Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T52037
(Former ID: TTDI02192)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Toll-like receptor 6 (TLR6)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
CD286
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
TLR6
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Clinical trial target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 1 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10] | |||||
| Function |
Specifically recognizes diacylated and, to a lesser extent, triacylated lipopeptides. In response to diacylated lipopeptides, forms the activation cluster TLR2:TLR6:CD14:CD36, this cluster triggers signaling from the cell surface and subsequently is targeted to the Golgi in a lipid-raft dependent pathway. Acts via MYD88 and TRAF6, leading to NF-kappa-B activation, cytokine secretion and the inflammatory response. Recognizes mycoplasmal macrophage-activating lipopeptide-2kD (MALP-2), soluble tuberculosis factor (STF), phenol-soluble modulin (PSM) and B. burgdorferi outer surface protein A lipoprotein (OspA-L) cooperatively with TLR2. In complex with TLR4, promotes sterile inflammation in monocytes/macrophages in response to oxidized low-density lipoprotein (oxLDL) or amyloid-beta 42. In this context, the initial signal is provided by oxLDL- or amyloid-beta 42-binding to CD36. This event induces the formation of a heterodimer of TLR4 and TLR6, which is rapidly internalized and triggers inflammatory response, leading to the NF-kappa-B-dependent production of CXCL1, CXCL2 and CCL9 cytokines, via MYD88 signaling pathway, and CCL5 cytokine, via TICAM1 signaling pathway, as well as IL1B secretion. Participates in the innate immune response to Gram-positive bacteria and fungi.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Toll-like receptor
