Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T77613
(Former ID: TTDI02454)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Phosphodiesterase 1B (PDE1B)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
PDES1B; PDE1B1; CamPDE 1B; Cam-PDE 1B; Calcium/calmodulindependent 3',5'cyclicnucleotide phosphodiesterase 1B; Calcium/calmodulin-dependent 3',5'-cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase 1B; 63 kDa CamPDE; 63 kDa Cam-PDE
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
PDE1B
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Patented-recorded target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 1 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Mild neurocognitive disorder [ICD-11: 6D71] | |||||
| Function |
Has a preference for cGMP as a substrate. Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase with a dual-specificity for the second messengers cAMP and cGMP, which are key regulators of many important physiological processes.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Phosphoric diester hydrolase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 3.1.4.17
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MELSPRSPPEMLEESDCPSPLELKSAPSKKMWIKLRSLLRYMVKQLENGEINIEELKKNL
EYTASLLEAVYIDETRQILDTEDELQELRSDAVPSEVRDWLASTFTQQARAKGRRAEEKP KFRSIVHAVQAGIFVERMFRRTYTSVGPTYSTAVLNCLKNLDLWCFDVFSLNQAADDHAL RTIVFELLTRHNLISRFKIPTVFLMSFLDALETGYGKYKNPYHNQIHAADVTQTVHCFLL RTGMVHCLSEIELLAIIFAAAIHDYEHTGTTNSFHIQTKSECAIVYNDRSVLENHHISSV FRLMQDDEMNIFINLTKDEFVELRALVIEMVLATDMSCHFQQVKTMKTALQQLERIDKPK ALSLLLHAADISHPTKQWLVHSRWTKALMEEFFRQGDKEAELGLPFSPLCDRTSTLVAQS QIGFIDFIVEPTFSVLTDVAEKSVQPLADEDSKSKNQPSFQWRQPSLDVEVGDPNPDVVS FRSTWVKRIQENKQKWKERAASGITNQMSIDELSPCEEEAPPSPAEDEHNQNGNLD Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: ITI-214 | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal structure of human PDE1B with inhibitor 3 | PDB:5B25 | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 1.90 Å | Mutation | No | [8] |
| PDB Sequence |
TYSTAVLNCL
158 KNLDLWCFDV168 FSLNQAADDH178 ALRTIVFELL188 TRHNLISRFK198 IPTVFLMSFL 208 DALETGYGKY218 KNPYHNQIHA228 ADVTQTVHCF238 LLRTGMVHCL248 SEIELLAIIF 258 AAAIHDYEHT268 GTTNSFHIQT278 KSECAIVYND288 RSVLENHHIS298 SVFRLMQDDE 308 MNIFINLTKD318 EFVELRALVI328 EMVLATDMSC338 HFQQVKTMKT348 ALQQLERIDK 358 PKALSLLLHA368 ADISHPTKQW378 LVHSRWTKAL388 MEEFFRQGDK398 EAELGLPFSP 408 LCDRTSTLVA418 QSQIGFIDFI428 VEPTFSVLTD438 VAEKSVQPLA448 GDPNPDVVSF 481 RSTWVKRIQE491 NKQKWKERAA501 SGITN
