Drug Information
| Drug General Information | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
D07TGY
|
|||
| Former ID |
DIB015590
|
|||
| Drug Name |
Indeloxazine
|
|||
| Synonyms |
Elen; Noin; Indeloxazine hydrochloride; YM-08054
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||
| Indication | Dementia [ICD-11: 6D80-6D86] | Approved | [1] | |
| Company |
Yamanouchi Pharmaceutical Co Ltd
|
|||
| Structure |
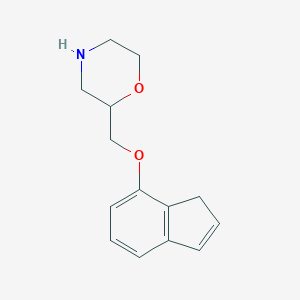 |
Download2D MOL |
||
| Formula |
C14H17NO2
|
|||
| Canonical SMILES |
C1COC(CN1)COC2=CC=CC3=C2CC=C3
|
|||
| InChI |
1S/C14H17NO2/c1-3-11-4-2-6-14(13(11)5-1)17-10-12-9-15-7-8-16-12/h1-4,6,12,15H,5,7-10H2
|
|||
| InChIKey |
MADRVGBADLFHMO-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|||
| CAS Number |
CAS 60929-23-9
|
|||
| PubChem Compound ID | ||||
| ChEBI ID |
CHEBI:5894
|
|||
| Target and Pathway | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target(s) | Monoamine oxidase type B (MAO-B) | Target Info | Modulator | [1] |
| BioCyc | Superpathway of tryptophan utilization | |||
| Tryptophan degradation via tryptamine | ||||
| Dopamine degradation | ||||
| Putrescine degradation III | ||||
| Noradrenaline and adrenaline degradation | ||||
| KEGG Pathway | Glycine, serine and threonine metabolism | |||
| Arginine and proline metabolism | ||||
| Histidine metabolism | ||||
| Tyrosine metabolism | ||||
| Phenylalanine metabolism | ||||
| Tryptophan metabolism | ||||
| Drug metabolism - cytochrome P450 | ||||
| Metabolic pathways | ||||
| Serotonergic synapse | ||||
| Dopaminergic synapse | ||||
| Cocaine addiction | ||||
| Amphetamine addiction | ||||
| Alcoholism | ||||
| Panther Pathway | Adrenaline and noradrenaline biosynthesis | |||
| 5-Hydroxytryptamine degredation | ||||
| Dopamine receptor mediated signaling pathway | ||||
| Pathway Interaction Database | Alpha-synuclein signaling | |||
| WikiPathways | Tryptophan metabolism | |||
| Dopamine metabolism | ||||
| Phase 1 - Functionalization of compounds | ||||
| References | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. 2015 | |||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

