Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T94471
|
|||||
| Target Name |
HUMAN complement C5 protein (C5)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
C3 and PZP-like alpha-2-macroglobulin domain-containing protein 4
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
C5
|
|||||
| Disease | [+] 2 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Neuromyelitis optica [ICD-11: 8A43] | |||||
| 2 | Paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria [ICD-11: 3A21] | |||||
| Function |
Activation of C5 by a C5 convertase initiates the spontaneous assembly of the late complement components, C5-C9, into the membrane attack complex. C5b has a transient binding site for C6. The C5b-C6 complex is the foundation upon which the lytic complex is assembled. Derived from proteolytic degradation of complement C5, C5 anaphylatoxin is a mediator of local inflammatory process. Binding to the receptor C5AR1 induces a variety of responses including intracellular calcium release, contraction of smooth muscle, increased vascular permeability, and histamine release from mast cells and basophilic leukocytes (PubMed:8182049). C5a is also a potent chemokine which stimulates the locomotion of polymorphonuclear leukocytes and directs their migration toward sites of inflammation.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Complement system
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| Sequence |
MGLLGILCFLIFLGKTWGQEQTYVISAPKIFRVGASENIVIQVYGYTEAFDATISIKSYP
DKKFSYSSGHVHLSSENKFQNSAILTIQPKQLPGGQNPVSYVYLEVVSKHFSKSKRMPIT YDNGFLFIHTDKPVYTPDQSVKVRVYSLNDDLKPAKRETVLTFIDPEGSEVDMVEEIDHI GIISFPDFKIPSNPRYGMWTIKAKYKEDFSTTGTAYFEVKEYVLPHFSVSIEPEYNFIGY KNFKNFEITIKARYFYNKVVTEADVYITFGIREDLKDDQKEMMQTAMQNTMLINGIAQVT FDSETAVKELSYYSLEDLNNKYLYIAVTVIESTGGFSEEAEIPGIKYVLSPYKLNLVATP LFLKPGIPYPIKVQVKDSLDQLVGGVPVTLNAQTIDVNQETSDLDPSKSVTRVDDGVASF VLNLPSGVTVLEFNVKTDAPDLPEENQAREGYRAIAYSSLSQSYLYIDWTDNHKALLVGE HLNIIVTPKSPYIDKITHYNYLILSKGKIIHFGTREKFSDASYQSINIPVTQNMVPSSRL LVYYIVTGEQTAELVSDSVWLNIEEKCGNQLQVHLSPDADAYSPGQTVSLNMATGMDSWV ALAAVDSAVYGVQRGAKKPLERVFQFLEKSDLGCGAGGGLNNANVFHLAGLTFLTNANAD DSQENDEPCKEILRPRRTLQKKIEEIAAKYKHSVVKKCCYDGACVNNDETCEQRAARISL GPRCIKAFTECCVVASQLRANISHKDMQLGRLHMKTLLPVSKPEIRSYFPESWLWEVHLV