Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T85435
(Former ID: TTDS00292)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Insulin receptor (INSR)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
IR; CD220 antigen; CD220
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
INSR
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Successful target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 2 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Acute diabete complication [ICD-11: 5A2Y] | |||||
| 2 | Type 2 diabetes mellitus [ICD-11: 5A11] | |||||
| Function |
Binding of insulin leads to phosphorylation of several intracellular substrates, including, insulin receptor substrates (IRS1, 2, 3, 4), SHC, GAB1, CBL and other signaling intermediates. Each of these phosphorylated proteins serve as docking proteins for other signaling proteins that contain Src-homology-2 domains (SH2 domain) that specifically recognize different phosphotyrosine residues, including the p85 regulatory subunit of PI3K and SHP2. Phosphorylation of IRSs proteins lead to the activation of two main signaling pathways: the PI3K-AKT/PKB pathway, which is responsible for most of the metabolic actions of insulin, and the Ras-MAPK pathway, which regulates expression of some genes and cooperates with the PI3K pathway to control cell growth and differentiation. Binding of the SH2 domains of PI3K to phosphotyrosines on IRS1 leads to the activation of PI3K and the generation of phosphatidylinositol-(3, 4, 5)-triphosphate (PIP3), a lipid second messenger, which activates several PIP3-dependent serine/threonine kinases, such as PDPK1 and subsequently AKT/PKB. The net effect of this pathway is to produce a translocation of the glucose transporter SLC2A4/GLUT4 from cytoplasmic vesicles to the cell membrane to facilitate glucose transport. Moreover, upon insulin stimulation, activated AKT/PKB is responsible for: anti-apoptotic effect of insulin by inducing phosphorylation of BAD; regulates the expression of gluconeogenic and lipogenic enzymes by controlling the activity of the winged helix or forkhead (FOX) class of transcription factors. Another pathway regulated by PI3K-AKT/PKB activation is mTORC1 signaling pathway which regulates cell growth and metabolism and integrates signals from insulin. AKT mediates insulin-stimulated protein synthesis by phosphorylating TSC2 thereby activating mTORC1 pathway. The Ras/RAF/MAP2K/MAPK pathway is mainly involved in mediating cell growth, survival and cellular differentiation of insulin. Phosphorylated IRS1 recruits GRB2/SOS complex, which triggers the activation of the Ras/RAF/MAP2K/MAPK pathway. In addition to binding insulin, the insulin receptor can bind insulin-like growth factors (IGFI and IGFII). Isoform Short has a higher affinity for IGFII binding. When present in a hybrid receptor with IGF1R, binds IGF1. shows that hybrid receptors composed of IGF1R and INSR isoform Long are activated with a high affinity by IGF1, with low affinity by IGF2 and not significantly activated by insulin, and that hybrid receptors composed of IGF1R and INSR isoform Short are activated by IGF1, IGF2 and insulin. In contrast, shows that hybrid receptors composed of IGF1R and INSR isoform Long and hybrid receptors composed of IGF1R and INSR isoform Short have similar binding characteristics, both bind IGF1 and have a low affinity for insulin. Receptor tyrosine kinase which mediates the pleiotropic actions of insulin.