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| Sequence |
MTKDKEPIVKSFHFVCLMIIIVGTRIQFSDGNEFAVDKSKRGLIHVPKDLPLKTKVLDMS
QNYIAELQVSDMSFLSELTVLRLSHNRIQLLDLSVFKFNQDLEYLDLSHNQLQKISCHPI VSFRHLDLSFNDFKALPICKEFGNLSQLNFLGLSAMKLQKLDLLPIAHLHLSYILLDLRN YYIKENETESLQILNAKTLHLVFHPTSLFAIQVNISVNTLGCLQLTNIKLNDDNCQVFIK FLSELTRGSTLLNFTLNHIETTWKCLVRVFQFLWPKPVEYLNIYNLTIIESIREEDFTYS KTTLKALTIEHITNQVFLFSQTALYTVFSEMNIMMLTISDTPFIHMLCPHAPSTFKFLNF TQNVFTDSIFEKCSTLVKLETLILQKNGLKDLFKVGLMTKDMPSLEILDVSWNSLESGRH KENCTWVESIVVLNLSSNMLTDSVFRCLPPRIKVLDLHSNKIKSVPKQVVKLEALQELNV AFNSLTDLPGCGSFSSLSVLIIDHNSVSHPSADFFQSCQKMRSIKAGDNPFQCTCELREF VKNIDQVSSEVLEGWPDSYKCDYPESYRGSPLKDFHMSELSCNITLLIVTIGATMLVLAV TVTSLCIYLDLPWYLRMVCQWTQTRRRARNIPLEELQRNLQFHAFISYSEHDSAWVKSEL VPYLEKEDIQICLHERNFVPGKSIVENIINCIEKSYKSIFVLSPNFVQSEWCHYELYFAH HNLFHEGSNNLILILLEPIPQNSIPNKYHKLKALMTQRTYLQWPKEKSKRGLFWANIRAA FNMKLTLVTENNDVKS Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 1 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | MALP-2S | Drug Info | Phase 1/2 | Pancreatic cancer | [2] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 1 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Modulator | [+] 1 Modulator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | MALP-2S | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phagosome | hsa04145 | Affiliated Target |
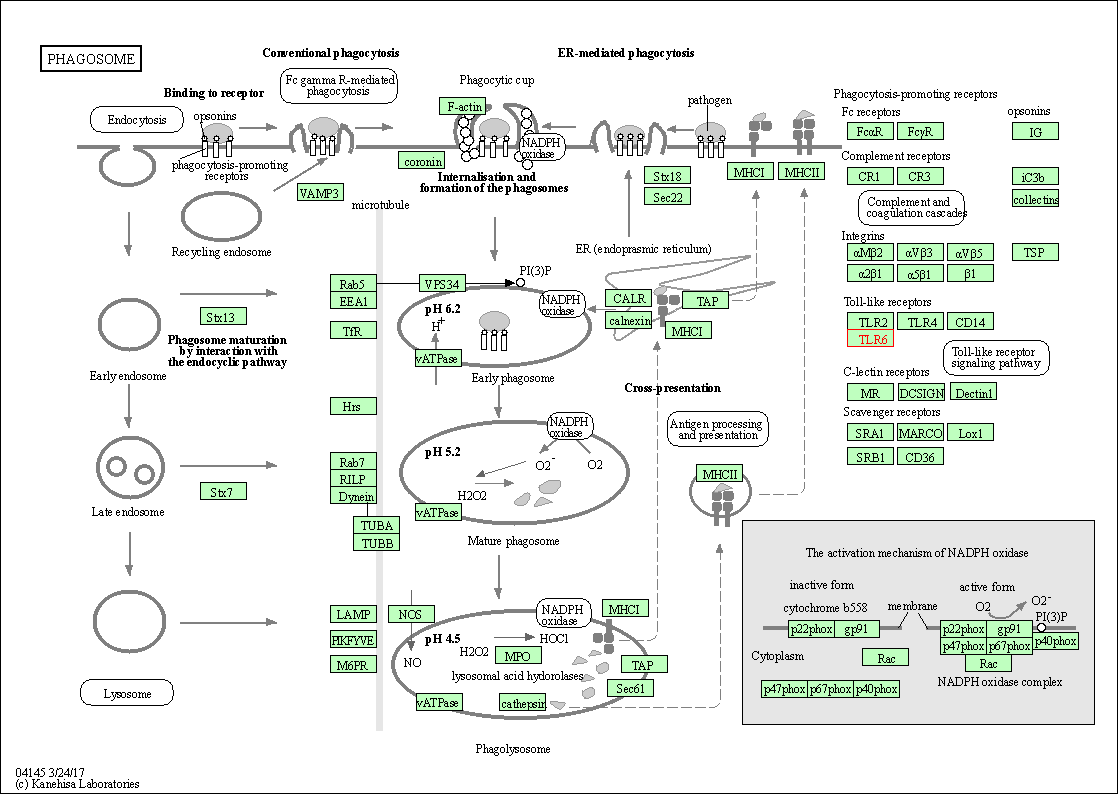
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Transport and catabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | hsa04620 | Affiliated Target |
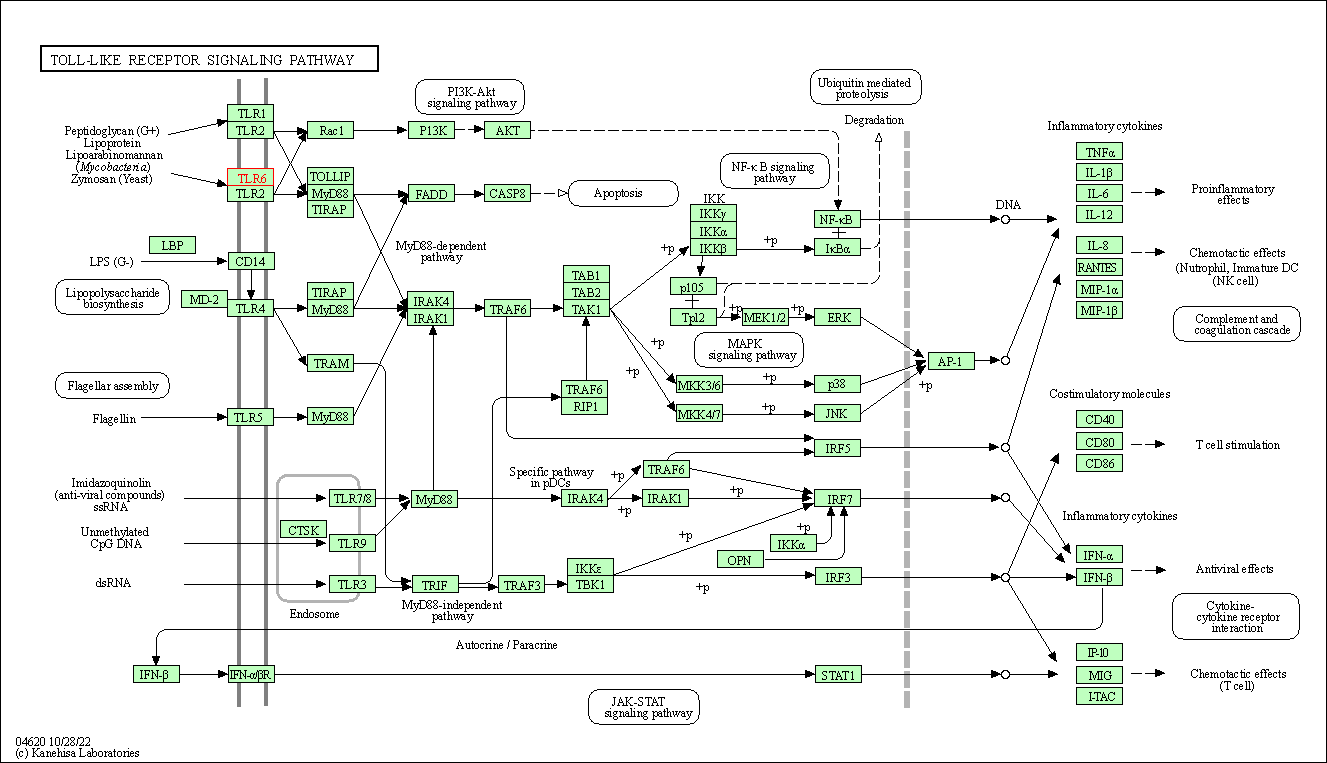
