Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T95108
|
|||||
| Target Name |
MHC class I antigen G (HLA-G)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
HLA G antigen; MHC class I antigen G
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
HLA-G
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Clinical trial target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 1 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||||
| Function |
Non-classical major histocompatibility class Ib molecule involved in immune regulatory processes at the maternal-fetal interface. In complex with B2M/beta-2 microglobulin binds a limited repertoire of nonamer self-peptides derived from intracellular proteins including histones and ribosomal proteins. Peptide-bound HLA-G-B2M complex acts as a ligand for inhibitory/activating KIR2DL4, LILRB1 and LILRB2 receptors on uterine immune cells to promote fetal development while maintaining maternal-fetal tolerance. Upon interaction with KIR2DL4 and LILRB1 receptors on decidual NK cells, it triggers NK cell senescence-associated secretory phenotype as a molecular switch to promote vascular remodeling and fetal growth in early pregnancy. Through interaction with KIR2DL4 receptor on decidual macrophages induces proinflammatory cytokine production mainly associated with tissue remodeling. Through interaction with LILRB2 receptor triggers differentiation of type 1 regulatory T cells and myeloid-derived suppressor cells, both of which actively maintain maternal-fetal tolerance. May play a role in balancing tolerance and antiviral-immunity at maternal-fetal interface by keeping in check the effector functions of NK, CD8+ T cells and B cells. Reprograms B cells toward an immune suppressive phenotype via LILRB1. May induce immune activation/suppression via intercellular membrane transfer (trogocytosis), likely enabling interaction with KIR2DL4, which resides mostly in endosomes. Through interaction with the inhibitory receptor CD160 on endothelial cells may control angiogenesis in immune privileged sites.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
MHC class I
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| Sequence |
MVVMAPRTLFLLLSGALTLTETWAGSHSMRYFSAAVSRPGRGEPRFIAMGYVDDTQFVRF
