Drug Information
| Drug General Information | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
D0C4RB
|
|||
| Former ID |
DNC001411
|
|||
| Drug Name |
Taxol
|
|||
| Synonyms |
C47H51NO14; weekly paclitaxel; Micellar Paclitaxel; Paclitaxel [USAN:INN:BAN]; SCHEMBL15000506; Benzenepropanoic acid, beta-(benzoylamino)-alpha-hydroxy-, 6,12b-bis(acetyloxy)-12-(benzoyloxy)-2a,3,4,4a,5,6,9,10,11,12,12a,12b-dodecahydro-4,11-dihydroxy-4a,8,13,13-tetramethyl-5-oxo-7,11-methano-1H-cyclodeca(3,4)benz(1,2-b)oxet-9-yl ester, (2aR-(2aalpha,4beta,4abeta,6beta,9alpha(alphaR*,betaS*),11alpha,12alpha,12aalpha,12balpha))-
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||
| Indication | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60-2C65] | Approved | [1] | |
| Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z; ICD-10: C76-C80; ICD-9: 140-229] | Approved | [2] | ||
| Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10] | Phase 3 | [3] | ||
| Gastric adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2B72; ICD-9: 151] | Phase 2 | [4] | ||
| Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73; ICD-10: C56; ICD-9: 183] | Phase 2 | [4] | ||
| Structure |
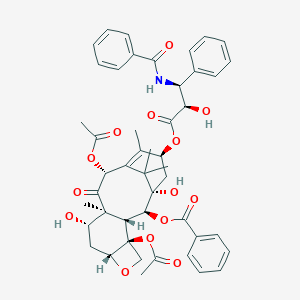 |
Download2D MOL
|
||
| Formula |
C47H51NO14
|
|||
| Canonical SMILES |
CC1=C2C(C(=O)C3(C(CC4C(C3C(C(C2(C)C)(CC1OC(=O)C(C(C5=CC=CC=C5)NC(=O)C6=CC=CC=C6)O)O)OC(=O)C7=CC=CC=C7)(CO4)OC(=O)C)O)C)OC(=O)C
|
|||
| InChI |
1S/C47H51NO14/c1-25-31(60-43(56)36(52)35(28-16-10-7-11-17-28)48-41(54)29-18-12-8-13-19-29)23-47(57)40(61-42(55)30-20-14-9-15-21-30)38-45(6,32(51)22-33-46(38,24-58-33)62-27(3)50)39(53)37(59-26(2)49)34(25)44(47,4)5/h7-21,31-33,35-38,40,51-52,57H,22-24H2,1-6H3,(H,48,54)/t31-,32-,33+,35-,36+,37+,38-,40-,45+,46-,47+/m0/s1
|
|||
| InChIKey |
RCINICONZNJXQF-MZXODVADSA-N
|
|||
| CAS Number |
CAS 33069-62-4
|
|||
| PubChem Compound ID | ||||
| PubChem Substance ID | ||||
| ChEBI ID |
CHEBI:45863
|
|||
| ADReCS Drug ID | BADD_D01653 | |||
| Interaction between the Drug and Microbe | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Metabolism of Drug Affected by Studied Microbe(s) | ||||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Bacteroidales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides fragilis HMW 615
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[5] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Paclitaxel can be metabolized by Bacteroides fragilis HMW 615 (log2FC = -0.367; p = 0.011). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides fragilis str. DS-208
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[5] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Paclitaxel can be metabolized by Bacteroides fragilis str. DS-208 (log2FC = -0.559; p = 0.02). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron 3731
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[5] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Paclitaxel can be metabolized by Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron 3731 (log2FC = -0.411; p = 0.049). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron 7330
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[5] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Paclitaxel can be metabolized by Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron 7330 (log2FC = -0.47; p = 0.002). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron VPI-5482
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[5] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Paclitaxel can be metabolized by Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron VPI-5482 (log2FC = -0.509; p = 0.034). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides uniformis ATCC 8492
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[5] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Paclitaxel can be metabolized by Bacteroides uniformis ATCC 8492 (log2FC = -0.572; p = 0.03). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides xylanisolvens DSM18836
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[5] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Paclitaxel can be metabolized by Bacteroides xylanisolvens DSM18836 (log2FC = -0.617; p = 0.014). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Odoribacter splanchnicus
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[5] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Paclitaxel can be metabolized by Odoribacter splanchnicus (log2FC = -0.661; p = 0.008). | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Eggerthellales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Eggerthella lenta ATCC 25559
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[5] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Paclitaxel can be metabolized by Eggerthella lenta ATCC 25559 (log2FC = -0.36; p = 0.044). | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Enterobacterales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Escherichia coli BW25113
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[5] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Paclitaxel can be metabolized by Escherichia coli BW25113 (log2FC = -0.507; p = 0.01). | |||
| The Abundace of Studied Microbe(s) Regulated by Drug | ||||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Eubacteriales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Clostridium perfringens
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[6] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Decrease | |||
| Experiment Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | The abundance of Clostridium perfringens was decreased by Paclitaxel (adjusted p-values: 2.59E-05). | |||
| References | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Paclitaxel directly binds to Bcl-2 and functionally mimics activity of Nur77. Cancer Res. 2009 Sep 1;69(17):6906-14. | |||
| REF 2 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. 2015 | |||
| REF 3 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||
| REF 4 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||
| REF 5 | Mapping human microbiome drug metabolism by gut bacteria and their genes. Nature. 2019 Jun;570(7762):462-467. | |||
| REF 6 | Extensive impact of non-antibiotic drugs on human gut bacteria. Nature. 2018 Mar 29;555(7698):623-628. | |||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

