Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T35289
(Former ID: TTDI02343)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
NKG2 D activating NK receptor (KLRK1)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
NKG2Dactivating NK receptor; NKG2D type II integral membrane protein; NKG2D; NKG2-D-activating NK receptor; NKG2-D type II integral membrane protein; NK cell receptor D; Killer cell lectinlike receptor subfamily K member 1; Killer cell lectin-like receptor subfamily K member 1; D12S2489E; CD314
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
KLRK1
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Clinical trial target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 5 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Crohn disease [ICD-11: DD70] | |||||
| 2 | Acute myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60] | |||||
| 3 | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||||
| 4 | Multiple myeloma [ICD-11: 2A83] | |||||
| 5 | Myelodysplastic syndrome [ICD-11: 2A37] | |||||
| Function |
Provides both stimulatory and costimulatory innate immune responses on activated killer (NK) cells, leading to cytotoxic activity. Acts as a costimulatory receptor for T-cell receptor (TCR) in CD8(+) T-cell-mediated adaptive immune responses by amplifying T-cell activation. Stimulates perforin-mediated elimination of ligand-expressing tumor cells. Signaling involves calcium influx, culminating in the expression of TNF-alpha. Participates in NK cell-mediated bone marrow graft rejection. May play a regulatory role in differentiation and survival of NK cells. Binds to ligands belonging to various subfamilies of MHC class I-related glycoproteins including MICA, MICB, RAET1E, RAET1G, RAET1L/ULBP6, ULBP1, ULBP2, ULBP3 (ULBP2>ULBP1>ULBP3) and ULBP4. Function as an activating and costimulatory receptor involved in immunosurveillance upon binding to various cellular stress-inducible ligands displayed at the surface of autologous tumor cells and virus-infected cells.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| Sequence |
MGWIRGRRSRHSWEMSEFHNYNLDLKKSDFSTRWQKQRCPVVKSKCRENASPFFFCCFIA
VAMGIRFIIMVAIWSAVFLNSLFNQEVQIPLTESYCGPCPKNWICYKNNCYQFFDESKNW YESQASCMSQNASLLKVYSKEDQDLLKLVKSYHWMGLVHIPTNGSWQWEDGSILSPNLLT IIEMQKGDCALYASSFKGYIENCSTPNTYICMQRTV Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 5 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | NN8555 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Crohn disease | [1] | |
| 2 | CM-CS1 T-cell | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Multiple myeloma | [2] | |
| 3 | CYAD-101 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Colorectal cancer | [3] | |