DSDSACPRMEPRAPWVEQEGPEYWEEETRNTKAHAQTDRMNLQTLRGYYNQSEASSHTLQ WMIGCDLGSDGRLLRGYEQYAYDGKDYLALNEDLRSWTAADTAAQISKRKCEAANVAEQR RAYLEGTCVEWLHRYLENGKEMLQRADPPKTHVTHHPVFDYEATLRCWALGFYPAEIILT WQRDGEDQTQDVELVETRPAGDGTFQKWAAVVVPSGEEQRYTCHVQHEGLPEPLMLRWKQ SSLPTIPIMGIVAGLVVLAAVVTGAAVAAVLWRKKSSD Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T52HO1 | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 1 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | TTX-080 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Solid tumour/cancer | [2] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 1 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Inhibitor | [+] 1 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | TTX-080 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Endocytosis | hsa04144 | Affiliated Target |
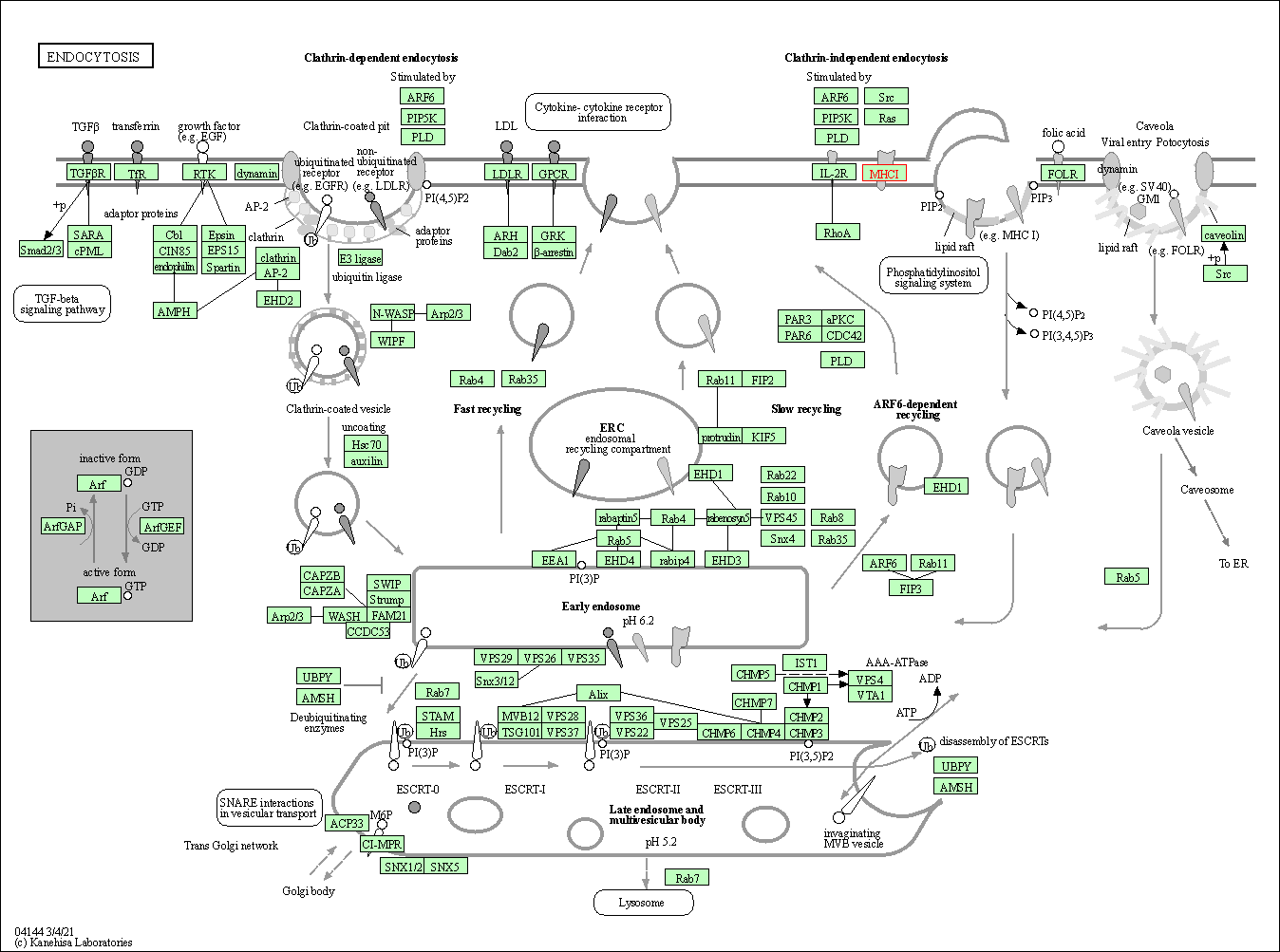
