Drug Information
| Drug General Information | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
D0TV6I
|
|||
| Former ID |
DCL000972
|
|||
| Drug Name |
Safinamide
|
|||
| Synonyms |
133865-89-1; Xadago; (S)-2-((4-((3-Fluorobenzyl)oxy)benzyl)amino)propanamide; Fce-26743; UNII-90ENL74SIG; (2S)-2-[[4-[(3-Fluorophenyl)methoxy]phenyl]methylamino]propanamide; EMD 1195686; 90ENL74SIG; CHEMBL396778; EMD-1195686; AK-77847; 2(s)-(4-(3-fluorobenzyloxy)benzylamino)propionamide; CHEMBL48582; Safinamide [USAN:INN]; 2-(4-(3-Fluorobenzyloxy)benzylamino)propionamide; AC1L2ZLK; Safinamide (USAN/INN); (S)-2-(((4-((3-Fluorophenyl)methoxy)phenyl)methyl)amino)propanamide; EC 603-772-2; SCHEMBL69350; Fce 26743; ON 019190.Na
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||
| Indication | Parkinson disease [ICD-11: 8A00.0; ICD-9: 332] | Approved | [1] | |
| Idiopathic parkinson disease [ICD-11: 8A00.0Z; ICD-9: 332] | Phase 3 | [2], [3] | ||
| Company |
Us Worldmeds
|
|||
| Structure |
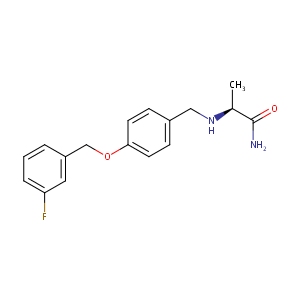 |
Download2D MOL |
||
| Formula |
C17H19FN2O2
|
|||
| Canonical SMILES |
CC(C(=O)N)NCC1=CC=C(C=C1)OCC2=CC(=CC=C2)F
|
|||
| InChI |
1S/C17H19FN2O2/c1-12(17(19)21)20-10-13-5-7-16(8-6-13)22-11-14-3-2-4-15(18)9-14/h2-9,12,20H,10-11H2,1H3,(H2,19,21)/t12-/m0/s1
|
|||
| InChIKey |
NEMGRZFTLSKBAP-LBPRGKRZSA-N
|
|||
| CAS Number |
CAS 133865-89-1
|
|||
| PubChem Compound ID | ||||
| PubChem Substance ID |
14825333, 14849630, 23920185, 26737944, 29309988, 46519220, 76856311, 93309595, 103526952, 103971166, 104375653, 124766868, 126651862, 128690685, 134338858, 134339406, 134339529, 135087308, 135626876, 137027831, 143315332, 152258889, 160826164, 162223650, 163092722, 163388329, 163686465, 163840927, 174006265, 174527236, 184816720, 196108862, 196409670, 198984441, 198991902, 204430311, 223621328, 223711810, 224284738, 226449995, 241032188, 249855421, 250205029, 252078194, 252166503, 252431202, 252494053
|
|||
| ChEBI ID |
CHEBI:134718
|
|||
| Target and Pathway | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target(s) | Monoamine oxidase type B (MAO-B) | Target Info | Inhibitor | [4], [5] |
| BioCyc | Superpathway of tryptophan utilization | |||
| Tryptophan degradation via tryptamine | ||||
| Dopamine degradation | ||||
| Putrescine degradation III | ||||
| Noradrenaline and adrenaline degradation | ||||
| KEGG Pathway | Glycine, serine and threonine metabolism | |||
| Arginine and proline metabolism | ||||
| Histidine metabolism | ||||
| Tyrosine metabolism | ||||
| Phenylalanine metabolism | ||||
| Tryptophan metabolism | ||||
| Drug metabolism - cytochrome P450 | ||||
| Metabolic pathways | ||||
| Serotonergic synapse | ||||
| Dopaminergic synapse | ||||
| Cocaine addiction | ||||
| Amphetamine addiction | ||||
| Alcoholism | ||||
| Panther Pathway | Adrenaline and noradrenaline biosynthesis | |||
| 5-Hydroxytryptamine degredation | ||||
| Dopamine receptor mediated signaling pathway | ||||
| Pathway Interaction Database | Alpha-synuclein signaling | |||
| WikiPathways | Tryptophan metabolism | |||
| Dopamine metabolism | ||||
| Phase 1 - Functionalization of compounds | ||||
| References | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. 2018 | |||
| REF 2 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 8291). | |||
| REF 3 | Drugs used to treat Parkinson's disease, present status and future directions. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2008 Oct;7(4):321-42. | |||
| REF 4 | Emerging drugs for epilepsy. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2007 Sep;12(3):407-22. | |||
| REF 5 | Emerging drugs for Parkinson's disease. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2006 Sep;11(3):403-17. | |||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