| 4 | NKR-2 CAR-T Cells | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Myelodysplastic syndrome | [4] | |
| 5 | NKR-2 cells | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Acute myeloid leukaemia | [5], [6] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 2 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Antagonist | [+] 1 Antagonist drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | NN8555 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| CAR-T-Cell-Therapy | [+] 4 CAR-T-Cell-Therapy drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | CM-CS1 T-cell | Drug Info | [2] | |||
| 2 | CYAD-101 | Drug Info | [3] | |||
| 3 | NKR-2 CAR-T Cells | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 4 | NKR-2 cells | Drug Info | [5], [6] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
| Protein Name | Pfam ID | Percentage of Identity (%) | E value |
|---|---|---|---|
| NKG2-F type II integral membrane protein (KLRC4) | 27.027 (20/74) | 4.14E-05 | |
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity | hsa04650 | Affiliated Target |
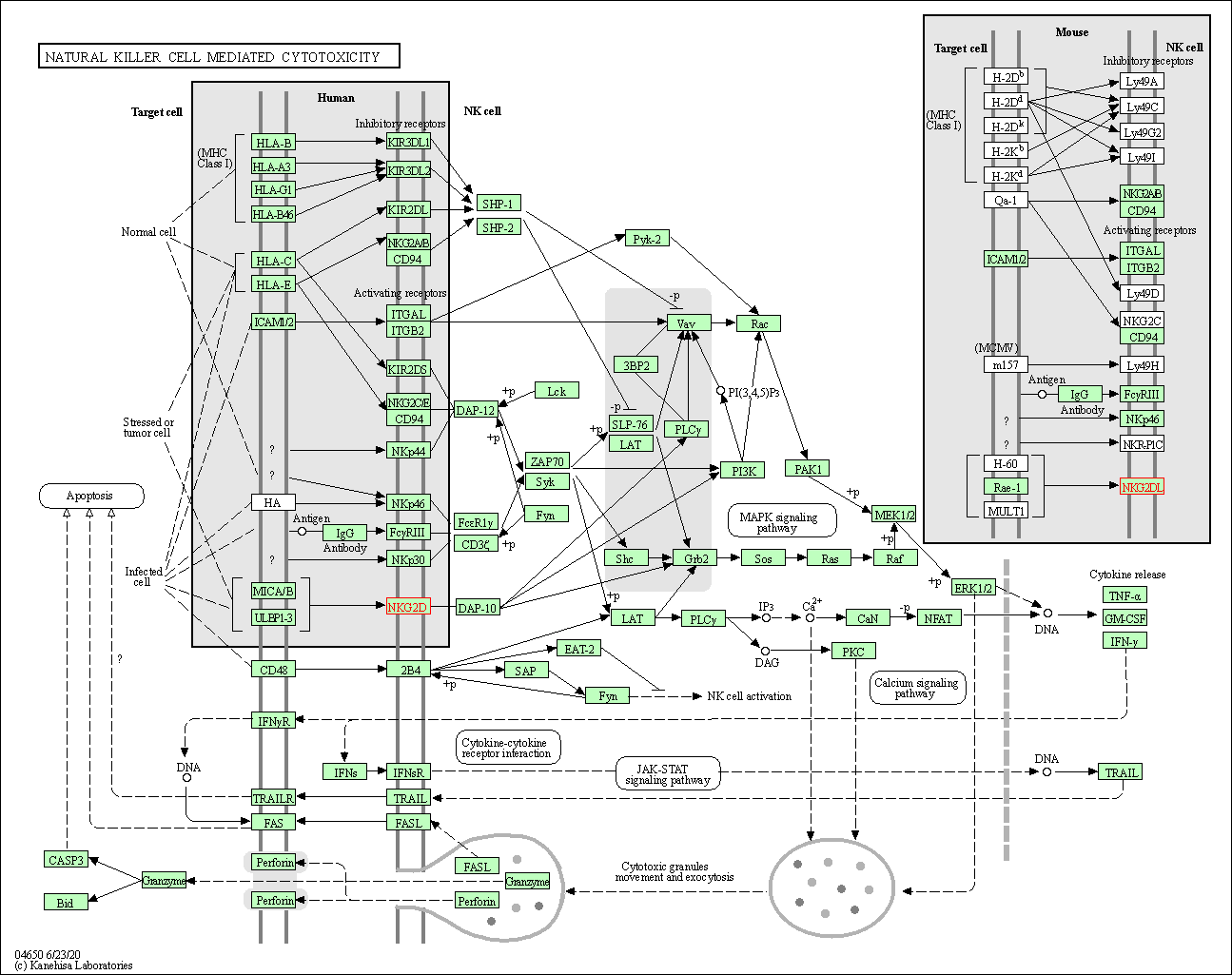
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Degree | 10 | Degree centrality | 1.07E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 1.42E-03 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 1.78E-01 | Radiality | 1.29E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 2.22E-02 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 3.20E+00 | Topological coefficient | 1.14E-01 | Eccentricity | 13 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 2 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT02203825) Safety Study of Chimeric Antigen Receptor Modified T-cells Targeting NKG2D-Ligands | |||||
| REF 3 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT03692429) alloSHRINK - Standard cHemotherapy Regimen and Immunotherapy With Allogeneic NKG2D-based CYAD-101 Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-cells | |||||
| REF 4 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT03612739) EPITHINK: Epigenetic Drug Treatment and Therapeutic Immunotherapy With NKR-2 | |||||
| REF 5 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT03310008) Dose Escalation and Dose Expansion Phase I Study to Assess the Safety and Clinical Activity of Multiple Doses of NKR-2 Administered Concurrently With FOLFOX in Colorectal Cancer With Potentially Resectable Liver Metastases | |||||
| REF 6 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT03370198) Hepatic Transarterial Administrations of NKR-2 in Patients With Unresectable Liver Metastases From Colorectal Cancer | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