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Transport and catabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Phagosome | hsa04145 | Affiliated Target |
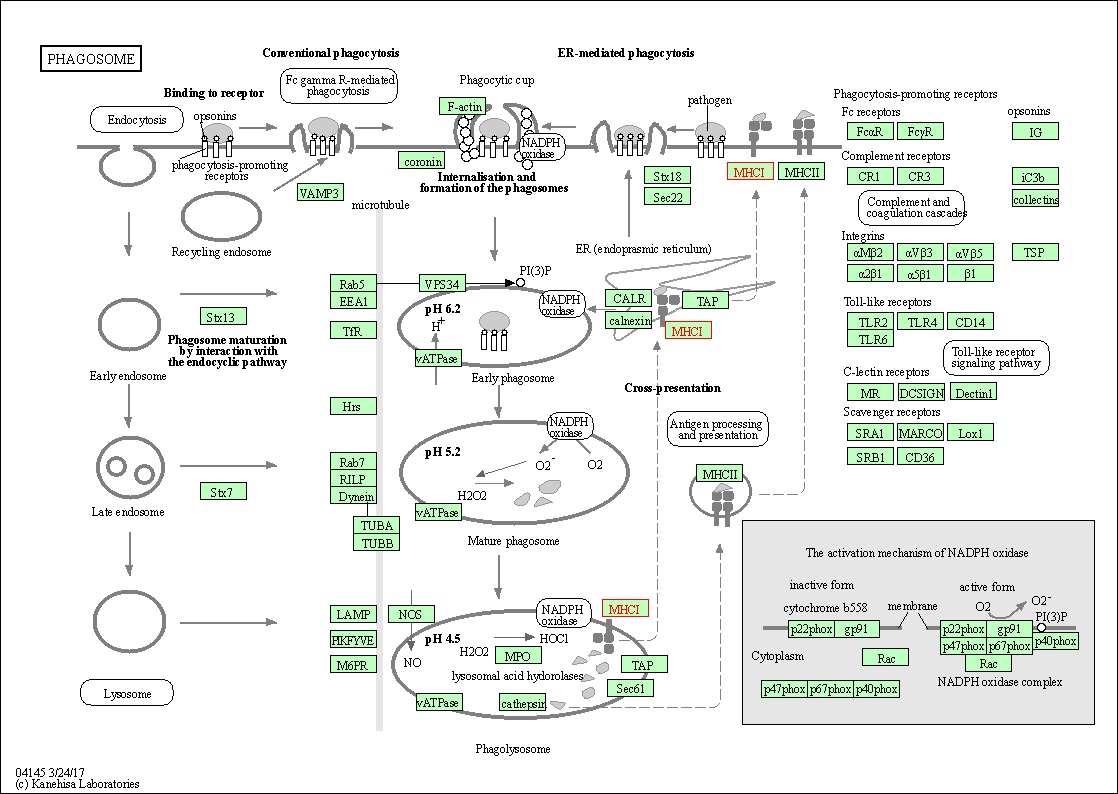
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Transport and catabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Cellular senescence | hsa04218 | Affiliated Target |
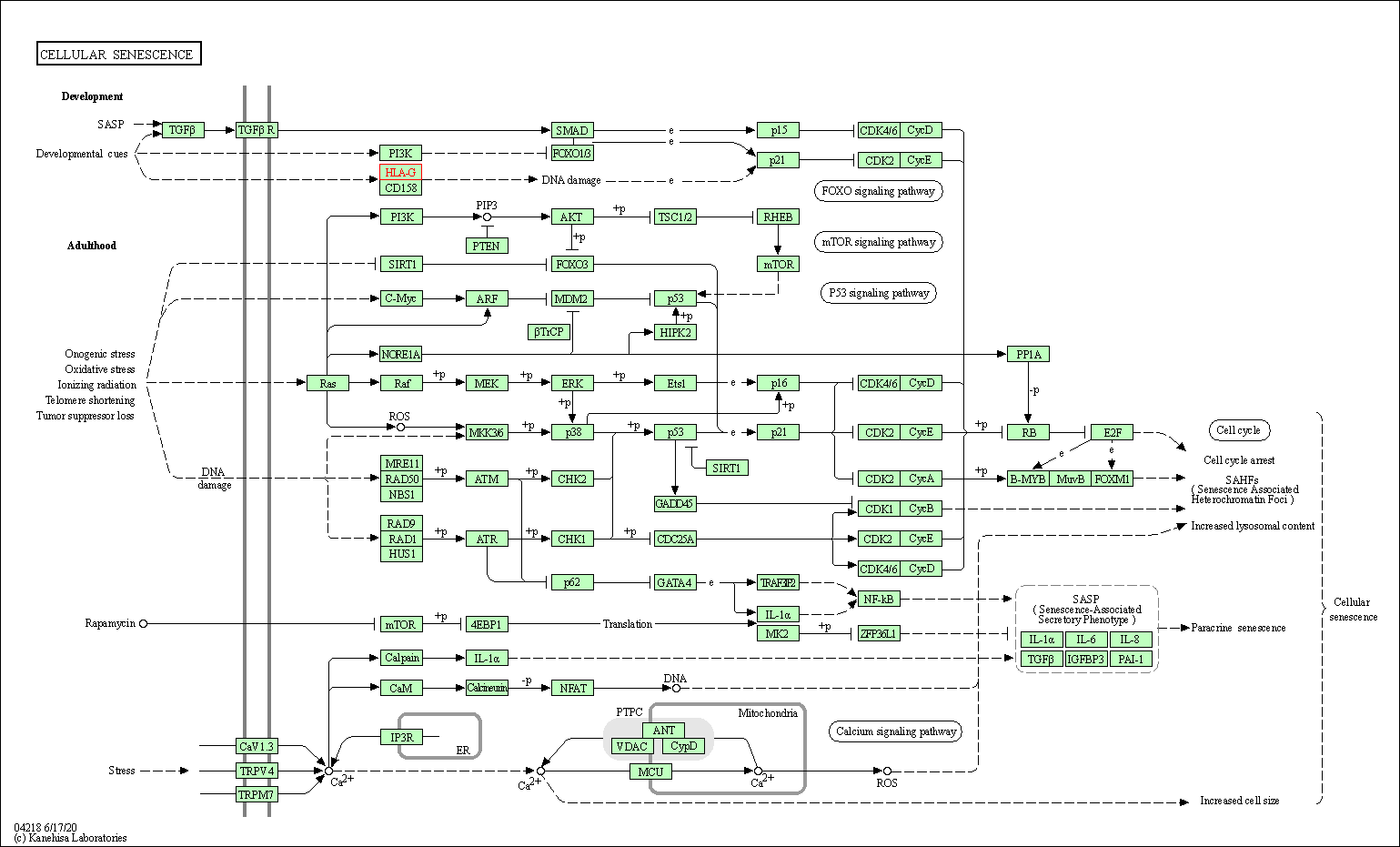
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Cell adhesion molecules | hsa04514 | Affiliated Target |
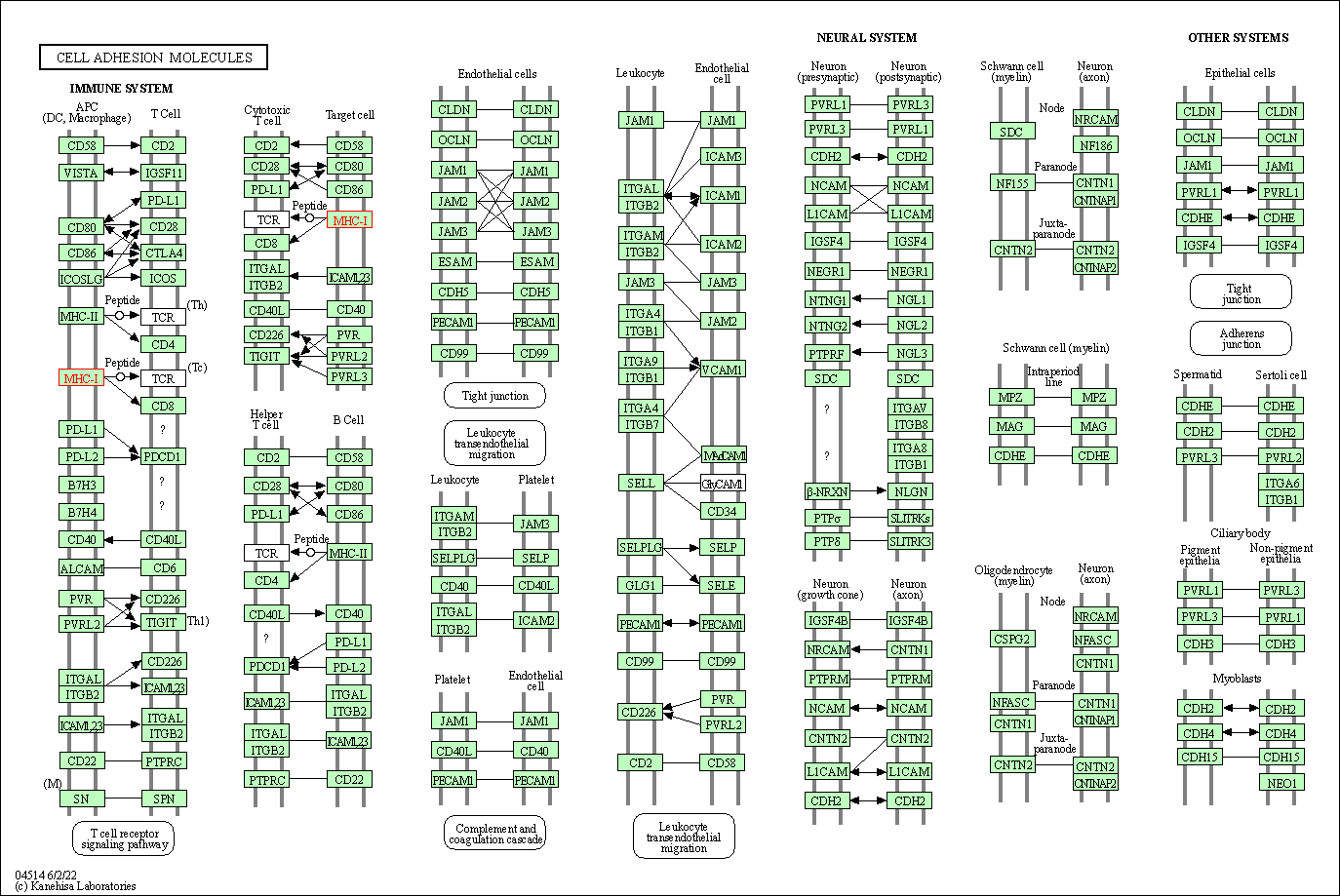
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signaling molecules and interaction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Antigen processing and presentation | hsa04612 | Affiliated Target |
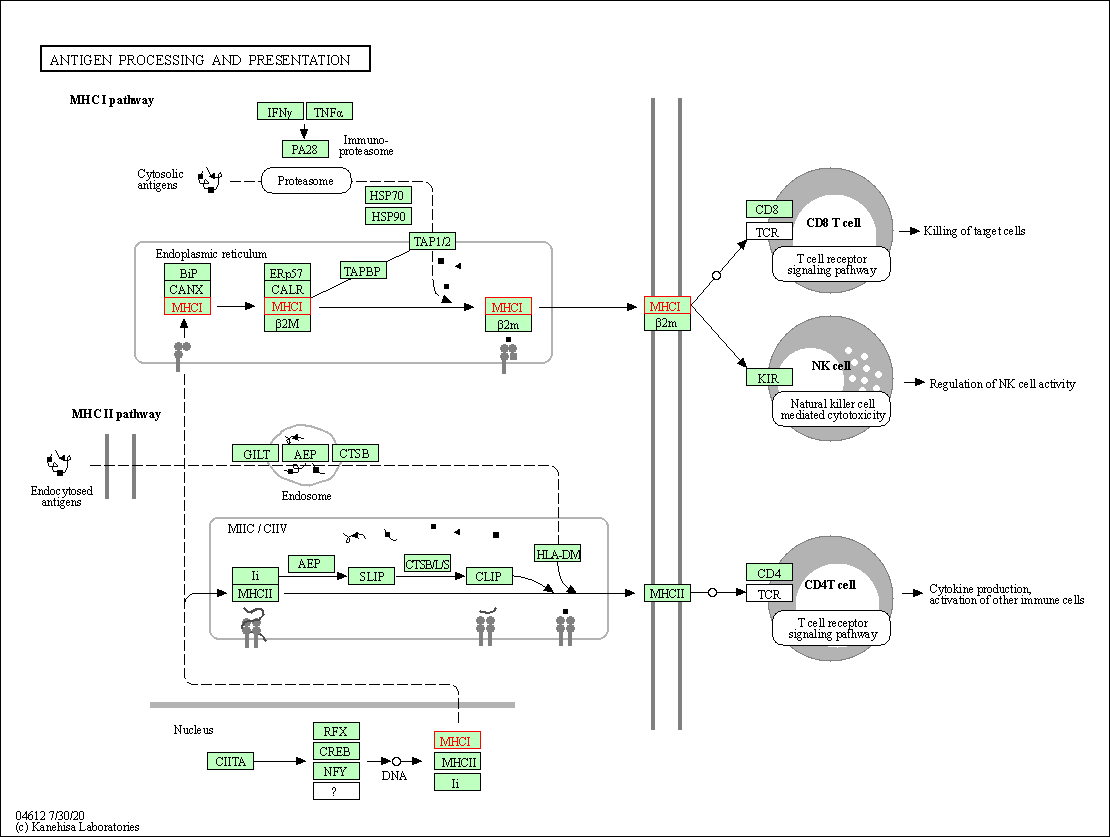
