Drug Information
| Drug General Information | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
D03DEI
|
|||
| Former ID |
DAP000794
|
|||
| Drug Name |
Sulfinpyrazone
|
|||
| Synonyms |
Anturan; Anturane; Anturanil; Anturano; Anturen; Anturidin; Diphenylpyrazone; Enturan; Enturen; Novopyrazone; Sulfinpirazona; Sulfinpyrazine; Sulfinpyrazon; Sulfinpyrazonum; Sulfoxyphenylpyrazolidin; Sulfoxyphenylpyrazolidine; Sulphinpyrazone; Apo Sulfinpyrazone; Apotex Brand of Sulfinpyrazone; Novartis Brand of Sulfinpyrazone; Nu Pharm Brand of Sulfinpyrazone; Nu Sulfinpyrazone; G 28315; Anturane (TN); Apo-Sulfinpyrazone; G 28,315; Nu-Pharm Brand of Sulfinpyrazone; Nu-Sulfinpyrazone; Sulfinpirazona [INN-Spanish]; Sulfinpyrazone (SPZ); Sulfinpyrazonum [INN-Latin]; USAF GE-13; Sulfinpyrazone [USAN:INN:JAN]; Sulfinpyrazone (JP15/USP/INN); (+/-)-SULFINPYRAZONE; 1,2-Diphenyl-3,5-dioxo-4-(2'-phenyl-sulfinyl-aethyl)-pyrazolidin; 1,2-Diphenyl-3,5-dioxo-4-(2'-phenyl-sulfinyl-aethyl)-pyrazolidin [German]; 1,2-Diphenyl-3,5-dioxo-4-(2-phenylsulfinylethyl) pyrazolidine; 1,2-Diphenyl-3,5-dioxo-4-(2-phenylsulfinylethyl)pyrazolidine; 1,2-Diphenyl-4-(2'-phenylsulfinethyl)-3,5-pyrazolidinedione; 1,2-Diphenyl-4-(2-(phenylsulfinyl)ethyl)-3,5-pyrazolidinedione; 1,2-Diphenyl-4-(phenylsulfinylethyl)-3,5-pyrazolidinedione; 1,2-Diphenyl-4-[2-(phenylsulfinyl)ethyl-3,5-pyrazolidinedione; 1,2-diphenyl-4-[2-(phenylsulfinyl)ethyl]pyrazolidine-3,5-dione; 4-(2-Benzenesulfinylethyl)-1,2-diphenylpyrazolidine-3,5-dione; 4-(Phenylsulfoxyethyl)-1,2-diphenyl-3,5-pyrazolidinedione; 4-[2-(benzenesulfinyl)ethyl]-1,2-diphenylpyrazolidine-3,5-dione
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||
| Indication | Gout [ICD-11: FA25; ICD-10: M10] | Approved | [1], [2], [3] | |
| Therapeutic Class |
Uricosuric Agents
|
|||
| Structure |
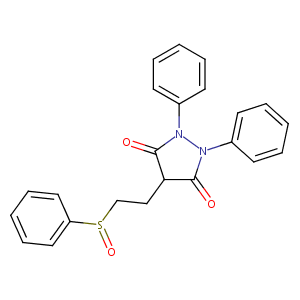 |
Download2D MOL |
||
| Formula |
C23H20N2O3S
|
|||
| Canonical SMILES |
C1=CC=C(C=C1)N2C(=O)C(C(=O)N2C3=CC=CC=C3)CCS(=O)C4=CC=CC=C4
|
|||
| InChI |
1S/C23H20N2O3S/c26-22-21(16-17-29(28)20-14-8-3-9-15-20)23(27)25(19-12-6-2-7-13-19)24(22)18-10-4-1-5-11-18/h1-15,21H,16-17H2
|
|||
| InChIKey |
MBGGBVCUIVRRBF-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|||
| CAS Number |
CAS 57-96-5
|
|||
| PubChem Compound ID | ||||
| PubChem Substance ID |
9525, 117338, 611476, 855982, 5632696, 7847515, 8149541, 8153281, 10321460, 11112139, 11335265, 11360504, 11363916, 11366478, 11369040, 11371640, 11374587, 11377202, 11461476, 11466318, 11467438, 11485183, 11486155, 11489140, 11490406, 11492660, 11494836, 14718483, 14879380, 24899841, 26611933, 26680609, 26747070, 26747071, 29224394, 46500625, 46504918, 47216628, 47290983, 47290984, 47440092, 47588838, 48110300, 48334323, 48416577, 49698736, 50029653, 50100985, 50661502, 53789714
|
|||
| ChEBI ID |
CHEBI:9342
|
|||
| ADReCS Drug ID | BADD_D02094 | |||
| SuperDrug ATC ID |
M04AB02
|
|||
| SuperDrug CAS ID |
cas=000057965
|
|||
| Interaction between the Drug and Microbe | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Metabolism of Drug Affected by Studied Microbe(s) | ||||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Bacteroidales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides fragilis ATCC43859
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[4] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Sulfinpyrazone can be metabolized by Bacteroides fragilis ATCC43859 (log2FC = -0.724; p = 0.044). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides fragilis HMW 610
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[4] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Sulfinpyrazone can be metabolized by Bacteroides fragilis HMW 610 (log2FC = -0.681; p = 0.025). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides fragilis HMW 615
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[4] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Sulfinpyrazone can be metabolized by Bacteroides fragilis HMW 615 (log2FC = -0.56; p = 0.017). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides fragilis NCTC 9343
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[4] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Sulfinpyrazone can be metabolized by Bacteroides fragilis NCTC 9343 (log2FC = -0.582; p = 0.029). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides fragilis str. DS-208
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[4] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Sulfinpyrazone can be metabolized by Bacteroides fragilis str. DS-208 (log2FC = -0.546; p = 0.017). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron 7330
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[4] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Sulfinpyrazone can be metabolized by Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron 7330 (log2FC = -0.443; p = 0.048). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides xylanisolvens DSM18836
