Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T18059
(Former ID: TTDNC00676)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Complement receptor type 2 (CD21)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
EpsteinBarr virus receptor; Epstein-Barr virus receptor; EBV receptor; Cr2; Complement C3d receptor; C3DR
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
CR2
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Clinical trial target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 1 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Diabetes mellitus [ICD-11: 5A10] | |||||
| Function |
Participates in B lymphocytes activation. Receptor for complement C3, for the Epstein-Barr virus on human B-cells and T-cells and for HNRNPU.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| Sequence |
MGAAGLLGVFLALVAPGVLGISCGSPPPILNGRISYYSTPIAVGTVIRYSCSGTFRLIGE
KSLLCITKDKVDGTWDKPAPKCEYFNKYSSCPEPIVPGGYKIRGSTPYRHGDSVTFACKT NFSMNGNKSVWCQANNMWGPTRLPTCVSVFPLECPALPMIHNGHHTSENVGSIAPGLSVT YSCESGYLLVGEKIINCLSSGKWSAVPPTCEEARCKSLGRFPNGKVKEPPILRVGVTANF FCDEGYRLQGPPSSRCVIAGQGVAWTKMPVCEEIFCPSPPPILNGRHIGNSLANVSYGSI VTYTCDPDPEEGVNFILIGESTLRCTVDSQKTGTWSGPAPRCELSTSAVQCPHPQILRGR MVSGQKDRYTYNDTVIFACMFGFTLKGSKQIRCNAQGTWEPSAPVCEKECQAPPNILNGQ KEDRHMVRFDPGTSIKYSCNPGYVLVGEESIQCTSEGVWTPPVPQCKVAACEATGRQLLT KPQHQFVRPDVNSSCGEGYKLSGSVYQECQGTIPWFMEIRLCKEITCPPPPVIYNGAHTG SSLEDFPYGTTVTYTCNPGPERGVEFSLIGESTIRCTSNDQERGTWSGPAPLCKLSLLAV QCSHVHIANGYKISGKEAPYFYNDTVTFKCYSGFTLKGSSQIRCKADNTWDPEIPVCEKE TCQHVRQSLQELPAGSRVELVNTSCQDGYQLTGHAYQMCQDAENGIWFKKIPLCKVIHCH PPPVIVNGKHTGMMAENFLYGNEVSYECDQGFYLLGEKKLQCRSDSKGHGSWSGPSPQCL RSPPVTRCPNPEVKHGYKLNKTHSAYSHNDIVYVDCNPGFIMNGSRVIRCHTDNTWVPGV PTCIKKAFIGCPPPPKTPNGNHTGGNIARFSPGMSILYSCDQGYLLVGEALLLCTHEGTW SQPAPHCKEVNCSSPADMDGIQKGLEPRKMYQYGAVVTLECEDGYMLEGSPQSQCQSDHQ WNPPLAVCRSRSLAPVLCGIAAGLILLTFLIVITLYVISKHRARNYYTDTSQKEAFHLEA REVYSVDPYNPAS Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 1 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | TT-30 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Autoimmune diabetes | [2] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 1 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Modulator | [+] 1 Modulator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | TT-30 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: 2-(Acetylamino)-2-Deoxy-a-D-Glucopyranose | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | CR2-C3D COMPLEX STRUCTURE | PDB:1GHQ | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.04 Å | Mutation | Yes | [3] |