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Kinase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 2.7.10.1
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MATGGRRGAAAAPLLVAVAALLLGAAGHLYPGEVCPGMDIRNNLTRLHELENCSVIEGHL
QILLMFKTRPEDFRDLSFPKLIMITDYLLLFRVYGLESLKDLFPNLTVIRGSRLFFNYAL VIFEMVHLKELGLYNLMNITRGSVRIEKNNELCYLATIDWSRILDSVEDNYIVLNKDDNE ECGDICPGTAKGKTNCPATVINGQFVERCWTHSHCQKVCPTICKSHGCTAEGLCCHSECL GNCSQPDDPTKCVACRNFYLDGRCVETCPPPYYHFQDWRCVNFSFCQDLHHKCKNSRRQG CHQYVIHNNKCIPECPSGYTMNSSNLLCTPCLGPCPKVCHLLEGEKTIDSVTSAQELRGC TVINGSLIINIRGGNNLAAELEANLGLIEEISGYLKIRRSYALVSLSFFRKLRLIRGETL EIGNYSFYALDNQNLRQLWDWSKHNLTITQGKLFFHYNPKLCLSEIHKMEEVSGTKGRQE RNDIALKTNGDQASCENELLKFSYIRTSFDKILLRWEPYWPPDFRDLLGFMLFYKEAPYQ NVTEFDGQDACGSNSWTVVDIDPPLRSNDPKSQNHPGWLMRGLKPWTQYAIFVKTLVTFS DERRTYGAKSDIIYVQTDATNPSVPLDPISVSNSSSQIILKWKPPSDPNGNITHYLVFWE RQAEDSELFELDYCLKGLKLPSRTWSPPFESEDSQKHNQSEYEDSAGECCSCPKTDSQIL KELEESSFRKTFEDYLHNVVFVPRKTSSGTGAEDPRPSRKRRSLGDVGNVTVAVPTVAAF PNTSSTSVPTSPEEHRPFEKVVNKESLVISGLRHFTGYRIELQACNQDTPEERCSVAAYV SARTMPEAKADDIVGPVTHEIFENNVVHLMWQEPKEPNGLIVLYEVSYRRYGDEELHLCV SRKHFALERGCRLRGLSPGNYSVRIRATSLAGNGSWTEPTYFYVTDYLDVPSNIAKIIIG PLIFVFLFSVVIGSIYLFLRKRQPDGPLGPLYASSNPEYLSASDVFPCSVYVPDEWEVSR EKITLLRELGQGSFGMVYEGNARDIIKGEAETRVAVKTVNESASLRERIEFLNEASVMKG FTCHHVVRLLGVVSKGQPTLVVMELMAHGDLKSYLRSLRPEAENNPGRPPPTLQEMIQMA AEIADGMAYLNAKKFVHRDLAARNCMVAHDFTVKIGDFGMTRDIYETDYYRKGGKGLLPV RWMAPESLKDGVFTTSSDMWSFGVVLWEITSLAEQPYQGLSNEQVLKFVMDGGYLDQPDN CPERVTDLMRMCWQFNPKMRPTFLEIVNLLKDDLHPSFPEVSFFHSEENKAPESEELEME FEDMENVPLDRSSHCQREEAGGRDGGSSLGFKRSYEEHIPYTHMNGGKKNGRILTLPRSN PS Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T88B8X | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approved Drug(s) | [+] 9 Approved Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Human neutral insulin | Drug Info | Approved | Diabetic complication | [2] | |
| 2 | Insulin Lyspro recombinant | Drug Info | Approved | Diabetic complication | [3] | |
| 3 | Insulin recombinant | Drug Info | Approved | Diabetic complication | [3] | |
| 4 | Insulin, porcine | Drug Info | Approved | Diabetic complication | [3] | |
| 5 | Insulin-glulisine | Drug Info | Approved | Diabetic complication | [4] | |
| 6 | Insulin-lispro | Drug Info | Approved | Diabetic complication | [2], [3], [5] | |
| 7 | Meglitinides | Drug Info | Approved | Type-2 diabetes | [1] | |
| 8 | Metformin arginine-hemisuccinimide | Drug Info | Approved | Type-2 diabetes | [6] | |
| 9 | Ryzodeq | Drug Info | Approved | Type-2 diabetes | [7] | |
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 19 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | NN5401 | Drug Info | Phase 3 | Diabetic complication | [8] | |
