Drug Information
| Drug General Information | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
D0AE9M
|
||||
| Former ID |
DNC012016
|
||||
| Drug Name |
Butyl-indol-1-yl-pyridin-4-yl-amine
|
||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||
| Indication | Discovery agent | Investigative | [1] | ||
| Structure |
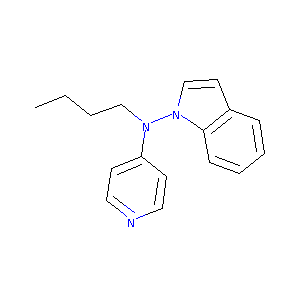
|
Download2D MOL |
|||
| Formula |
C17H19N3
|
||||
| Canonical SMILES |
CCCCN(C1=CC=NC=C1)N2C=CC3=CC=CC=C32
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C17H19N3/c1-2-3-13-19(16-8-11-18-12-9-16)20-14-10-15-6-4-5-7-17(15)20/h4-12,14H,2-3,13H2,1H3
|
||||
| InChIKey |
OSRPQIAWURAKDF-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem Compound ID | |||||
| Target and Pathway | |||||
| Target(s) | Alpha-2C adrenergic receptor | Target Info | Inhibitor | [1] | |
| Alpha-2B adrenergic receptor | Target Info | Inhibitor | [1] | ||
| Alpha-2A adrenergic receptor | Target Info | Inhibitor | [1] | ||
| KEGG Pathway | cGMP-PKG signaling pathway | ||||
| Neuroactive ligand-receptor interactionhsa04022:cGMP-PKG signaling pathway | |||||
| Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction | |||||
| PANTHER Pathway | Alpha adrenergic receptor signaling pathway | ||||
| Heterotrimeric G-protein signaling pathway-Gi alpha and Gs alpha mediated pathwayP00002:Alpha adrenergic receptor signaling pathway | |||||
| Reactome | Adrenoceptors | ||||
| Adrenaline signalling through Alpha-2 adrenergic receptor | |||||
| Adrenaline,noradrenaline inhibits insulin secretion | |||||
| G alpha (i) signalling events | |||||
| G alpha (z) signalling events | |||||
| Surfactant metabolismR-HSA-390696:Adrenoceptors | |||||
| G alpha (z) signalling eventsR-HSA-390696:Adrenoceptors | |||||
| Surfactant metabolism | |||||
| WikiPathways | Monoamine GPCRs | ||||
| GPCRs, Class A Rhodopsin-like | |||||
| Platelet Aggregation (Plug Formation) | |||||
| Integration of energy metabolism | |||||
| GPCR ligand binding | |||||
| GPCR downstream signalingWP58:Monoamine GPCRs | |||||
| GPCR downstream signaling | |||||
| References | |||||
| REF 1 | J Med Chem. 1996 Jan 19;39(2):570-81.Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of N-propyl-N-(4-pyridinyl)-1H-indol-1-amine (besipirdine) and related analogs as potential therapeutic agents for Alzheimer's disease. | ||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