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Degree | 8 | Degree centrality | 8.59E-04 | Betweenness centrality | 2.21E-05 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.18E-01 | Radiality | 1.38E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 6.43E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 3.05E+01 | Topological coefficient | 2.26E-01 | Eccentricity | 12 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KEGG Pathway | [+] 4 KEGG Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Phagosome | |||||
| 2 | Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | |||||
| 3 | Chagas disease (American trypanosomiasis) | |||||
| 4 | Tuberculosis | |||||
| NetPath Pathway | [+] 3 NetPath Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | IL5 Signaling Pathway | |||||
| 2 | IL2 Signaling Pathway | |||||
| 3 | TCR Signaling Pathway | |||||
| Panther Pathway | [+] 1 Panther Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Toll receptor signaling pathway | |||||
| PID Pathway | [+] 1 PID Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Endogenous TLR signaling | |||||
| Reactome | [+] 4 Reactome Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | MyD88:Mal cascade initiated on plasma membrane | |||||
| 2 | Toll Like Receptor TLR6:TLR2 Cascade | |||||
| 3 | MyD88 deficiency (TLR2/4) | |||||
| 4 | IRAK4 deficiency (TLR2/4) | |||||
| WikiPathways | [+] 4 WikiPathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | |||||
| 2 | Toll-Like Receptors Cascades | |||||
| 3 | MyD88:Mal cascade initiated on plasma membrane | |||||
| 4 | Regulation of toll-like receptor signaling pathway | |||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Failure of mycoplasma lipoprotein MALP-2 to induce NK cell activation through dendritic cell TLR2. Microbes Infect. 2011 Apr;13(4):350-8. | |||||
| REF 2 | Intratumoural injection of the toll-like receptor-2/6 agonist 'macrophage-activating lipopeptide-2' in patients with pancreatic carcinoma: a phase ... Br J Cancer. 2007 Sep 3;97(5):598-604. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