| 2 | Metformin glycinate | Drug Info | Phase 2/3 | Type-2 diabetes | [9] | |
| 3 | DM-71 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Type-2 diabetes | [10] | |
| 4 | DM-99 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Alzheimer disease | [11] | |
| 5 | EGS-21 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Crohn disease | [12] | |
| 6 | Mitoglitazone | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Type-2 diabetes | [13] | |
| 7 | MSDC-0602 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Type-2 diabetes | [14] | |
| 8 | NP-01 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Type-2 diabetes | [15] | |
| 9 | RZ358 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Congenital hyperinsulinism | [16] | |
| 10 | S-707106 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Type-2 diabetes | [17] | |
| 11 | TAK-379 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Type-2 diabetes | [18] | |
| 12 | Tesofensine | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Pain | [19] | |
| 13 | VVP-808 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Type-2 diabetes | [20] | |
| 14 | AEW-541 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Multiple myeloma | [21] | |
| 15 | AGT-182 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Hunter syndrome | [22] | |
| 16 | Insulin oral sublingual | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Type-1 diabetes | [23] | |
| 17 | Insulin transdermal | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Type-1/2 diabetes | [24] | |
| 18 | ISF-402 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Type-2 diabetes | [25] | |
| 19 | NN-1218 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Diabetic complication | [26] | |
| Discontinued Drug(s) | [+] 6 Discontinued Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | AKP-020 | Drug Info | Discontinued in Phase 2 | Type-2 diabetes | [27] | |
| 2 | DM-83 | Drug Info | Discontinued in Phase 2 | Type-2 diabetes | [28] | |
| 3 | EML-336 | Drug Info | Discontinued in Phase 2 | Type-2 diabetes | [29] | |
| 4 | KW-2450 | Drug Info | Discontinued in Phase 1/2 | Breast cancer | [30] | |
| 5 | CLX-0900 | Drug Info | Terminated | Hyperlipidaemia | [31] | |
| 6 | TER-16998 | Drug Info | Terminated | Diabetic complication | [32] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 7 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Binder | [+] 6 Binder drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Human neutral insulin | Drug Info | [33] | |||
| 2 | Insulin Lyspro recombinant | Drug Info | [33] | |||
| 3 | Insulin recombinant | Drug Info | [33] | |||
| 4 | Insulin, porcine | Drug Info | [34] | |||
| 5 | Insulin-glulisine | Drug Info | [35] | |||
| 6 | Insulin-lispro | Drug Info | [36] | |||
| Stimulator | [+] 2 Stimulator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Meglitinides | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 2 | DM-83 | Drug Info | [38] | |||