|
|||||
|
|
TYR222
3.719
HIS223
3.916
MET336
3.905
PHE340
3.922
ASP370
4.232
ILE371
3.547
HIS373
3.293
PRO374
4.624
THR385
4.411
LEU388
3.345
MET389
4.224
|
|||||
| Ligand Name: 7,8-Dimethoxy-N-[(2s)-1-(3-Methyl-1h-Pyrazol-5-Yl)propan-2-Yl]quinazolin-4-Amine | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal structure of human PDE1B bound to inhibitor 19A (7,8-dimethoxy-N-[(2S)-1-(3-methyl-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)propan-2-yl]quinazolin-4-amine) | PDB:4NPW | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 1.90 Å | Mutation | No | [9] |
| PDB Sequence |
YSTAVLNCLK
159 NLDLWCFDVF169 SLNQAADDHA179 LRTIVFELLT189 RHNLISRFKI199 PTVFLMSFLD 209 ALETGYGKYK219 NPYHNQIHAA229 DVTQTVHCFL239 LRTGMVHCLS249 EIELLAIIFA 259 AAIHDYEHTG269 TTNSFHIQTK279 SECAIVYNDR289 SVLENHHISS299 VFRLMQDDEM 309 NIFINLTKDE319 FVELRALVIE329 MVLATDMSCH339 FQQVKTMKTA349 LQQLERIDKP 359 KALSLLLHAA369 DISHPTKQWL379 VHSRWTKALM389 EEFFRQGDKE399 AELGLPFSPL 409 CDRTSTLVAQ419 SQIGFIDFIV429 EPTFSVLTDV439 AEKSVQVVSF481 RSTWVKRIQE 491 NKQKWKERAA501 S
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purine metabolism | hsa00230 | Affiliated Target |
