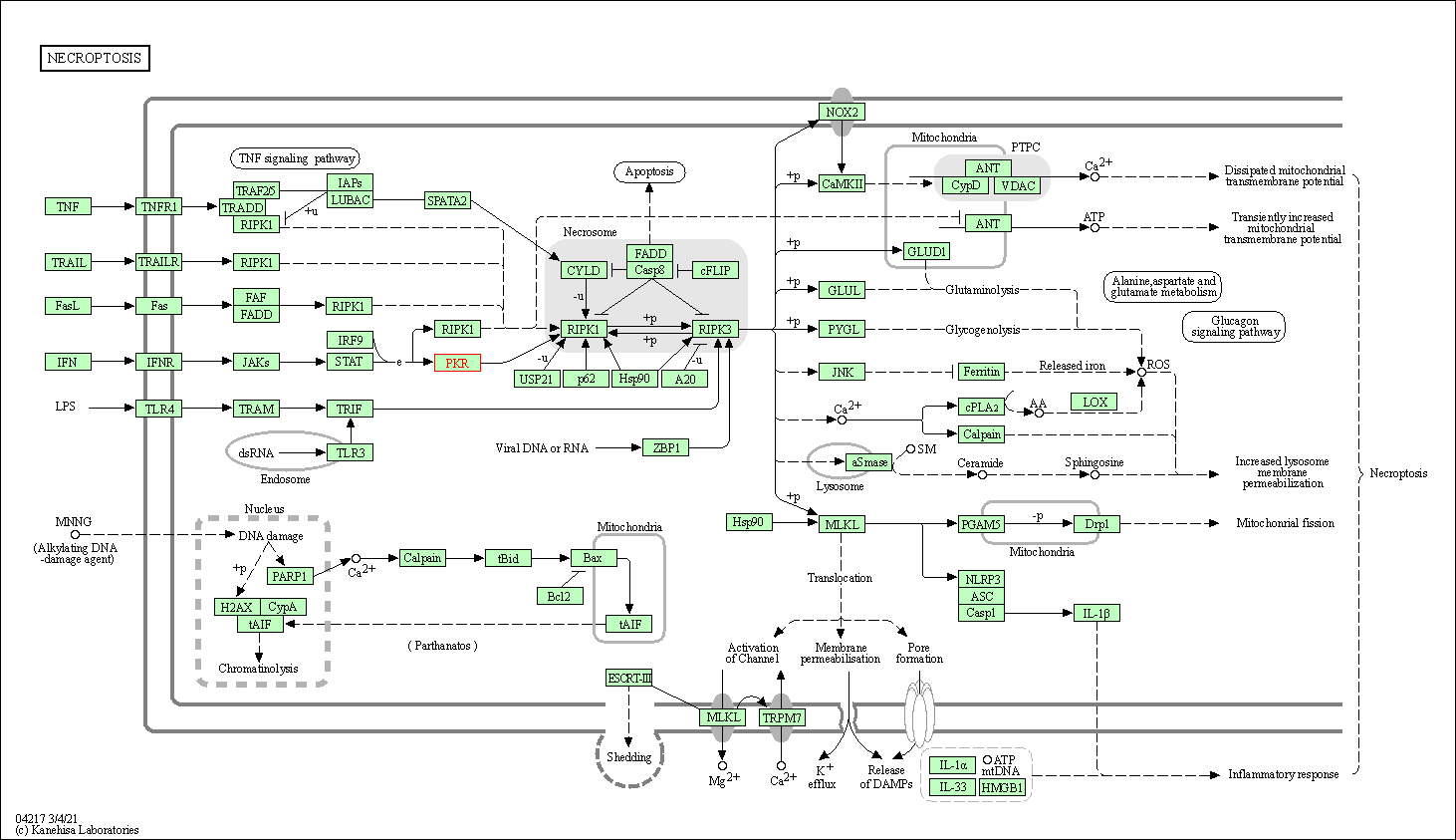
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum | hsa04141 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Genetic Information Processing => Folding, sorting and degradation | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Necroptosis | hsa04217 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Degree | 10 | Degree centrality | 1.07E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 4.72E-04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.44E-01 | Radiality | 1.43E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 8.89E-02 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 6.38E+01 | Topological coefficient | 1.12E-01 | Eccentricity | 12 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Panther Pathway | [+] 1 Panther Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Apoptosis signaling pathway | |||||
| PID Pathway | [+] 3 PID Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Signaling events mediated by TCPTP | |||||
| 2 | Ceramide signaling pathway | |||||
| 3 | PDGFR-beta signaling pathway | |||||
| Reactome | [+] 1 Reactome Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | ISG15 antiviral mechanism | |||||
| WikiPathways | [+] 4 WikiPathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Type II interferon signaling (IFNG) | |||||
| 2 | Host Interactions with Influenza Factors | |||||
| 3 | Integrated Pancreatic Cancer Pathway | |||||
| 4 | Translation Factors | |||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Identification of new inhibitors of protein kinase R guided by statistical modeling. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2011 Jul 1;21(13):4108-14. | |||||
| REF 2 | Heterocycle-substituted pyridyl benzothiophenes as kinase inhibitors. US9650366. | |||||
| REF 3 | Small molecule inhibitors of the RNA-dependent protein kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003 Aug 15;308(1):50-7. | |||||
| REF 4 | Structural Basis of Protein Kinase R Autophosphorylation. Biochemistry. 2019 Jul 9;58(27):2967-2977. | |||||
| REF 5 | Higher-order substrate recognition of eIF2alpha by the RNA-dependent protein kinase PKR. Cell. 2005 Sep 23;122(6):887-900. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