| Inhibitor | [+] 11 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Metformin arginine-hemisuccinimide | Drug Info | [37] | |||
| 2 | Metformin glycinate | Drug Info | [39] | |||
| 3 | Tesofensine | Drug Info | [44] | |||
| 4 | AEW-541 | Drug Info | [45] | |||
| 5 | 4-((1H-indazol-6-ylamino)methyl)benzene-1,2-diol | Drug Info | [52] | |||
| 6 | 4-((naphthalen-2-ylamino)methyl)benzene-1,2-diol | Drug Info | [52] | |||
| 7 | GSK-1838705A | Drug Info | [53] | |||
| 8 | L-betagamma-meATP | Drug Info | [54] | |||
| 9 | NVP-TAE684 | Drug Info | [55] | |||
| 10 | PMID24900237C15 | Drug Info | [56] | |||
| 11 | VVP-100X | Drug Info | [38] | |||
| Modulator | [+] 20 Modulator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Ryzodeq | Drug Info | [38] | |||
| 2 | NN5401 | Drug Info | [38] | |||
| 3 | DM-71 | Drug Info | [38] | |||
| 4 | EGS-21 | Drug Info | [40] | |||
| 5 | Mitoglitazone | Drug Info | [41] | |||
| 6 | MSDC-0602 | Drug Info | [42] | |||
| 7 | S-707106 | Drug Info | [38] | |||
| 8 | TAK-379 | Drug Info | [38] | |||
| 9 | VVP-808 | Drug Info | [38] | |||
| 10 | Insulin oral sublingual | Drug Info | [38] | |||
| 11 | Insulin transdermal | Drug Info | [46] | |||
| 12 | ISF-402 | Drug Info | [47] | |||
| 13 | NN-1218 | Drug Info | [48] | |||
| 14 | EML-336 | Drug Info | [38] | |||
| 15 | KW-2450 | Drug Info | [50] | |||
| 16 | CLX-0900 | Drug Info | [51] | |||
| 17 | DC-9703 | Drug Info | [38] | |||
| 18 | FPT-038 | Drug Info | [38] | |||
| 19 | Quick-acting insulin | Drug Info | [38] | |||
| 20 | RHIIP | Drug Info | [57] | |||
| Agonist | [+] 3 Agonist drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | DM-99 | Drug Info | [38] | |||
| 2 | NP-01 | Drug Info | [38] | |||
| 3 | AD10-1025 | Drug Info | [38] | |||
| Enhancer | [+] 1 Enhancer drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | AKP-020 | Drug Info | [49] | |||
| Activator | [+] 1 Activator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | TER-16998 | Drug Info | [38] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: Adenosine triphosphate | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal structure of the insulin receptor kinase in complex with IRS2 KRLB peptide and ATP | PDB:3BU5 | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.10 Å | Mutation | Yes | [58] |
| PDB Sequence |
DEWEVSREKI
996 TLLRELGQGM1009 VYEGNARDII1019 KGEAETRVAV1029 KTVNESASLR1039 ERIEFLNEAS 1049 VMKGFTCHHV1059 VRLLGVVSKG1069 QPTLVVMELM1079 AHGDLKSYLR1089 SLRPEAENNP 1099 GRPPPTLQEM1109 IQMAAEIADG1119 MAYLNAKKFV1129 HRDLAARNCM1139 VAHDFTVKIG 1149 DFGMTRDIET1160 DRKGGKGLLP1172 VRWMAPESLK1182 DGVFTTSSDM1192 WSFGVVLWEI 1202 TSLAEQPYQG1212 LSNEQVLKFV1222 MDGGYLDQPD1232 NCPERVTDLM1242 RMCWQFNPNM 1252 RPTFLEIVNL1262 LKDDLHPSFP1272 EVSFFHSEEN1282 K
|
|||||
|
|
LEU1002
4.129
GLY1003
4.029
GLN1004
4.055
GLY1008
4.977
VAL1010
4.146
ALA1028
3.584
LYS1030
2.760
GLU1047
3.046
VAL1060
4.092
MET1076
3.587
GLU1077
2.783
|
|||||
| Ligand Name: L-betagamma-meATP | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal structure of the activated insulin receptor tyrosine kinase dimer | PDB:4XLV | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.30 Å | Mutation | Yes | [59] |