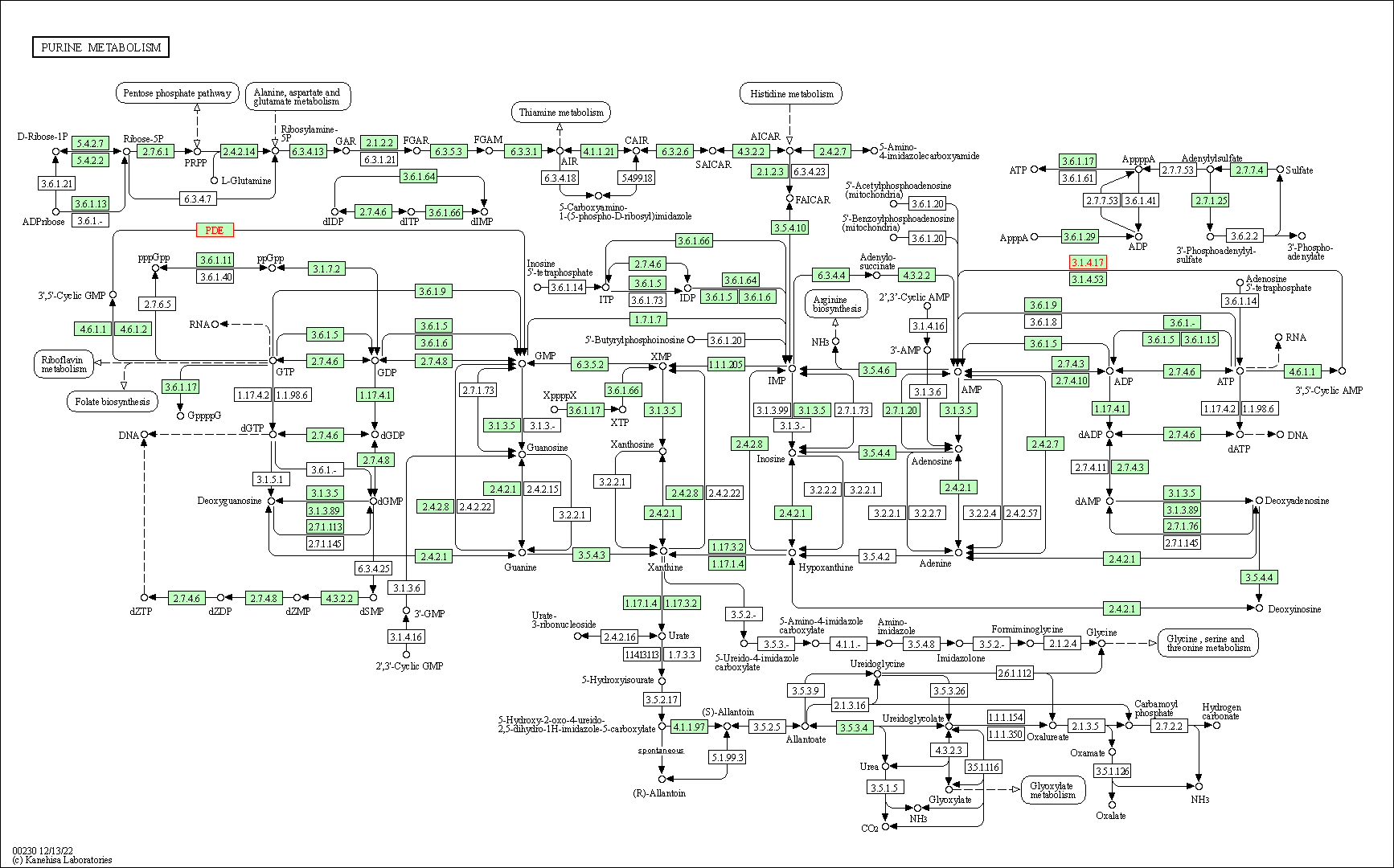
|
| Class: Metabolism => Nucleotide metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Calcium signaling pathway | hsa04020 | Affiliated Target |
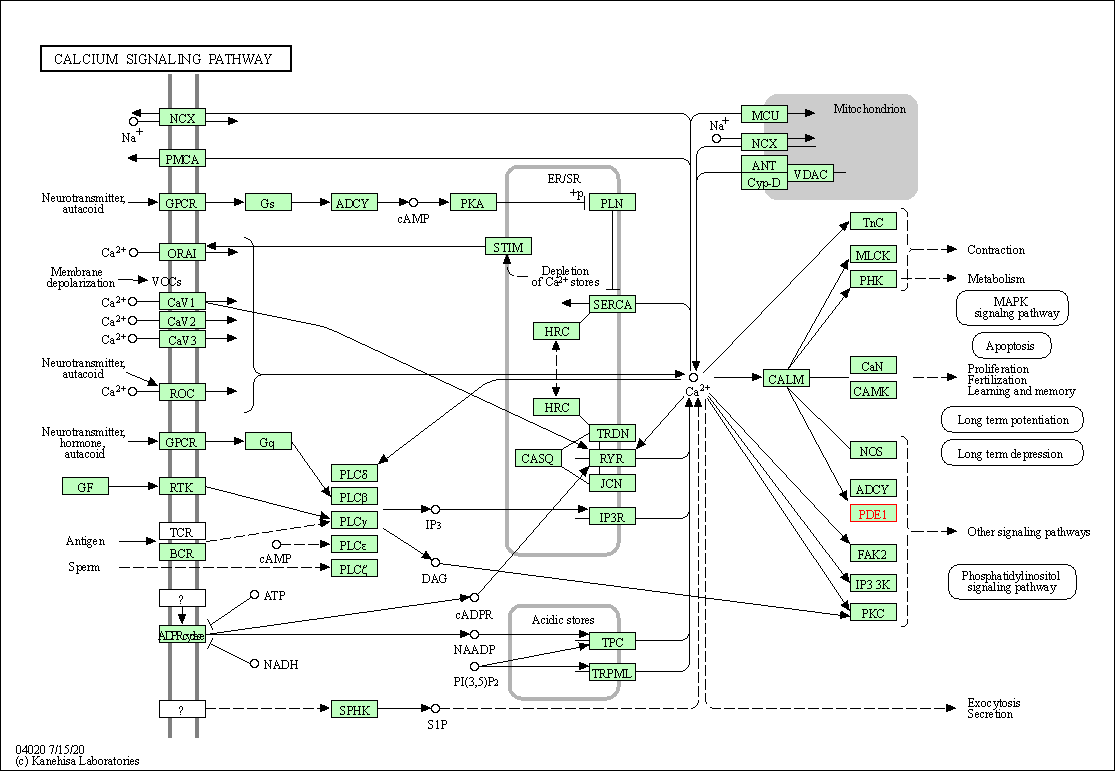
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Olfactory transduction | hsa04740 | Affiliated Target |
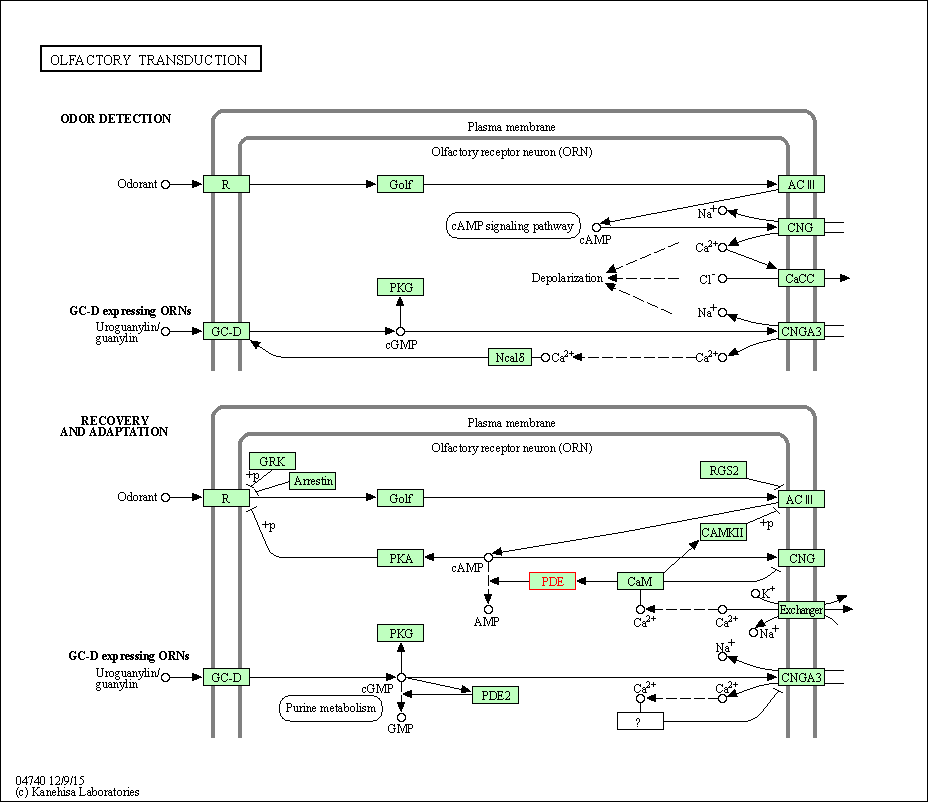
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Sensory system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Taste transduction | hsa04742 | Affiliated Target |
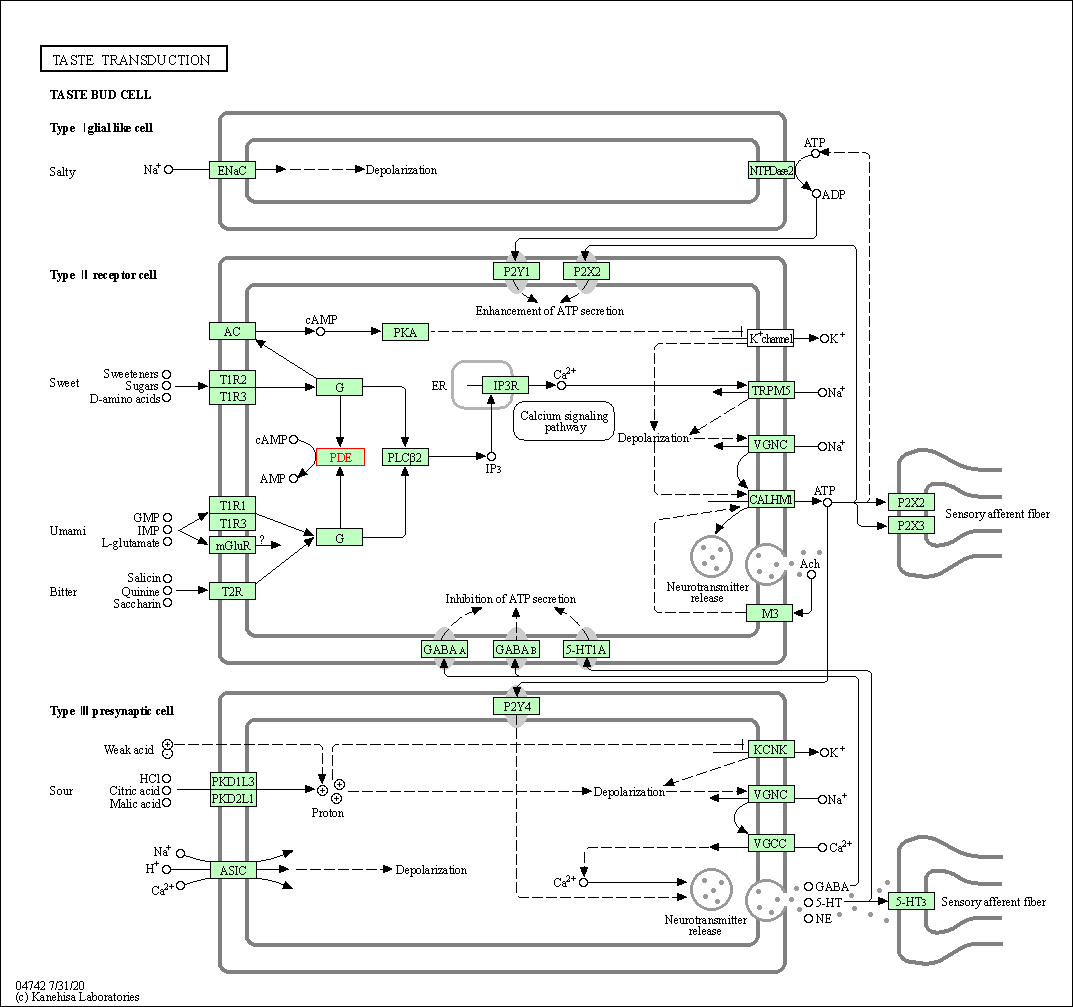
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Sensory system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Renin secretion | hsa04924 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KEGG Pathway | [+] 3 KEGG Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Purine metabolism | |||||
| 2 | Calcium signaling pathway | |||||
| 3 | Morphine addiction | |||||
| Reactome | [+] 2 Reactome Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | cGMP effects | |||||
| 2 | G alpha (s) signalling events | |||||
| WikiPathways | [+] 3 WikiPathways | + | ||||
| 1 | G Protein Signaling Pathways | |||||