PRRKQLQFALPDSLTTWEIQGVGISNTGICVADTVKAKVFKDVFLEMNIPYSVVRGEQIQ LKGTVYNYRTSGMQFCVKMSAVEGICTSESPVIDHQGTKSSKCVRQKVEGSSSHLVTFTV LPLEIGLHNINFSLETWFGKEILVKTLRVVPEGVKRESYSGVTLDPRGIYGTISRRKEFP YRIPLDLVPKTEIKRILSVKGLLVGEILSAVLSQEGINILTHLPKGSAEAELMSVVPVFY VFHYLETGNHWNIFHSDPLIEKQKLKKKLKEGMLSIMSYRNADYSYSVWKGGSASTWLTA FALRVLGQVNKYVEQNQNSICNSLLWLVENYQLDNGSFKENSQYQPIKLQGTLPVEAREN SLYLTAFTVIGIRKAFDICPLVKIDTALIKADNFLLENTLPAQSTFTLAISAYALSLGDK THPQFRSIVSALKREALVKGNPPIYRFWKDNLQHKDSSVPNTGTARMVETTAYALLTSLN LKDINYVNPVIKWLSEEQRYGGGFYSTQDTINAIEGLTEYSLLVKQLRLSMDIDVSYKHK GALHNYKMTDKNFLGRPVEVLLNDDLIVSTGFGSGLATVHVTTVVHKTSTSEEVCSFYLK IDTQDIEASHYRGYGNSDYKRIVACASYKPSREESSSGSSHAVMDISLPTGISANEEDLK ALVEGVDQLFTDYQIKDGHVILQLNSIPSSDFLCVRFRIFELFEVGFLSPATFTVYEYHR PDKQCTMFYSTSNIKIQKVCEGAACKCVEADCGQMQEELDLTISAETRKQTACKPEIAYA YKVSITSITVENVFVKYKATLLDIYKTGEAVAEKDSEITFIKKVTCTNAELVKGRQYLIM GKEALQIKYNFSFRYIYPLDSLTWIEYWPRDTTCSSCQAFLANLDEFAEDIFLNGC Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drugs in Phase 2 Trial | [+] 1 | + | ||||
| 1 | Eculizumab | Drug Info | Approved | Neuromyelitis optica | [2] | |
| Drugs in Phase 3 Trial | [+] 1 | + | ||||