| PDB Sequence |
SASDVFPSSV
983 YVPDEWEVSR993 EKITLLRELG1003 QGSFGMVYEG1013 NARDIIKGEA1023 ETRVAVKTVN 1033 ESASLRERIE1043 FLNEASVMKG1053 FTCHHVVRLL1063 GVVSKGQPTL1073 VVMELMAHGD 1083 LKSYLRSLRP1093 EAENNPGRPP1103 PTLQEMIQMA1113 AEIADGMAYL1123 NAKKFVHRDL 1133 AARNCMVAHD1143 FTVKIGDFGM1153 TRDIETDRKG1166 GKGLLPVRWM1176 APESLKDGVF 1186 TTSSDMWSFG1196 VVLWEITSLA1206 EQPYQGLSNE1216 QVLKFVMDGG1226 YLDQPDNCPE 1236 RVTDLMRMCW1246 QFNPNMRPTF1256 LEIVNLLKDD1266 LHPSFPEVSF1276 FHSEENK |
|||||
|
|
LEU1002
3.632
GLY1003
3.952
GLY1005
3.477
SER1006
4.767
PHE1007
3.797
GLY1008
4.163
VAL1010
3.587
ALA1028
3.426
LYS1030
2.763
GLU1043
3.295
GLU1047
2.894
VAL1060
3.938
MET1076
2.881
|
|||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
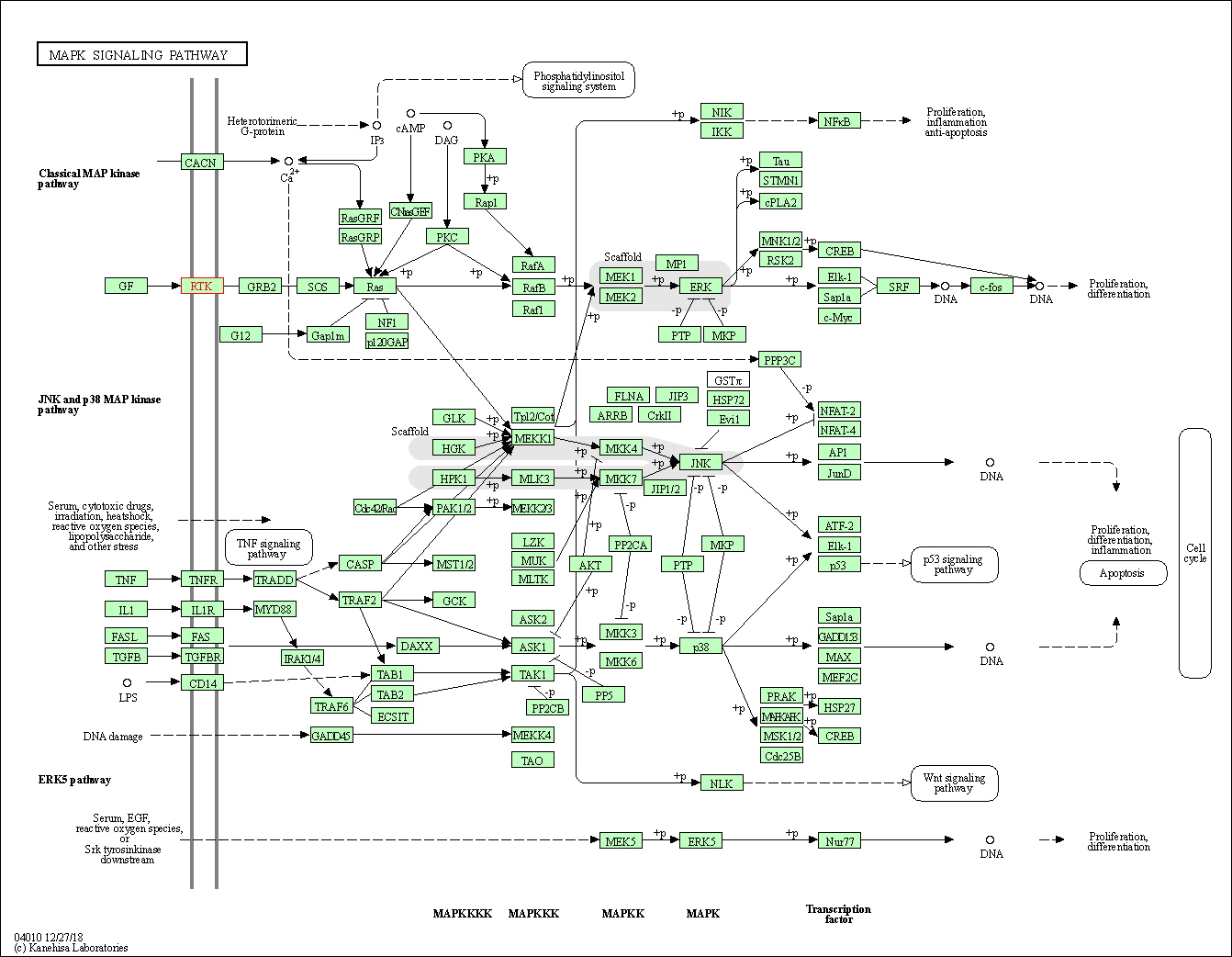
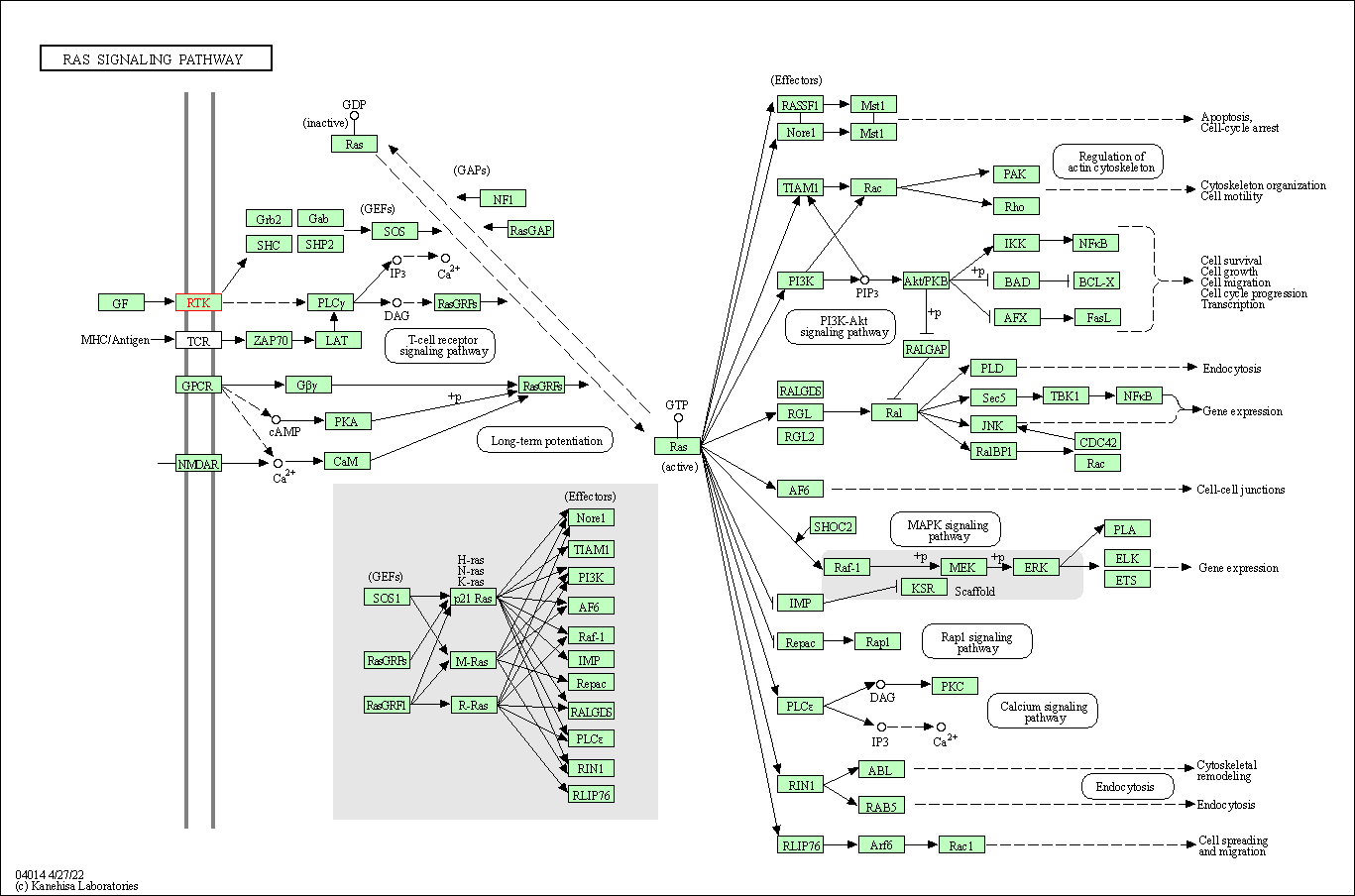
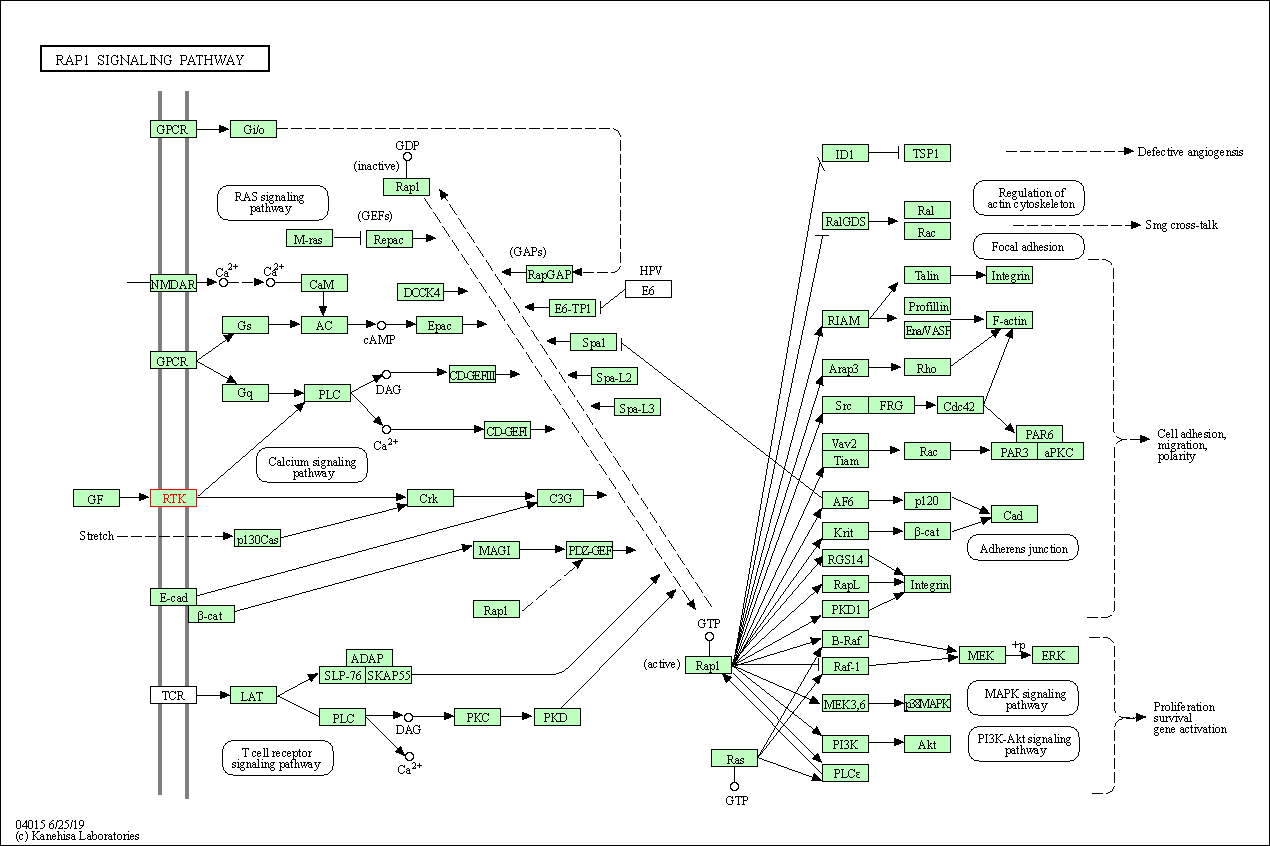
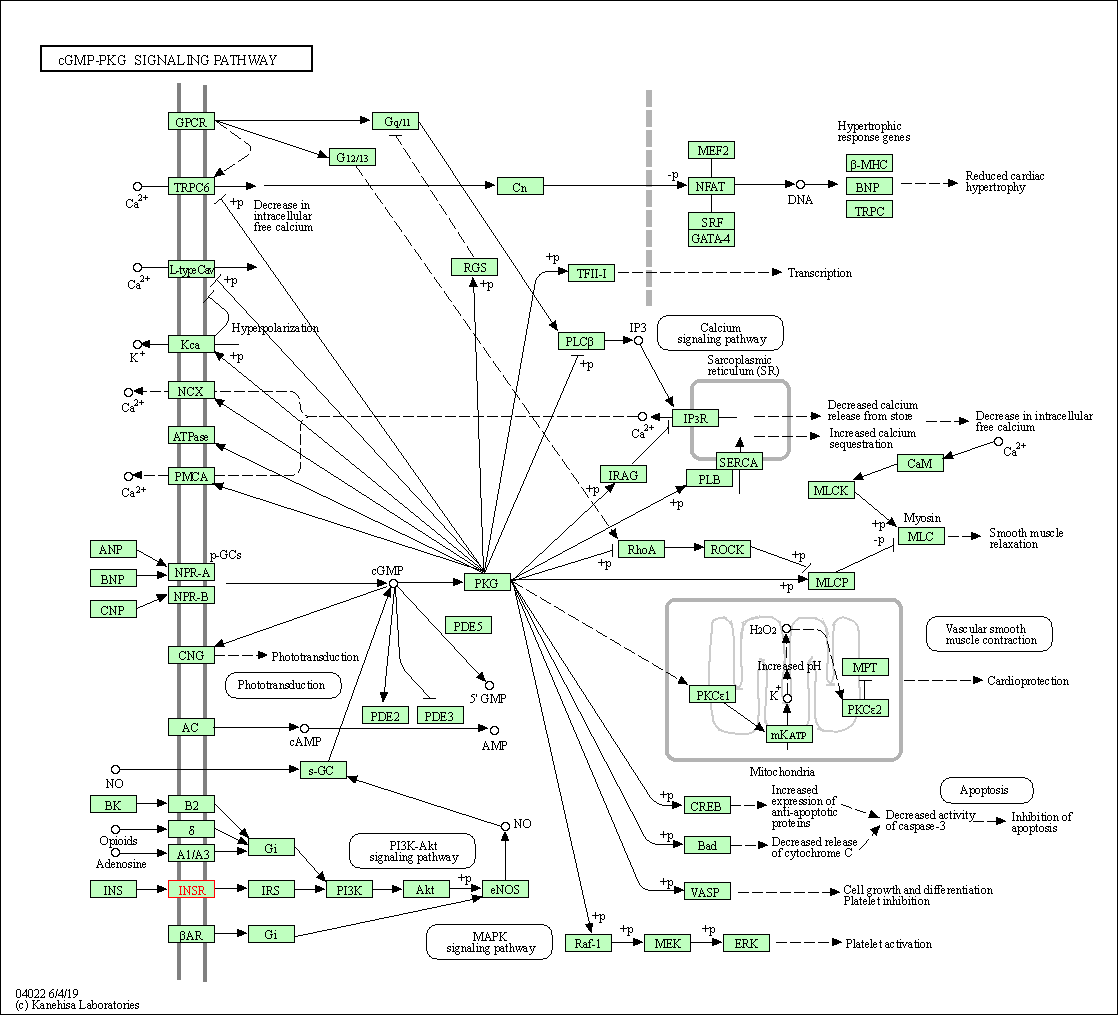
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| MAPK signaling pathway | hsa04010 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Ras signaling pathway | hsa04014 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Rap1 signaling pathway | hsa04015 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| cGMP-PKG signaling pathway | hsa04022 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| HIF-1 signaling pathway | hsa04066 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| FoxO signaling pathway | hsa04068 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Phospholipase D signaling pathway | hsa04072 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
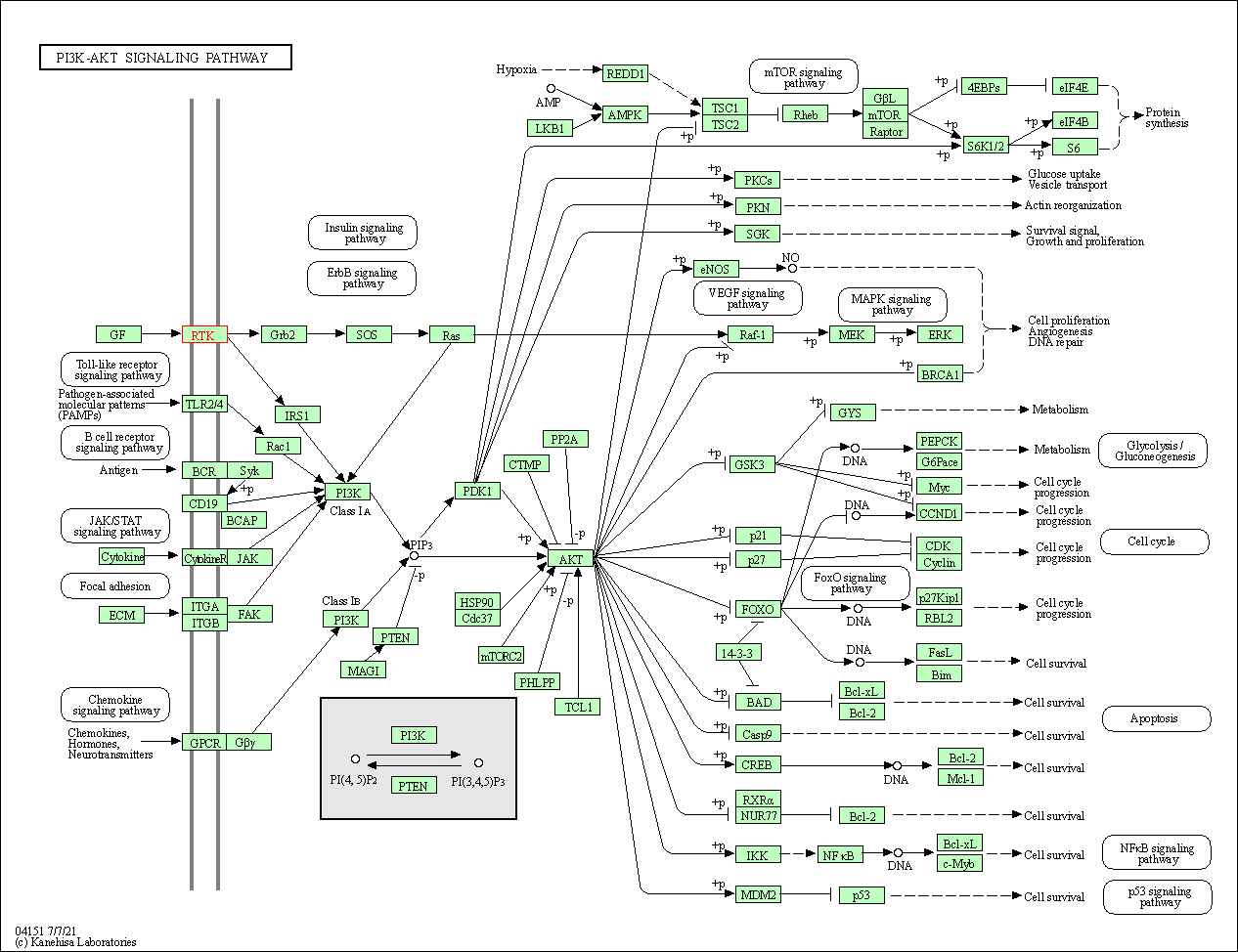
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
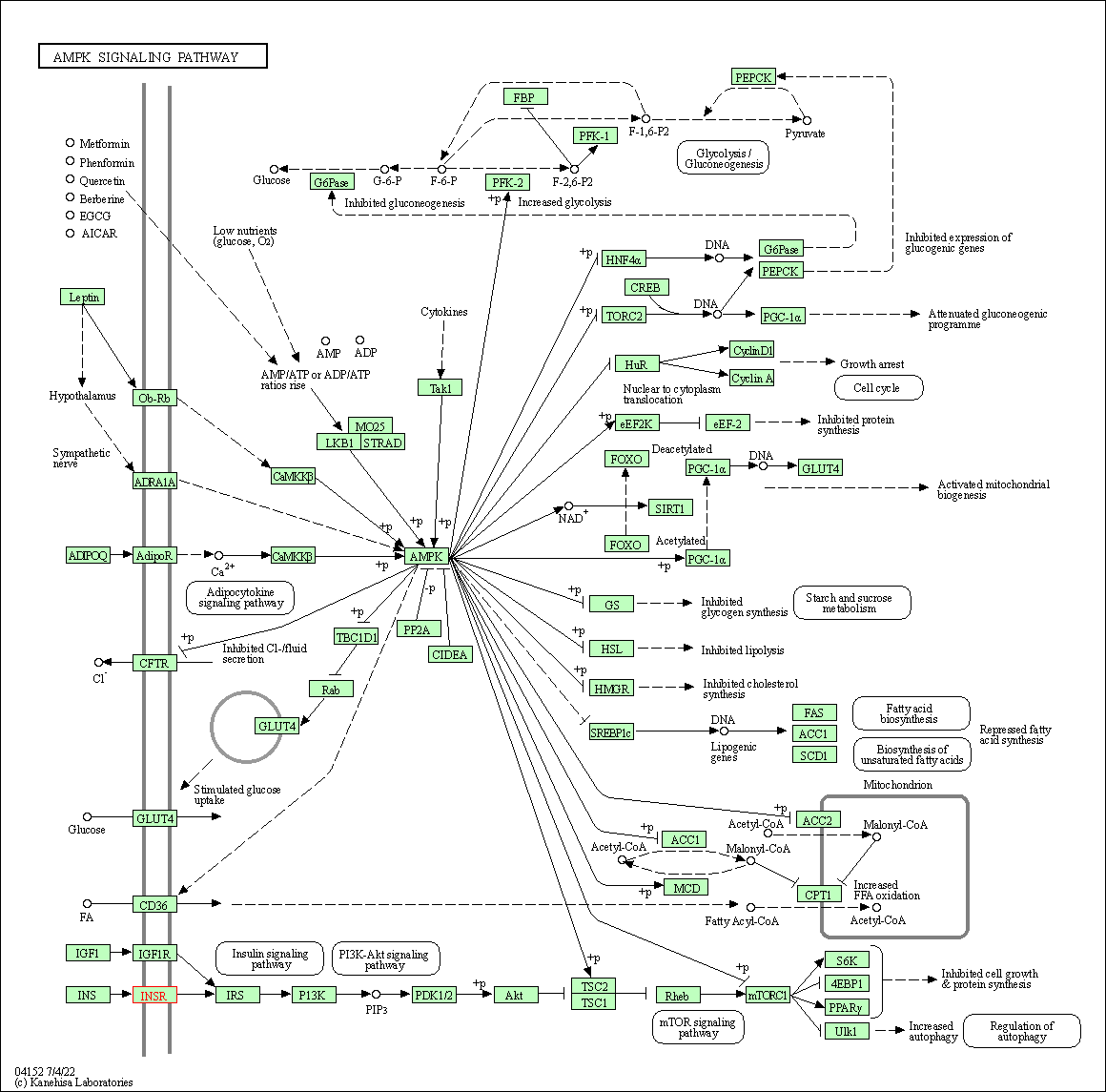
| AMPK signaling pathway | hsa04152 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
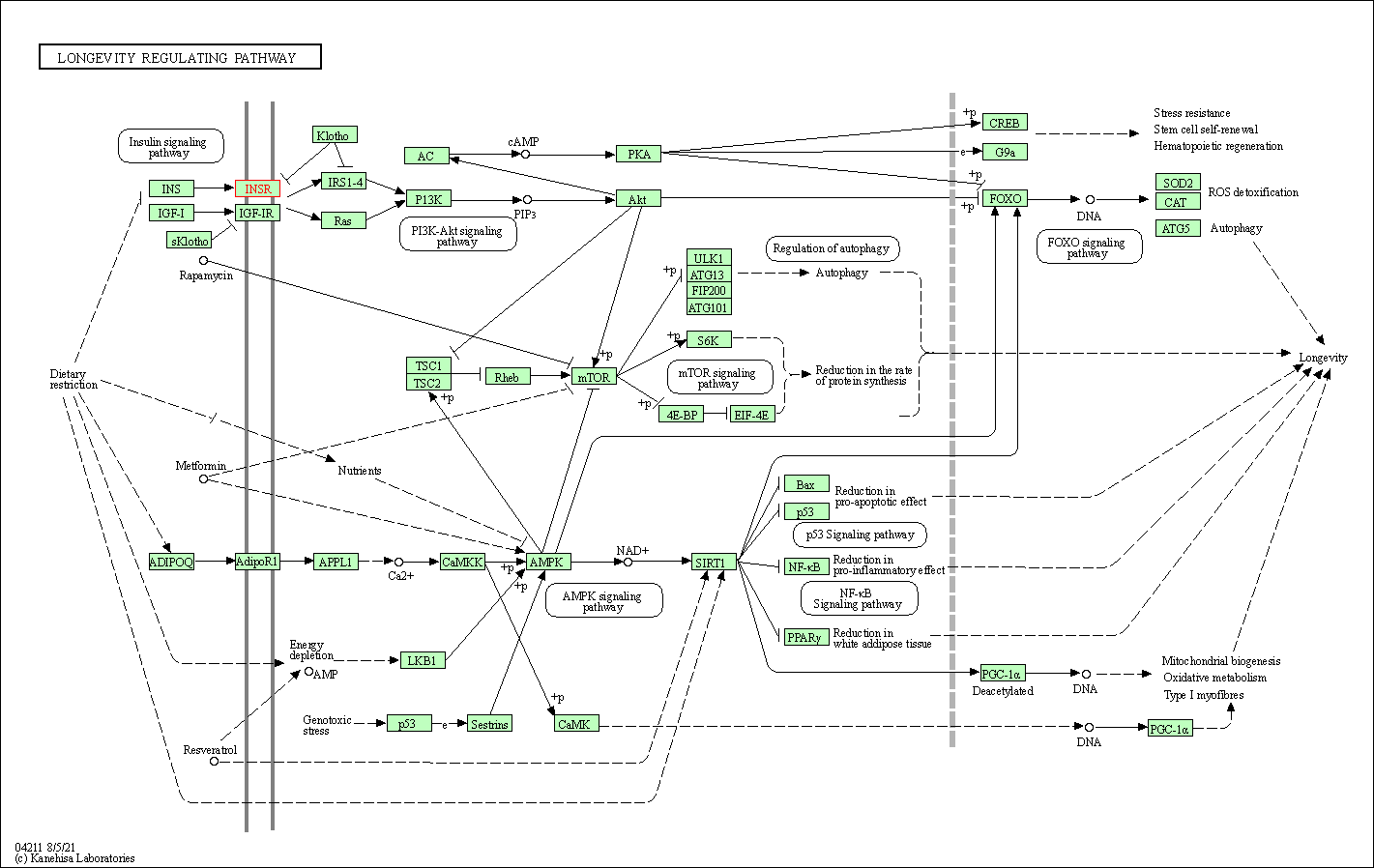
| Longevity regulating pathway | hsa04211 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Aging | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
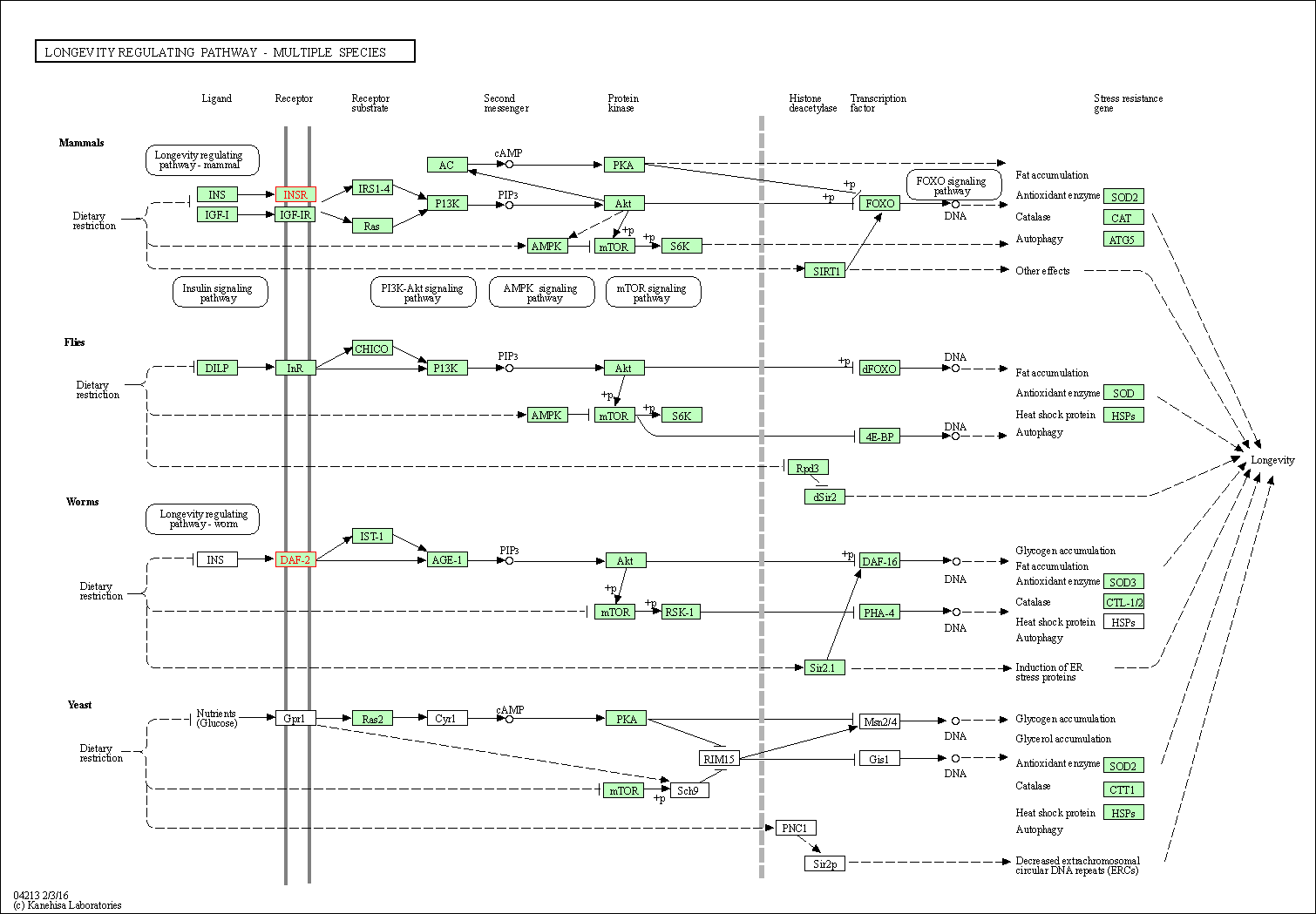
| Longevity regulating pathway - multiple species | hsa04213 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Aging | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
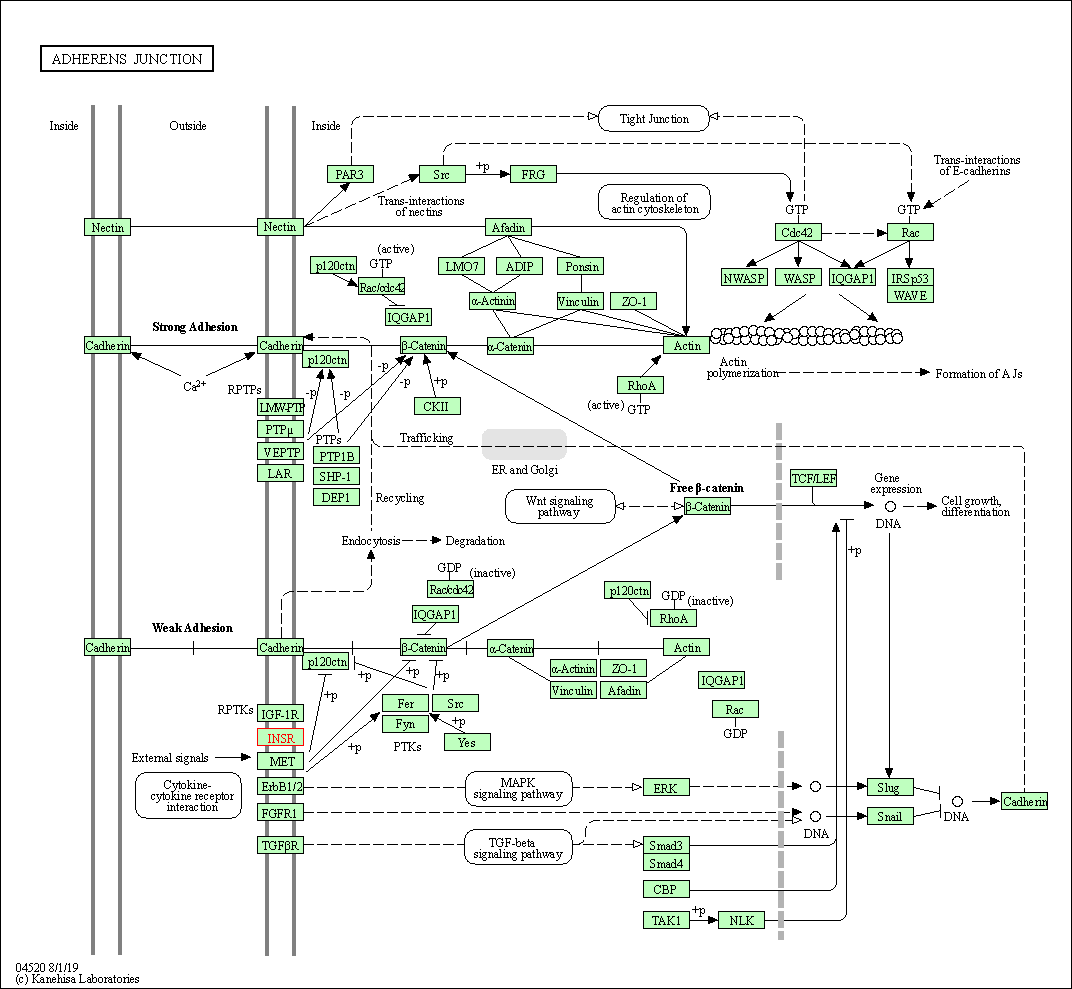
| Adherens junction | hsa04520 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cellular community - eukaryotes | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
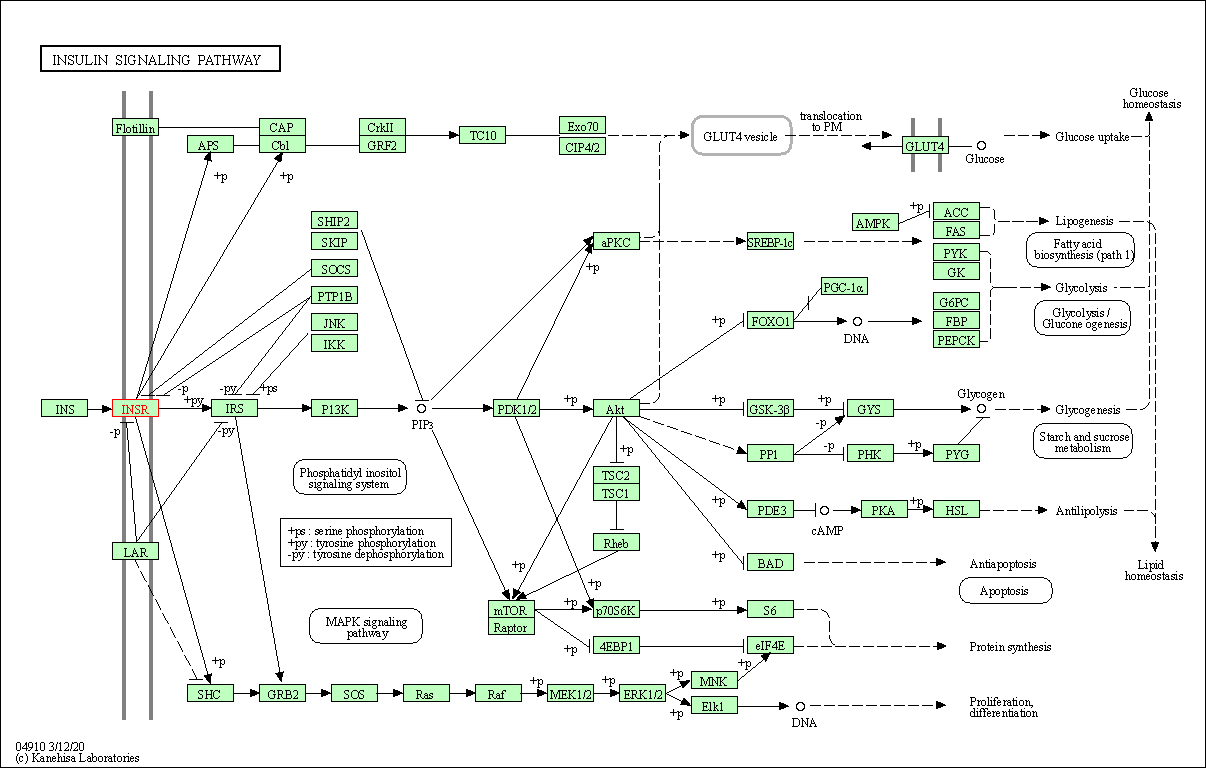
| Insulin signaling pathway | hsa04910 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
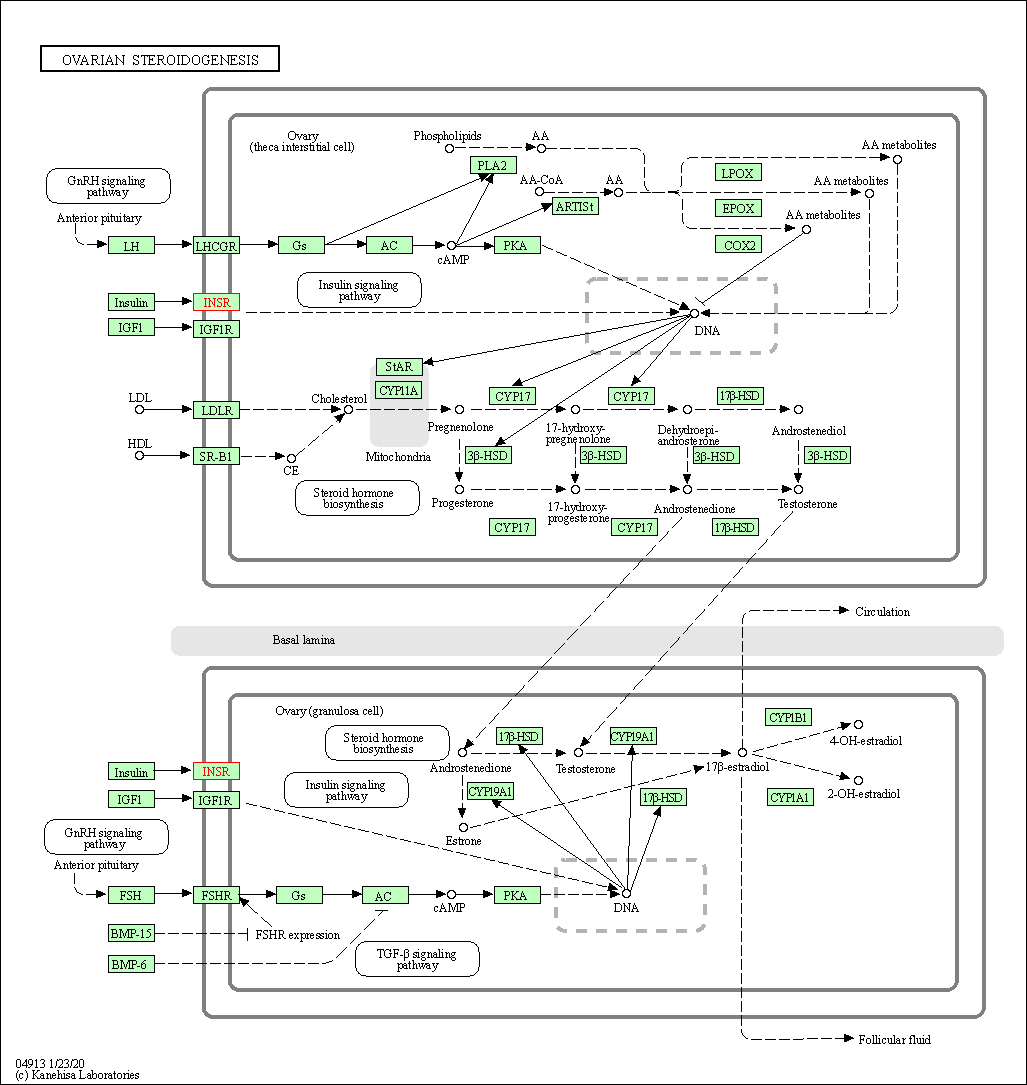
| Ovarian steroidogenesis | hsa04913 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
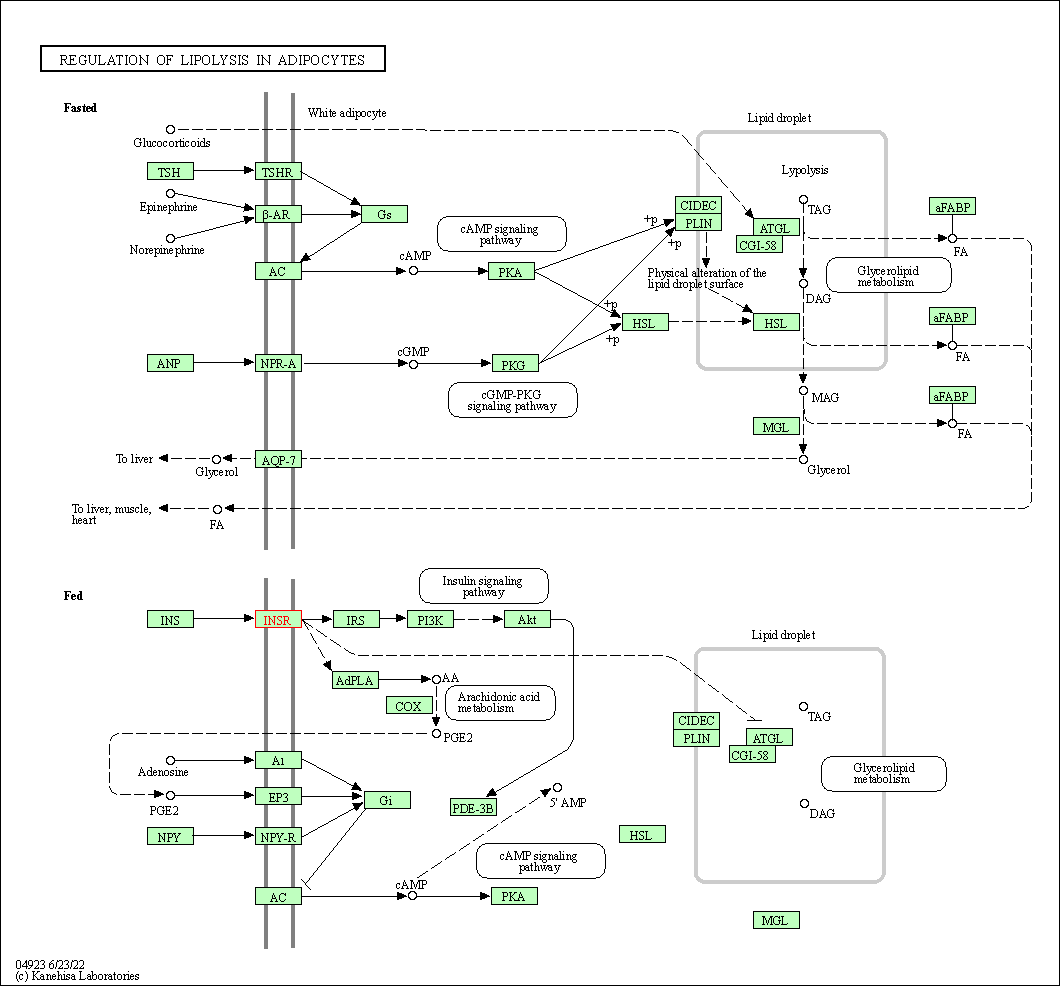
