Drug Information
| Drug General Information | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
D0U6FT
|
||||
| Former ID |
DIB011656
|
||||
| Drug Name |
GSI-136
|
||||
| Synonyms |
WAY-179642; WAY-208983; WAY-GSI-A; WAY-GSI-B; Gamma-secretase inhibitors (oral, Alzheimer's disease), Wyeth
|
||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||
| Indication | Alzheimer disease [ICD9: 331; ICD10:G30] | Phase 1 | [1] | ||
| Company |
Wyeth
|
||||
| Structure |
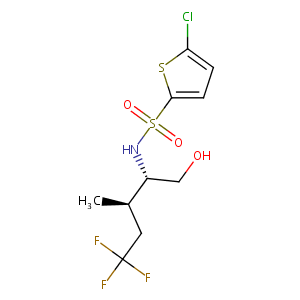
|
Download2D MOL |
|||
| Formula |
C11H18ClNO3S2
|
||||
| Canonical SMILES |
c1(ccc(s1)Cl)S(=O)(=O)N[C@@H]([C@@H](CC(F)(F)F)C)CO
|
||||
| PubChem Compound ID | |||||
| Target and Pathway | |||||
| Target(s) | Gamma-secretase | Target Info | Modulator | [2] | |
| KEGG Pathway | Notch signaling pathway | ||||
| Alzheimer's disease | |||||
| PANTHER Pathway | Alzheimer disease-amyloid secretase pathway | ||||
| Alzheimer disease-presenilin pathway | |||||
| Notch signaling pathway | |||||
| Pathway Interaction Database | Notch signaling pathway | ||||
| Presenilin action in Notch and Wnt signaling | |||||
| p75(NTR)-mediated signaling | |||||
| Syndecan-3-mediated signaling events | |||||
| Reactome | Nuclear signaling by ERBB4 | ||||
| Regulated proteolysis of p75NTR | |||||
| NRIF signals cell death from the nucleus | |||||
| Activated NOTCH1 Transmits Signal to the Nucleus | |||||
| Constitutive Signaling by NOTCH1 PEST Domain Mutants | |||||
| Constitutive Signaling by NOTCH1 HD+PEST Domain Mutants | |||||
| NOTCH2 Activation and Transmission of Signal to the Nucleus | |||||
| EPH-ephrin mediated repulsion of cells | |||||
| WikiPathways | Notch Signaling Pathway | ||||
| Signaling by ERBB4 | |||||
| Signaling by NOTCH3 | |||||
| Signaling by NOTCH4 | |||||
| Signaling by NOTCH1 | |||||
| Signaling by NOTCH2 | |||||
| Notch Signaling Pathway | |||||
| Signalling by NGF | |||||
| References | |||||
| REF 1 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT00719394) Study Evaluating Safety of GSI 136 in Young and Elderly Japanese Males. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | ||||
| REF 2 | Interpreting expression profiles of cancers by genome-wide survey of breadth of expression in normal tissues. Genomics 2005 Aug;86(2):127-41. | ||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

