Drug Information
| Drug General Information | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
D00ECO
|
||||
| Former ID |
DNC001327
|
||||
| Drug Name |
SIB-1553A
|
||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||
| Indication | Alzheimer disease [ICD9: 331; ICD10:G30] | Discontinued in Phase 2 | [1] | ||
| Structure |
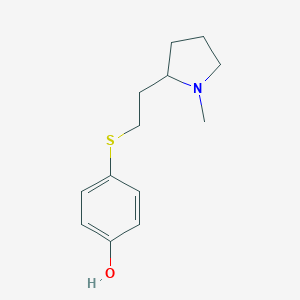
|
Download2D MOL |
|||
| Formula |
C13H20ClNOS
|
||||
| Canonical SMILES |
CN1CCCC1CCSC2=CC=C(C=C2)O.Cl
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C13H19NOS.ClH/c1-14-9-2-3-11(14)8-10-16-13-6-4-12(15)5-7-13;/h4-7,11,15H,2-3,8-10H2,1H3;1H
|
||||
| InChIKey |
RJSVKPQKXSMZMT-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| CAS Number |
CAS 205887-54-3
|
||||
| PubChem Compound ID | |||||
| PubChem Substance ID | |||||
| Target and Pathway | |||||
| Target(s) | Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor | Target Info | Agonist | [2] | |
| Neuronal acetylcholine receptor protein, beta-4 chain | Target Info | Agonist | [3] | ||
| KEGG Pathway | Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction | ||||
| Cholinergic synapse | |||||
| PANTHER Pathway | Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor signaling pathway | ||||
| Nicotine pharmacodynamics pathway | |||||
| Reactome | Highly sodium permeable acetylcholine nicotinic receptors | ||||
| Highly calcium permeable postsynaptic nicotinic acetylcholine receptors | |||||
| Highly calcium permeable nicotinic acetylcholine receptors | |||||
| WikiPathways | SIDS Susceptibility Pathways | ||||
| Neurotransmitter Receptor Binding And Downstream Transmission In The Postsynaptic Cell | |||||
| Nicotine Activity on Chromaffin Cells | |||||
| References | |||||
| REF 1 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800009631) | ||||
| REF 2 | The potential of subtype-selective neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonists as therapeutic agents. Life Sci. 1998;62(17-18):1601-6. | ||||
| REF 3 | SIB-1553A, (+/-)-4-[[2-(1-methyl-2-pyrrolidinyl)ethyl]thio]phenol hydrochloride, a subtype-selective ligand for nicotinic acetylcholine receptors with putative cognitive-enhancing properties: effectson working and reference memory performances in aged rodents and nonhuman primates. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2001 Oct;299(1):297-306. | ||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