| Regulation of lipolysis in adipocytes | hsa04923 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Aldosterone-regulated sodium reabsorption | hsa04960 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Excretory system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 21 | Degree centrality | 2.26E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 3.37E-04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.34E-01 | Radiality | 1.41E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 3.19E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 4.24E+01 | Topological coefficient | 1.12E-01 | Eccentricity | 12 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Co-Targets | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-Targets | ||||||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Expression Profile (TEP) |
||||||
| Drug Resistance Mutation (DRM) |
||||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | New drugs for type 2 diabetes mellitus: what is their place in therapy Drugs. 2008;68(15):2131-62. | |||||
| REF 2 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. 2015 | |||||
| REF 3 | Natural products as sources of new drugs over the last 25 years. J Nat Prod. 2007 Mar;70(3):461-77. | |||||
| REF 4 | 2004 approvals: the demise of the blockbuster. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2005 Feb;4(2):93-4. | |||||
| REF 5 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800002887) | |||||
| REF 6 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals. | |||||
| REF 7 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of Novo nordisk. | |||||
| REF 8 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01059812) A Pan Asian Trial Comparing Efficacy and Safety of NN5401 and Biphasic Insulin Aspart 30 in Type 2 Diabetes. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 9 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT00940472) Study on DMMET-01 Versus Metformin on Improvement of Metabolic Control in Naive Type 2 Diabetes Patients. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 10 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of DiaMedica Inc. | |||||
| REF 11 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800030024) | |||||
| REF 12 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800020751) | |||||
| REF 13 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01103414) Study to Evaluate the Safety, Tolerability and Efficacy of Three Dose Levels of Mitoglitazone in Type 2 Diabetic Patients. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 14 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01280695) A Randomized, Double-Blind, Comparator- and Placebo-Controlled, Multiple-Dose Study to Evaluate the Safety, Tolerability and Efficacy of Three Dose Levels of MSDC-0602 in Type 2 Diabetic Patients. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 15 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of Medesis Pharma SA. | |||||
| REF 16 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04538989) An Open-Label Multiple-Dose Study of RZ358 in Patients With Congenital Hyperinsulinism. U.S.National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 17 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800031641) | |||||