| 1 | Ravulizumab | Drug Info | Approved | Paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria | [3] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 1 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Inhibitor | [+] 2 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Ravulizumab | Drug Info | [1], [4] | |||
| 2 | Eculizumab | Drug Info | [1], [5] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: N-(2-Acetamido)Iminodiacetic Acid | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal structure of human complement C5 in complex with the K8 bovine knob domain peptide. | PDB:7AD7 | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.30 Å | Mutation | No | [6] |
| PDB Sequence |
EQTYVISAPK
29 IFRVGASENI39 VIQVYGYTEA49 FDATISIKSY59 PDKKFSYSSG69 HVHLSSENKF 79 QNSAILTIQP89 KQLPGGQNPV99 SYVYLEVVSK109 HFSKSKRMPI119 TYDNGFLFIH 129 TDKPVYTPDQ139 SVKVRVYSLN149 DDLKPAKRET159 VLTFIDPEGS169 EVDMVEEIDH 179 IGIISFPDFK189 IPSNPRYGMW199 TIKAKYKEDF209 STTGTAYFEV219 KEYVLPHFSV 229 SIEPEYNFIG239 YKNFKNFEIT249 IKARYFYNKV259 VTEADVYITF269 GIREDLKDDQ 279 KEMMQTAMQN289 TMLINGIAQV299 TFDSETAVKE309 LSYYSLEDLN319 NKYLYIAVTV 329 IESTGGFSEE339 AEIPGIKYVL349 