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity | hsa04650 | Affiliated Target |
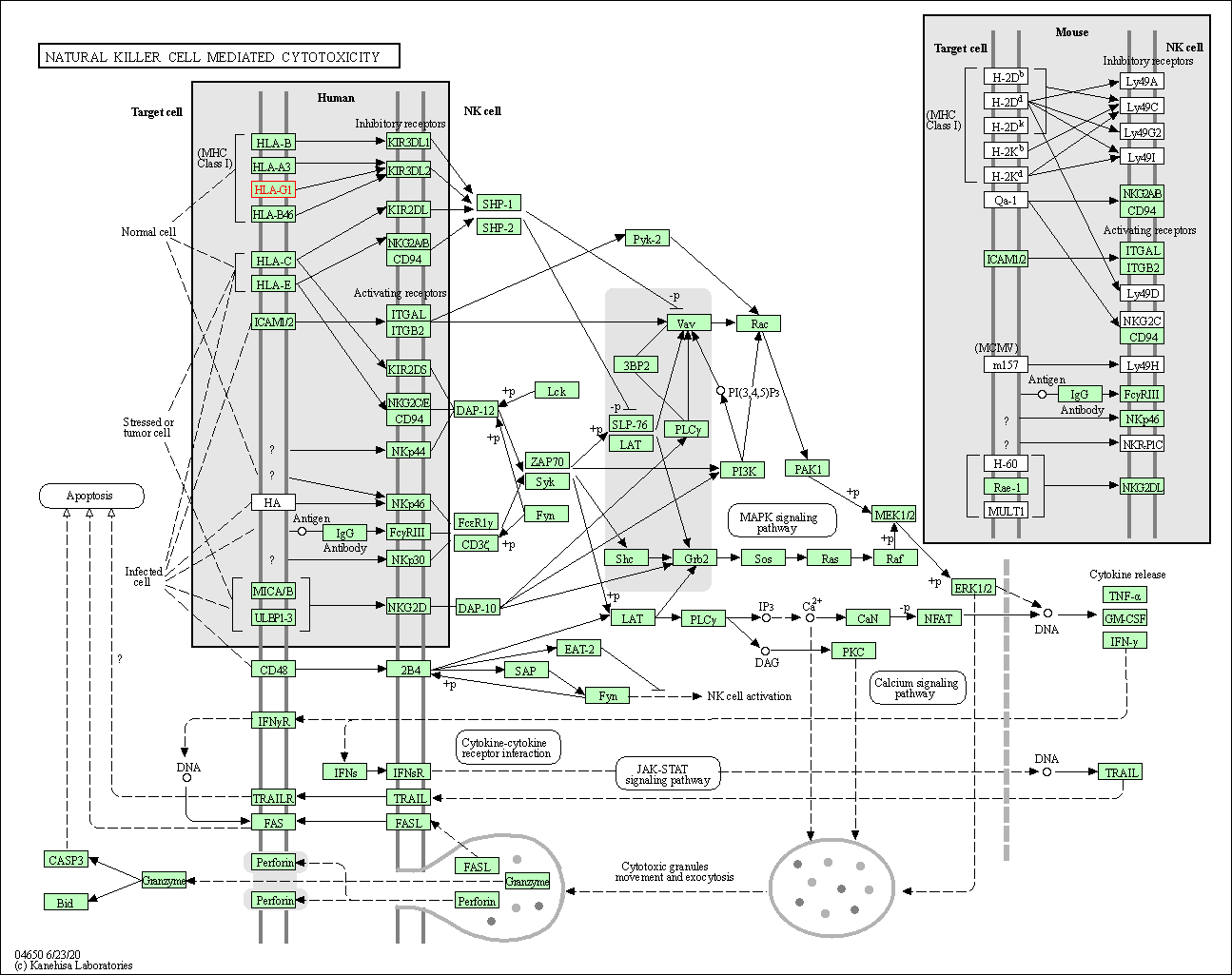
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 9 | Degree centrality | 9.67E-04 | Betweenness centrality | 2.71E-04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 1.88E-01 | Radiality | 1.32E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 2.50E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 1.14E+01 | Topological coefficient | 2.00E-01 | Eccentricity | 12 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of Tizona Therapeutics. | |||||
| REF 2 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04485013) TTX-080 HLA-G Antagonist in Subjects With Advanced Cancers. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