| REF 18 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT00722917) Efficacy and Safety of TAK-379 in Adult Subjects With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 19 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT00153010) An Evaluation of Three Doses of NS 2330 in Patients With Mild to Moderate Dementia of the Alzheimer's Type. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 20 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800029155) | |||||
| REF 21 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800019974) | |||||
| REF 22 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 23 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of Biodel. | |||||
| REF 24 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800024972) | |||||
| REF 25 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of Dia-B Tech. | |||||
| REF 26 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01121289) A Trial Investigating NN1218 in Subjects With Type 1 Diabetes. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 27 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800026051) | |||||
| REF 28 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800030050) | |||||
| REF 29 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800016521) | |||||
| REF 30 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800030562) | |||||
| REF 31 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800013573) | |||||
| REF 32 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800007187) | |||||
| REF 33 | Knockouts model the 100 best-selling drugs--will they model the next 100 Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2003 Jan;2(1):38-51. | |||||
| REF 34 | Acidic residues on the N-terminus of proinsulin C-Peptide are important for the folding of insulin precursor. J Biochem. 2002 Jun;131(6):855-9. | |||||
| REF 35 | Insulin glulisine: a review of its use in the management of diabetes mellitus. Drugs. 2009;69(8):1035-57. | |||||
| REF 36 | Hope for insulin mimetic oral antidiabetic drugs. Eur J Endocrinol. 1999 Dec;141(6):561-2. | |||||
| REF 37 | Metformin (Glucophage) inhibits tyrosine phosphatase activity to stimulate the insulin receptor tyrosine kinase. Biochem Pharmacol. 2004 Jun 1;67(11):2081-91. | |||||
| REF 38 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Target id: 1800). | |||||
| REF 39 | Effect of Metformin Glycinate on Glycated Hemoglobin A1c Concentration and Insulin Sensitivity in Drug-Naive Adult Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2012 December; 14(12): 1140-1144. | |||||
| REF 40 | Ceramides and glucosylceramides are independent antagonists of insulin signaling. J Biol Chem. 2014 Jan 10;289(2):723-34. | |||||
| REF 41 | An evaluation of MSDC-0160, a prototype mTOT modulating insulin sensitizer, in patients with mild Alzheimer's disease. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2014;11(6):564-73. | |||||