SPYKLNLVAT359 PLFLKPGIPY369 PIKVQVKDSL 379 DQLVGGVPVT389 LNAQTIDVNQ399 ETSDLDPSKS409 VTRVDDGVAS419 FVLNLPSGVT 429 VLEFNVKTDA439 PDLPEENQAR449 EGYRAIAYSS459 LSQSYLYIDW469 TDNHKALLVG 479 EHLNIIVTPK489 SPYIDKITHY499 NYLILSKGKI509 IHFGTREKFS519 DASYQSINIP 529 VTQNMVPSSR539 LLVYYIVTGE549 QTAELVSDSV559 WLNIEEKCGN569 QLQVHLSPDA 579 DAYSPGQTVS589 LNMATGMDSW599 VALAAVDSAV609 YGFQFLEKSD631 LGCGAGGGLN 641 NANVFHLAGL651 TFLTNANADD661 SQCKE
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction | hsa04080 | Affiliated Target |
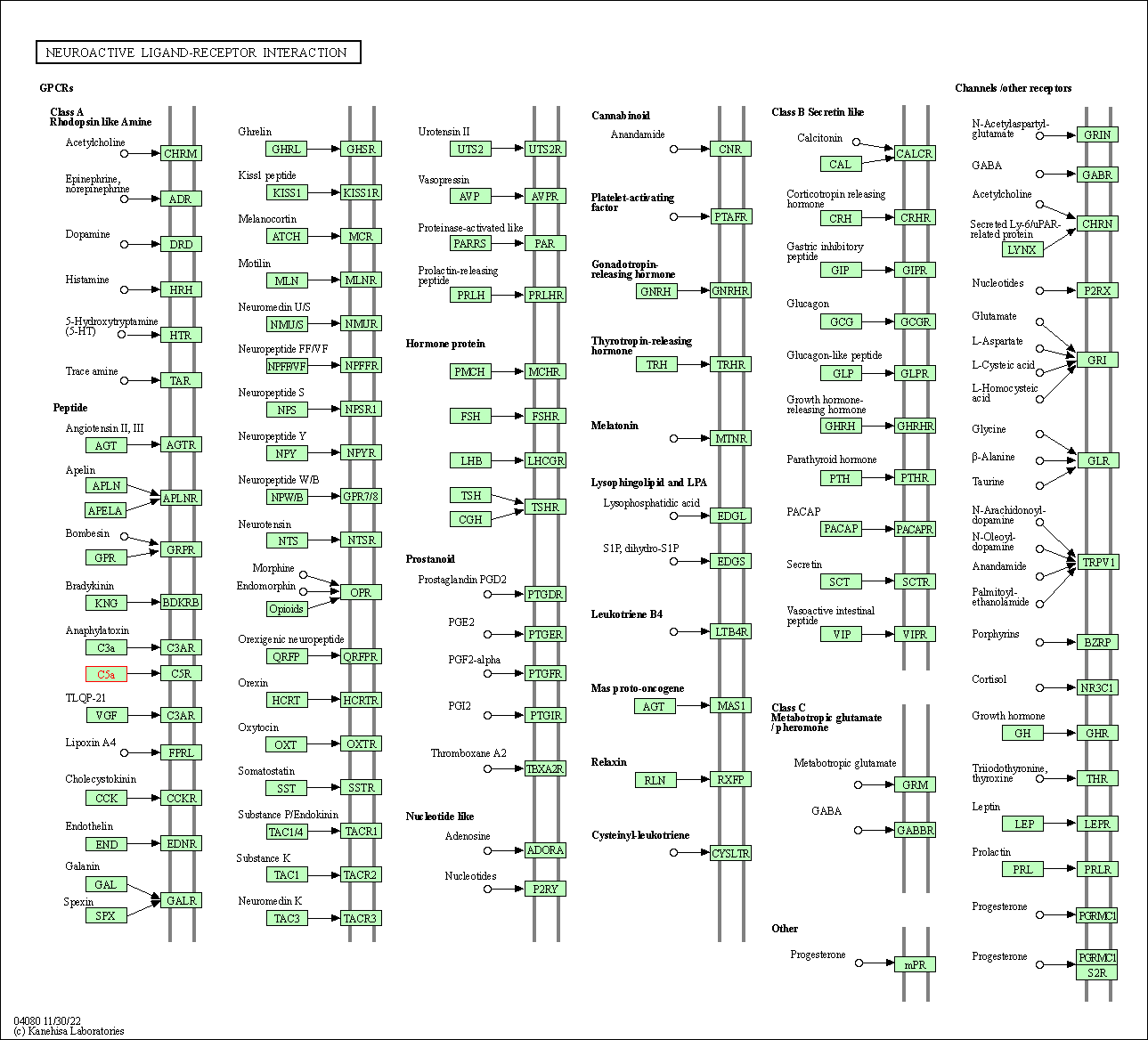
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signaling molecules and interaction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Complement and coagulation cascades | hsa04610 | Affiliated Target |
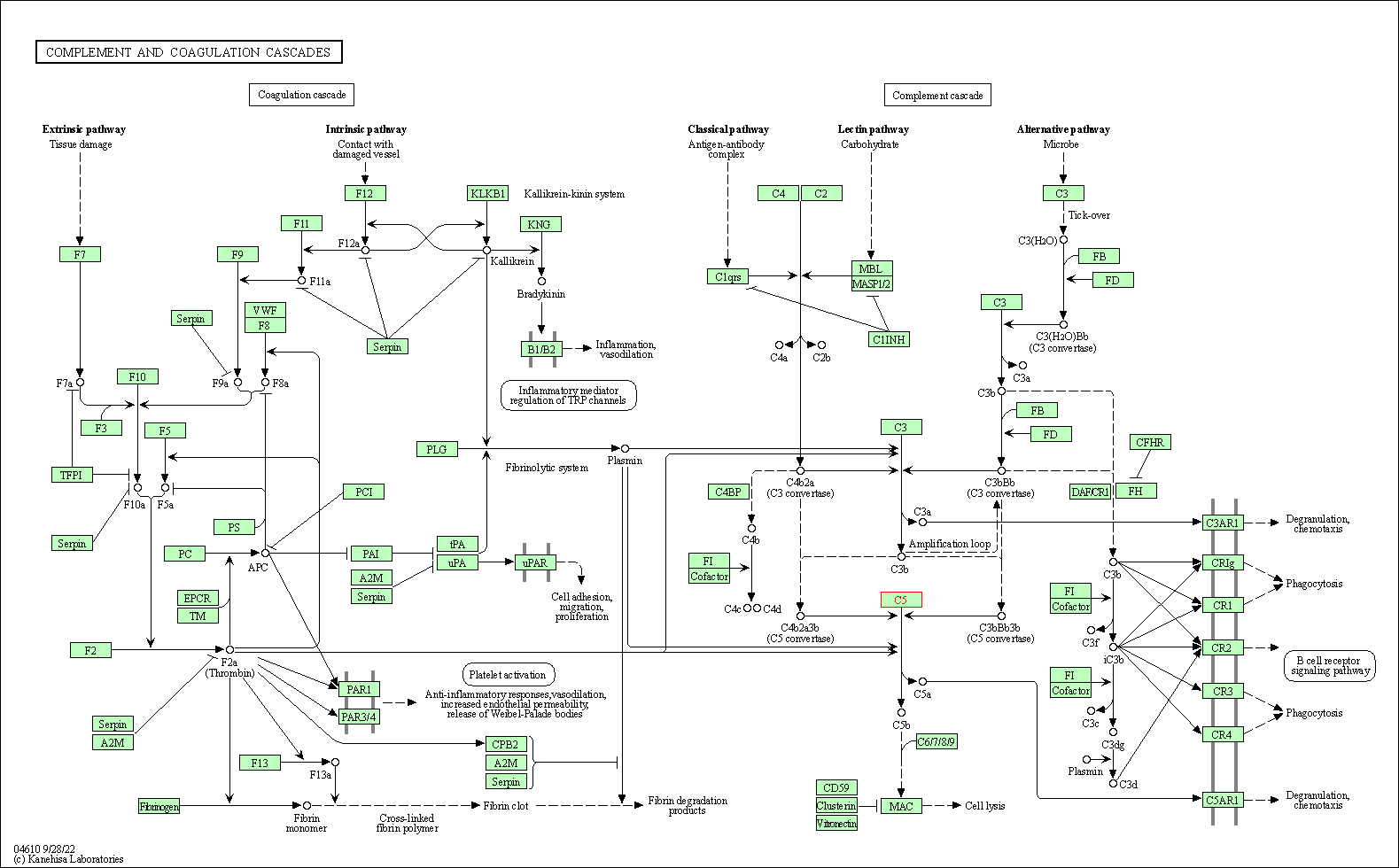
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Neutrophil extracellular trap formation | hsa04613 | Affiliated Target |
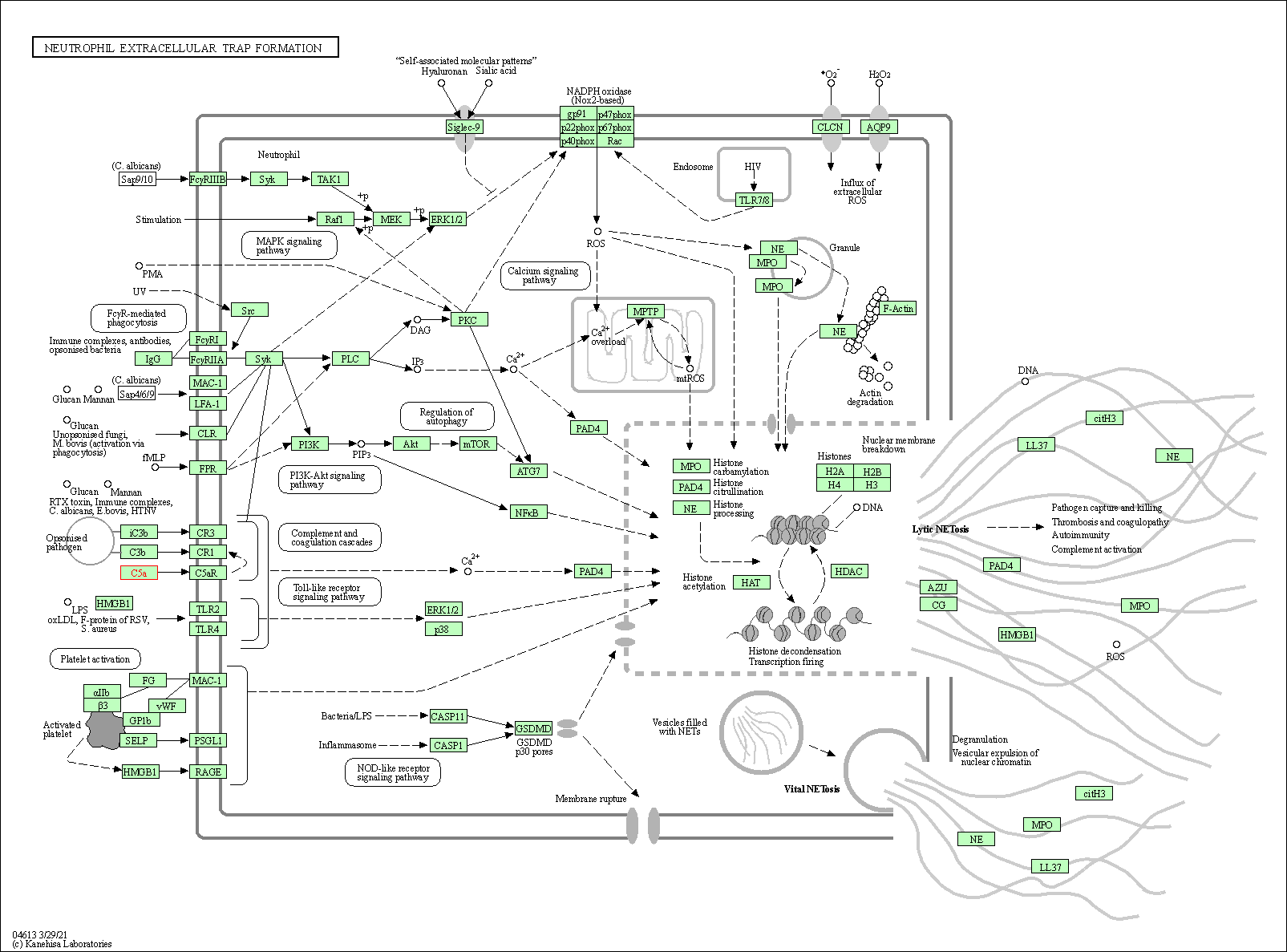
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Regulation of actin cytoskeleton | hsa04810 | Affiliated Target |
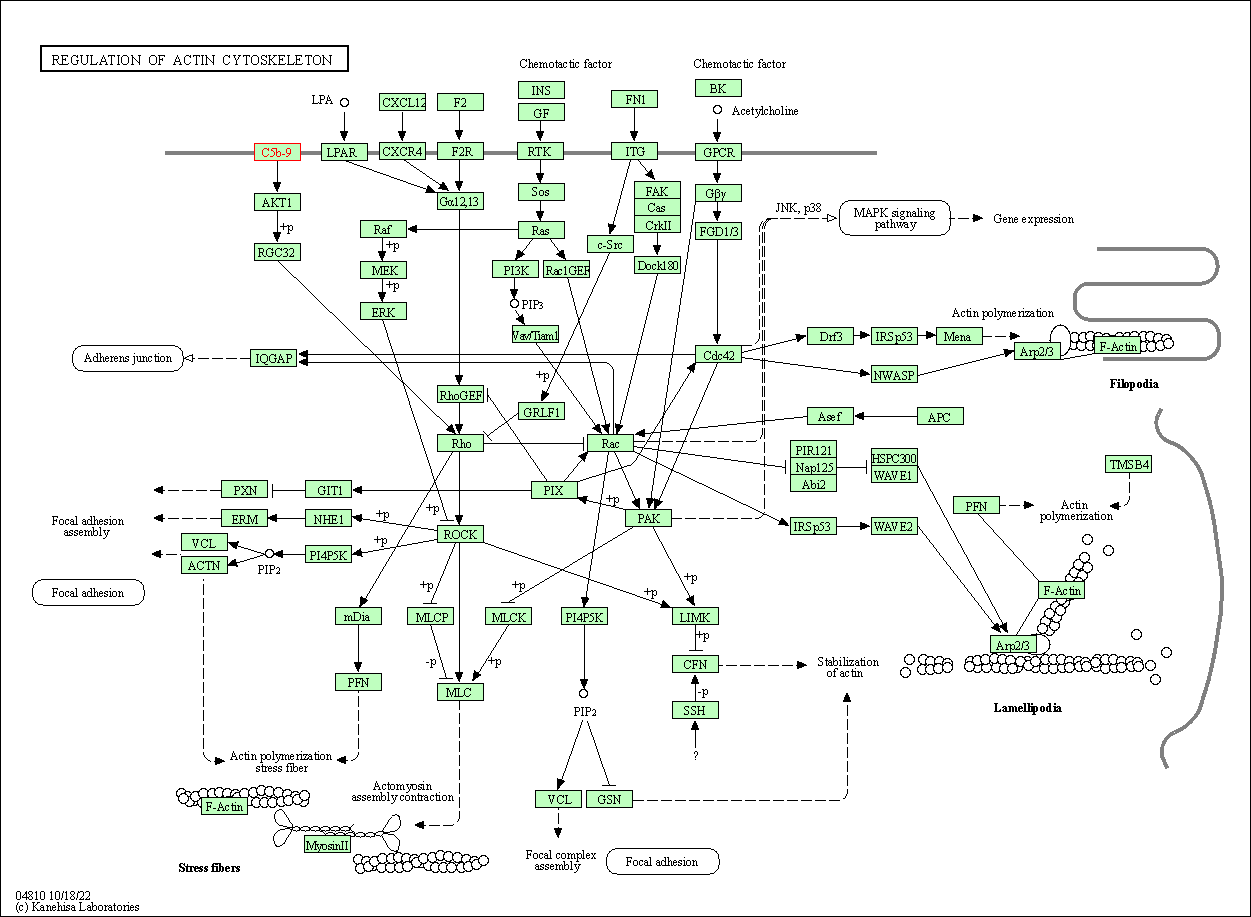
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell motility | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Degree | 11 | Degree centrality | 1.18E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 8.19E-04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 1.72E-01 | Radiality | 1.27E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 2.91E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 5.36E+00 | Topological coefficient | 2.42E-01 | Eccentricity | 14 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Complement as a target in COVID-19 Nat Rev Immunol. 2020 Apr 23. | |||||
| REF 2 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. 2015 | |||||
| REF 3 | FDA Approved Drug Products from FDA Official Website. 2019. Application Number: (BLA) 761108. | |||||
| REF 4 | ULTOMIRIS (ravulizumab cwvz) | |||||
| REF 5 | FDA Approved Drug Products from FDA Official Website. 2019. Application Number: (BLA) 125166. | |||||
| REF 6 | The allosteric modulation of complement C5 by knob domain peptides. Elife. 2021 Feb 11;10:e63586. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