| 2 | DAG and IP3 signaling | |||||
| 3 | Opioid Signalling | |||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Target id: 1295). | |||||
| REF 2 | Substituted thiophene- and furan-fused azolopyrimidine-5-(6H)-one compounds. US10092575. | |||||
| REF 3 | Inhibitors of phosphodiesterase 11 (PDE11). US9173884. | |||||
| REF 4 | 1H-pyrazolo[4,3-b]pyridines as PDE1 inhibitors. US10034861. | |||||
| REF 5 | Therapeutic thiophene-, furan-, and pyridine-fused azolopyrimidin-5-(6h)-ones. US10105367. | |||||
| REF 6 | Organic compounds. US9598426. | |||||
| REF 7 | Antiplatelet and antiproliferative effects of SCH 51866, a novel type 1 and type 5 phosphodiesterase inhibitor. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1996 Dec;28(6):862-9. | |||||
| REF 8 | Discovery of Potent and Selective Inhibitors of Phosphodiesterase 1 for the Treatment of Cognitive Impairment Associated with Neurodegenerative and Neuropsychiatric Diseases. J Med Chem. 2016 Feb 11;59(3):1149-64. | |||||
| REF 9 | Small-molecule phosphodiesterase probes: discovery of potent and selective CNS-penetrable quinazoline inhibitors of PDE1. doi:10.1039/C4MD00113C. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