| REF 42 | Insulin resistance and metabolic derangements in obese mice are ameliorated by a novel peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma-sparing thiazolidinedione. J Biol Chem. 2012 Jul 6;287(28):23537-48. | |||||
| REF 43 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of Rezolute | |||||
| REF 44 | The novel triple monoamine reuptake inhibitor tesofensine induces sustained weight loss and improves glycemic control in the diet-induced obese rat: comparison to sibutramine and rimonabant. Eur J Pharmacol. 2010 Jun 25;636(1-3):88-95. | |||||
| REF 45 | Inhibition of the insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF1R) tyrosine kinase as a novel cancer therapy approach. J Med Chem. 2009 Aug 27;52(16):4981-5004. | |||||
| REF 46 | Transdermal drug delivery of insulin with ultradeformable carriers. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2003;42(5):461-74. | |||||
| REF 47 | Ability of GHTD-amide and analogs to enhance insulin activity through zinc chelation and dispersal of insulin oligomers. Peptides. 2009 Jun;30(6):1088-97. | |||||
| REF 48 | Ultrafast-Acting Insulins: State of the Art. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2012 July; 6(4): 728-742. | |||||
| REF 49 | Effect of vanadium on insulin and leptin in Zucker diabetic fatty rats. Mol Cell Biochem. 2001 Feb;218(1-2):93-6. | |||||
| REF 50 | Interpreting expression profiles of cancers by genome-wide survey of breadth of expression in normal tissues. Genomics 2005 Aug;86(2):127-41. | |||||
| REF 51 | CLX-0901 (Calyx Therapeutics). Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2001 May;2(5):650-3. | |||||
| REF 52 | ATP non-competitive IGF-1 receptor kinase inhibitors as lead anti-neoplastic and anti-papilloma agents. Eur J Pharmacol. 2007 May 7;562(1-2):1-11. | |||||
| REF 53 | GSK1838705A inhibits the insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor and anaplastic lymphoma kinase and shows antitumor activity in experimental models of human cancers. Mol Cancer Ther. 2009 Oct;8(10):2811-20. | |||||
| REF 54 | How many drug targets are there Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006 Dec;5(12):993-6. | |||||
| REF 55 | Identification of NVP-TAE684, a potent, selective, and efficacious inhibitor of NPM-ALK. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Jan 2;104(1):270-5. | |||||
| REF 56 | Discovery of a potent inhibitor of anaplastic lymphoma kinase with in vivo antitumor activity. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2010 Sep 1;1(9):493-8. | |||||
| REF 57 | PROMAXX inhaled insulin: safe and efficacious administration with a commercially available dry powder inhaler. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2009 May;11(5):455-9. | |||||
| REF 58 | Structural and biochemical characterization of the KRLB region in insulin receptor substrate-2. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2008 Mar;15(3):251-8. | |||||
| REF 59 | The insulin and IGF1 receptor kinase domains are functional dimers in the activated state. Nat Commun. 2015 Mar 11;6:6406. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