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[4] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Sulfinpyrazone can be metabolized by Bacteroides xylanisolvens DSM18836 (log2FC = -0.544; p = 0.034). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Odoribacter splanchnicus
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[4] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Sulfinpyrazone can be metabolized by Odoribacter splanchnicus (log2FC = -0.638; p = 0.012). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Parabacteroides johnsonii DSM 18315
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[4] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Sulfinpyrazone can be metabolized by Parabacteroides johnsonii DSM 18315 (log2FC = -0.402; p = 0.039). | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Eggerthellales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Eggerthella lenta ATCC 25559
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[4] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Sulfinpyrazone can be metabolized by Eggerthella lenta ATCC 25559 (log2FC = -0.912; p = 0.043). | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Enterobacterales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Escherichia coli BW25113
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[4] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Sulfinpyrazone can be metabolized by Escherichia coli BW25113 (log2FC = -0.511; p = 0.035). | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Gut microbiota | ||||
| Studied Microbe: Anaerobic bacterium unspecific | [5], [6] | |||
| Metabolic Reaction | Sulfoxide reduction | |||
| Resulting Metabolite | Sulindac sulfide; sulinpyrzone sulfide | |||
| Metabolic Effect | Increase activity | |||
| Description | Sulfinpyrazone can be metabolized to Sulindac sulfide and sulinpyrzone sulfide by unspecific Anaerobic bacterium through sulfoxide reduction, which results in the increase of the drug's activity. | |||
| Studied Microbe: Gut microbiota unspecific | [5], [7], [8], [9] | |||
| Metabolic Reaction | Sulfoxide reduction | |||
| Resulting Metabolite | Sulindac sulfide | |||
| Metabolic Effect | Increase activity | |||
| Description | Sulfinpyrazone can be metabolized to Sulindac sulfide by gut microbiota through sulfoxide reduction, which results in the increase of the drug's activity. | |||
| Drug Resistance Mutation (DRM) | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DRM | DRM Info | |||
| Target and Pathway | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target(s) | Multidrug resistance-associated protein 1 (ABCC1) | Target Info | Modulator | [10], [11], [12] |
| KEGG Pathway | ABC transporters | |||
| Sphingolipid signaling pathway | ||||
| Vitamin digestion and absorption | ||||
| MicroRNAs in cancer | ||||
| NetPath Pathway | IL6 Signaling Pathway | |||
| Pathway Interaction Database | S1P1 pathway | |||
| Sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) pathway | ||||
| Reactome | Cobalamin (Cbl, vitamin B12) transport and metabolism | |||
| ABC-family proteins mediated transport | ||||
| WikiPathways | Arachidonic acid metabolism | |||
| Irinotecan Pathway | ||||
| Metabolism of water-soluble vitamins and cofactors | ||||
| References | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 5826). | |||
| REF 2 | FDA Approved Drug Products from FDA Official Website. 2009. Application Number: (NDA) 011556. | |||
| REF 3 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. 2015 | |||
| REF 4 | Mapping human microbiome drug metabolism by gut bacteria and their genes. Nature. 2019 Jun;570(7762):462-467. | |||
| REF 5 | The influence of gut microbiota on drug metabolism and toxicity. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2016;12(1):31-40. | |||
| REF 6 | Faecal microflora and beta-glucuronidase expression are altered in an irinotecan-induced diarrhea model in rats. Cancer Biol Ther. 2008 Dec;7(12):1919-25. | |||
| REF 7 | Human gut microbiota plays a role in the metabolism of drugs. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2016 Sep;160(3):317-26. | |||
| REF 8 | Potential Implications of Gut Microbiota in Drug Pharmacokinetics and Bioavailability. Pharmacotherapy. 2020 Jul;40(7):704-712. | |||
| REF 9 | An Ex Vivo Fermentation Screening Platform to Study Drug Metabolism by Human Gut Microbiota. Drug Metab Dispos. 2018 Nov;46(11):1596-1607. | |||
| REF 10 | Species-dependent transport and modulation properties of human and mouse multidrug resistance protein 2 (MRP2/Mrp2, ABCC2/Abcc2). Drug Metab Dispos. 2008 Apr;36(4):631-40. | |||
| REF 11 | Mutation of a single conserved tryptophan in multidrug resistance protein 1 (MRP1/ABCC1) results in loss of drug resistance and selective loss of o... J Biol Chem. 2001 May 11;276(19):15616-24. | |||
| REF 12 | Genome duplications and other features in 12 Mb of DNA sequence from human chromosome 16p and 16q. Genomics. 1999 Sep 15;60(3):295-308. | |||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