| PDB Sequence |
AISCGSPPPI
10 LNGRISYYST20 PIAVGTVIRY30 SCSGTFRLIG40 EKSLLCITKD50 KVDGTWDKPA 60 PKCEYFNKYS70 SCPEPIVPGG80 YKIRGSTPYR90 HGDSVTFACK100 TNFSMNGNKS 110 VWCQANNMWG120 PTRLPTCVS
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Complement and coagulation cascades | hsa04610 | Affiliated Target |
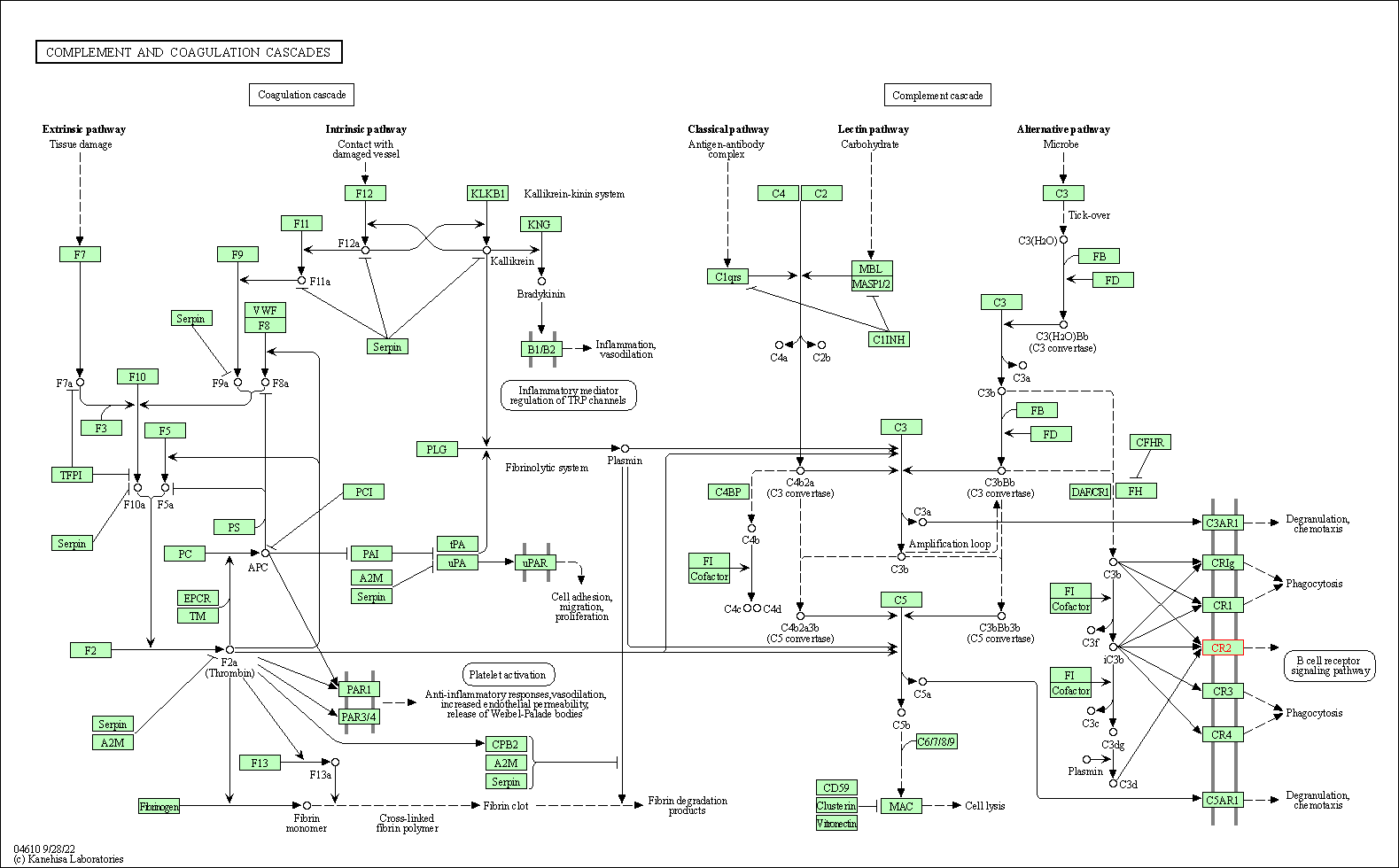
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Hematopoietic cell lineage | hsa04640 | Affiliated Target |
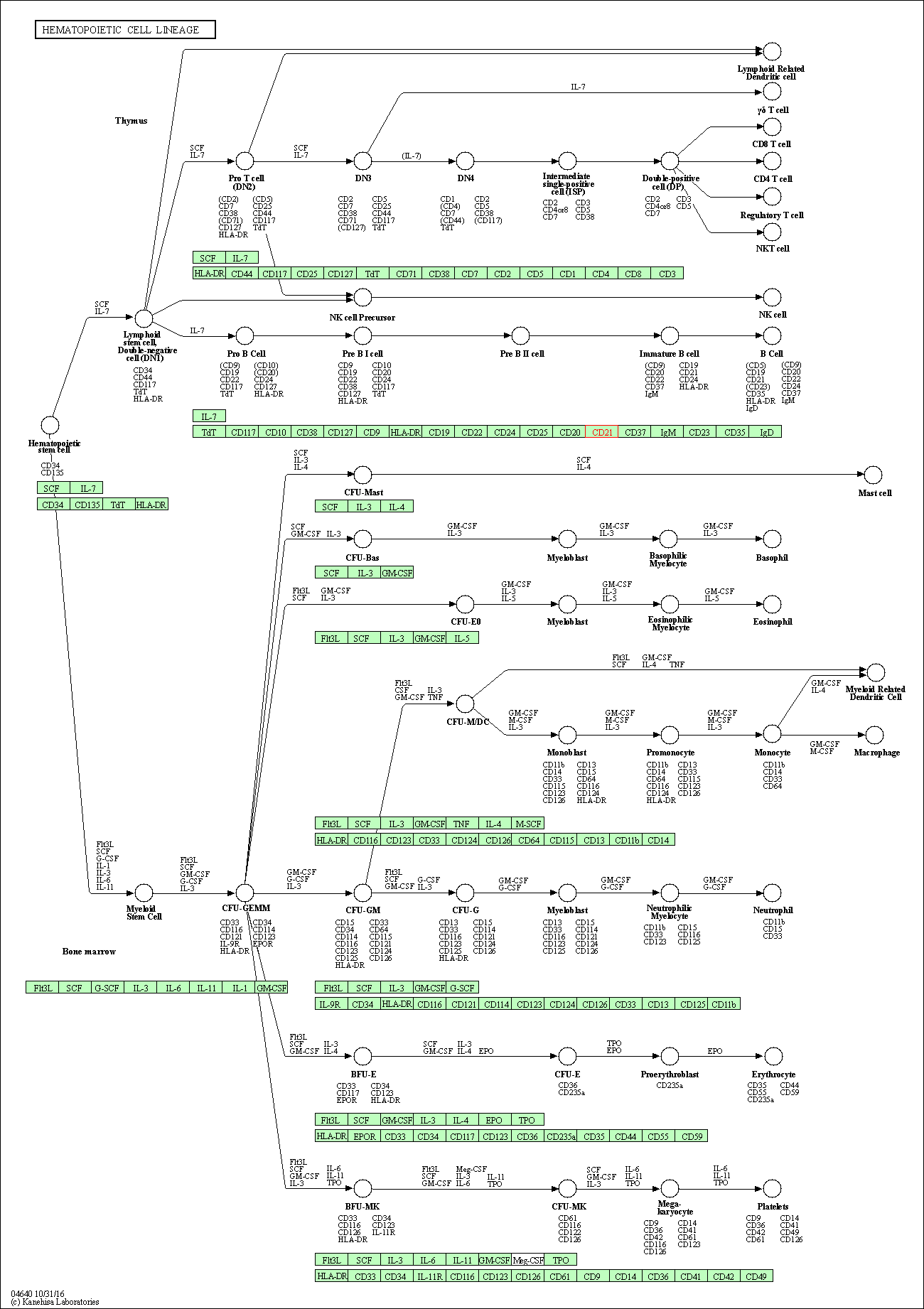
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| B cell receptor signaling pathway | hsa04662 | Affiliated Target |
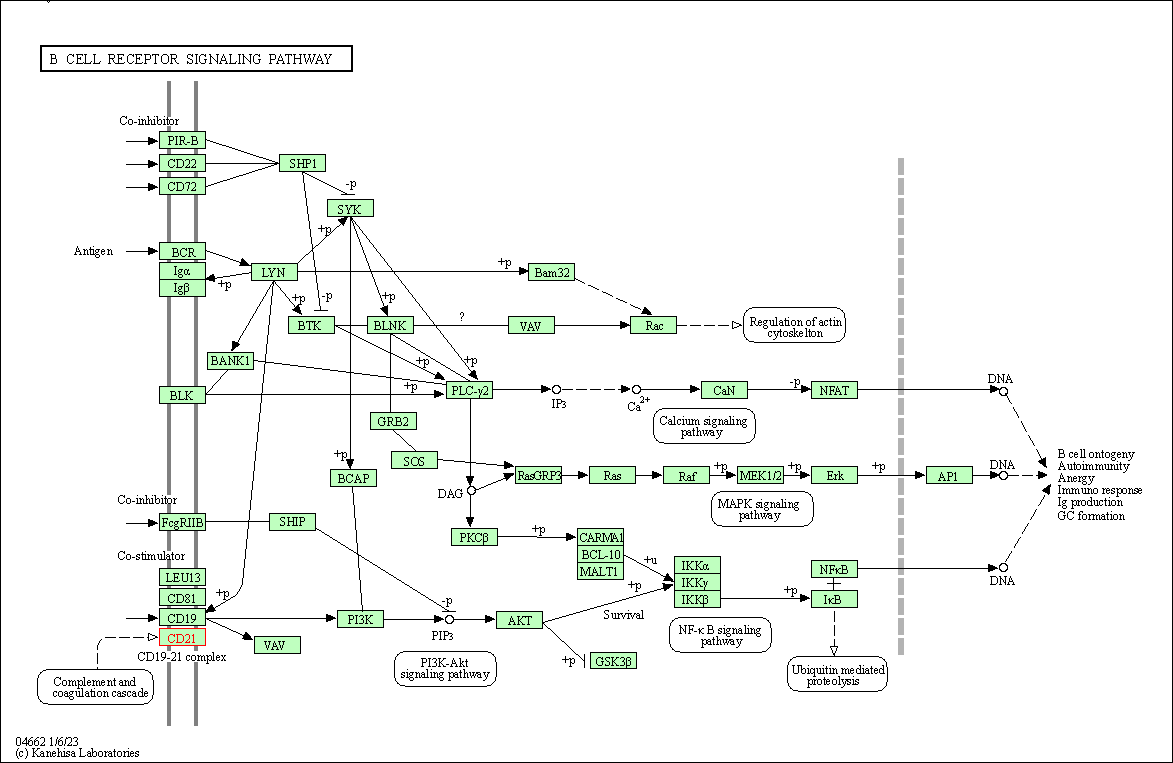
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Degree | 4 | Degree centrality | 4.30E-04 | Betweenness centrality | 2.85E-04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 1.94E-01 | Radiality | 1.33E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 1.67E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 1.30E+01 | Topological coefficient | 2.66E-01 | Eccentricity | 12 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KEGG Pathway | [+] 4 KEGG Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Complement and coagulation cascades | |||||
| 2 | Hematopoietic cell lineage | |||||
| 3 | B cell receptor signaling pathway | |||||
| 4 | Epstein-Barr virus infection | |||||
| NetPath Pathway | [+] 3 NetPath Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | IL2 Signaling Pathway | |||||
| 2 | Notch Signaling Pathway | |||||
| 3 | TCR Signaling Pathway | |||||
| WikiPathways | [+] 3 WikiPathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Complement and Coagulation Cascades | |||||
| 2 | Human Complement System | |||||
| 3 | B Cell Receptor Signaling Pathway | |||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | The complement receptor 2/factor H fusion protein TT30 protects paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria erythrocytes from complement-mediated hemolysis and C3 fragment. Blood. 2012 Jun 28;119(26):6307-16. | |||||
| REF 2 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01335165) Safety and Pharmacokinetics of TT30 in Subjects With Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria (PNH). U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 3 | Structure of complement receptor 2 in complex with its C3d ligand. Science. 2001 Jun 1;292(5522):1725-8. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

