Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T91605
|
|||||
| Target Name |
E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase TRIM37 (TRIM37)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Tripartite motif-containing protein 37; RING-type E3 ubiquitin transferase TRIM37; Mulibrey nanism protein
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
TRIM37
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Literature-reported target
|
[1] | ||||
| Function |
E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase required to prevent centriole reduplication (PubMed:15885686, PubMed:23769972). Probably acts by ubiquitinating positive regulators of centriole reduplication (PubMed:23769972). Mediates monoubiquitination of 'Lys-119' of histone H2A (H2AK119Ub), a specific tag for epigenetic transcriptional repression: associates with some Polycomb group (PcG) multiprotein PRC2-like complex and mediates repression of target genes (PubMed:25470042). Has anti-HIV activity (PubMed:24317724).
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
TRIM/RBCC family
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 2.3.2.27
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MDEQSVESIAEVFRCFICMEKLRDARLCPHCSKLCCFSCIRRWLTEQRAQCPHCRAPLQL
RELVNCRWAEEVTQQLDTLQLCSLTKHEENEKDKCENHHEKLSVFCWTCKKCICHQCALW GGMHGGHTFKPLAEIYEQHVTKVNEEVAKLRRRLMELISLVQEVERNVEAVRNAKDERVR EIRNAVEMMIARLDTQLKNKLITLMGQKTSLTQETELLESLLQEVEHQLRSCSKSELISK SSEILMMFQQVHRKPMASFVTTPVPPDFTSELVPSYDSATFVLENFSTLRQRADPVYSPP LQVSGLCWRLKVYPDGNGVVRGYYLSVFLELSAGLPETSKYEYRVEMVHQSCNDPTKNII REFASDFEVGECWGYNRFFRLDLLANEGYLNPQNDTVILRFQVRSPTFFQKSRDQHWYIT QLEAAQTSYIQQINNLKERLTIELSRTQKSRDLSPPDNHLSPQNDDALETRAKKSACSDM LLEGGPTTASVREAKEDEEDEEKIQNEDYHHELSDGDLDLDLVYEDEVNQLDGSSSSASS TATSNTEENDIDEETMSGENDVEYNNMELEEGELMEDAAAAGPAGSSHGYVGSSSRISRR THLCSAATSSLLDIDPLILIHLLDLKDRSSIENLWGLQPRPPASLLQPTASYSRKDKDQR KQQAMWRVPSDLKMLKRLKTQMAEVRCMKTDVKNTLSEIKSSSAASGDMQTSLFSADQAA LAACGTENSGRLQDLGMELLAKSSVANCYIRNSTNKKSNSPKPARSSVAGSLSLRRAVDP GENSRSKGDCQTLSEGSPGSSQSGSRHSSPRALIHGSIGDILPKTEDRQCKALDSDAVVV AVFSGLPAVEKRRKMVTLGANAKGGHLEGLQMTDLENNSETGELQPVLPEGASAAPEEGM SSDSDIECDTENEEQEEHTSVGGFHDSFMVMTQPPDEDTHSSFPDGEQIGPEDLSFNTDE NSGR Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Pathway Affiliation
|
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis | hsa04120 | Affiliated Target |
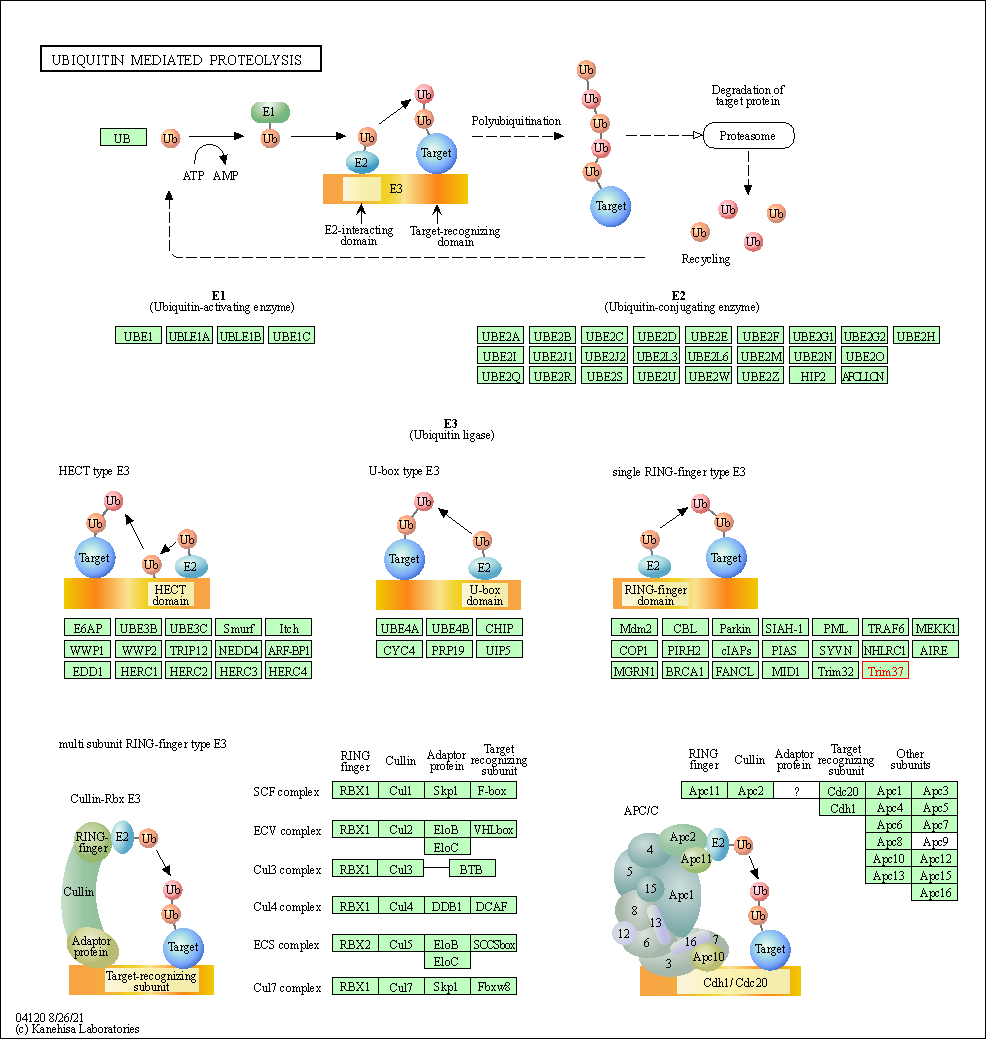
|
| Class: Genetic Information Processing => Folding, sorting and degradation | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KEGG Pathway | [+] 1 KEGG Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis | |||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | TRIM37 promotes tumor cell proliferation and drug resistance in pediatric osteosarcoma. Oncol Lett. 2017 Dec;14(6):6365-6372. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

