Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T09092
(Former ID: TTDR00138)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Interleukin-10 (IL10)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
IL-10; Cytokine synthesis inhibitory factor; CSIF
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
IL10
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Clinical trial target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 1 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10] | |||||
| Function |
Mechanistically, IL10 binds to its heterotetrameric receptor comprising IL10RA and IL10RB leading to JAK1 and STAT2-mediated phosphorylation of STAT3. In turn, STAT3 translocates to the nucleus where it drives expression of anti-inflammatory mediators. Targets antigen-presenting cells (APCs) such as macrophages and monocytes and inhibits their release of pro-inflammatory cytokines including granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor /GM-CSF, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor/G-CSF, IL-1 alpha, IL-1 beta, IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-alpha. Interferes also with antigen presentation by reducing the expression of MHC-class II and co-stimulatory molecules, thereby inhibiting their ability to induce T cell activation. In addition, controls the inflammatory response of macrophages by reprogramming essential metabolic pathways including mTOR signaling. Major immune regulatory cytokine that acts on many cells of the immune system where it has profound anti-inflammatory functions, limiting excessive tissue disruption caused by inflammation.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Cytokine: interleukin
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| Sequence |
MHSSALLCCLVLLTGVRASPGQGTQSENSCTHFPGNLPNMLRDLRDAFSRVKTFFQMKDQ
LDNLLLKESLLEDFKGYLGCQALSEMIQFYLEEVMPQAENQDPDIKAHVNSLGENLKTLR LRLRRCHRFLPCENKSKAVEQVKNAFNKLQEKGIYKAMSEFDIFINYIEAYMTMKIRN Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T69NG6 | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 5 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | AM0010 | Drug Info | Phase 3 | Pancreatic ductal carcinoma | [2], [3] | |
| 2 | F-8-IL-10 fusion protein | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Endometriosis | [4] | |
| 3 | Ilodecakin | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Sarcoidosis | [5] | |
| 4 | XT-150 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Knee osteoarthritis | [6] | |
| 5 | AG019 | Drug Info | Phase 1/2 | Type-1 diabetes | [7] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 2 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Modulator | [+] 3 Modulator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | AM0010 | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 2 | F-8-IL-10 fusion protein | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 3 | Ilodecakin | Drug Info | [9] | |||
| Activator | [+] 1 Activator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Ankinara | Drug Info | [11] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
| Protein Name | Pfam ID | Percentage of Identity (%) | E value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Interleukin-22 (IL22) | 28.846 (30/104) | 4.00E-03 |
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
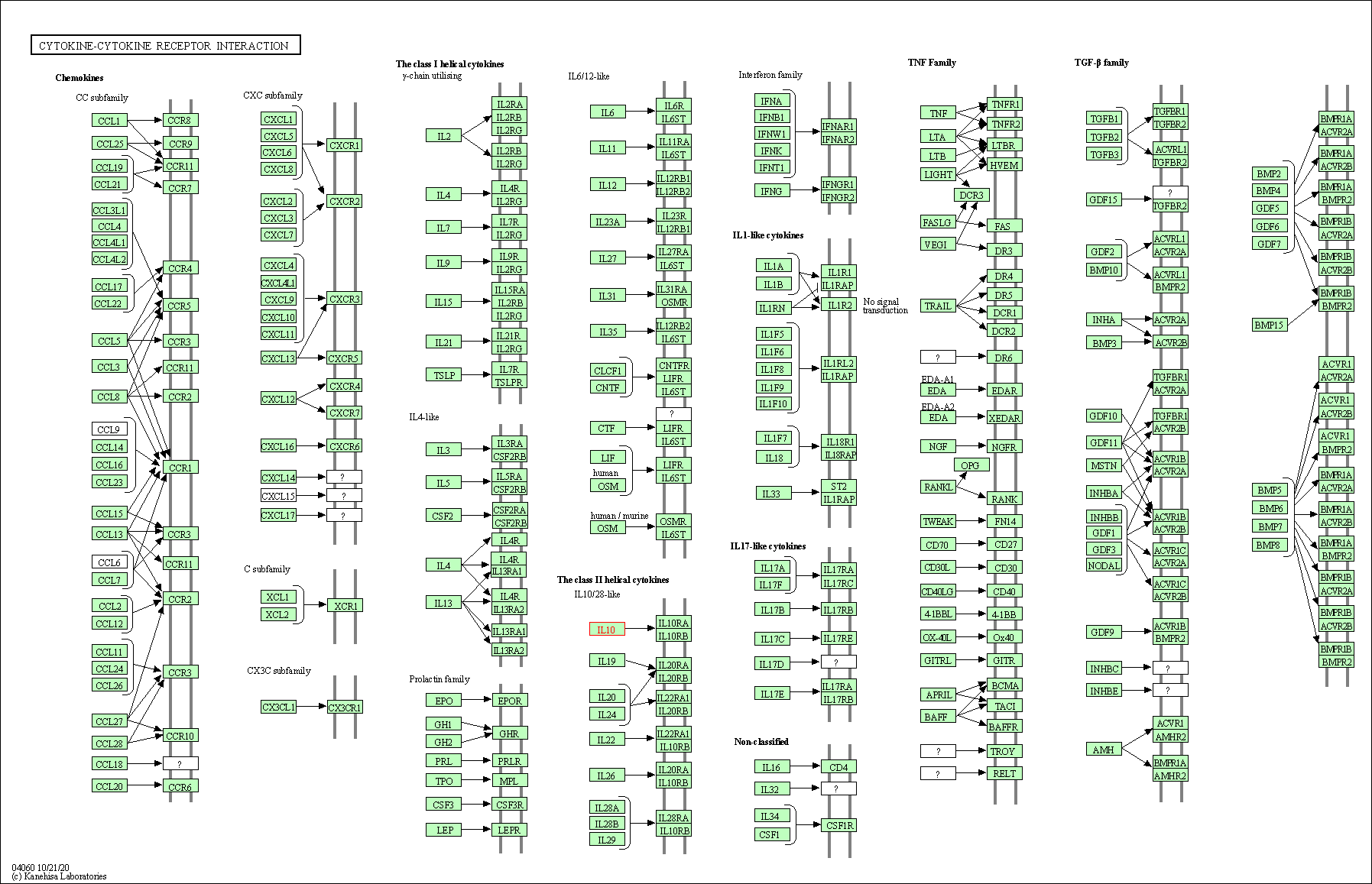
| Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction | hsa04060 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signaling molecules and interaction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
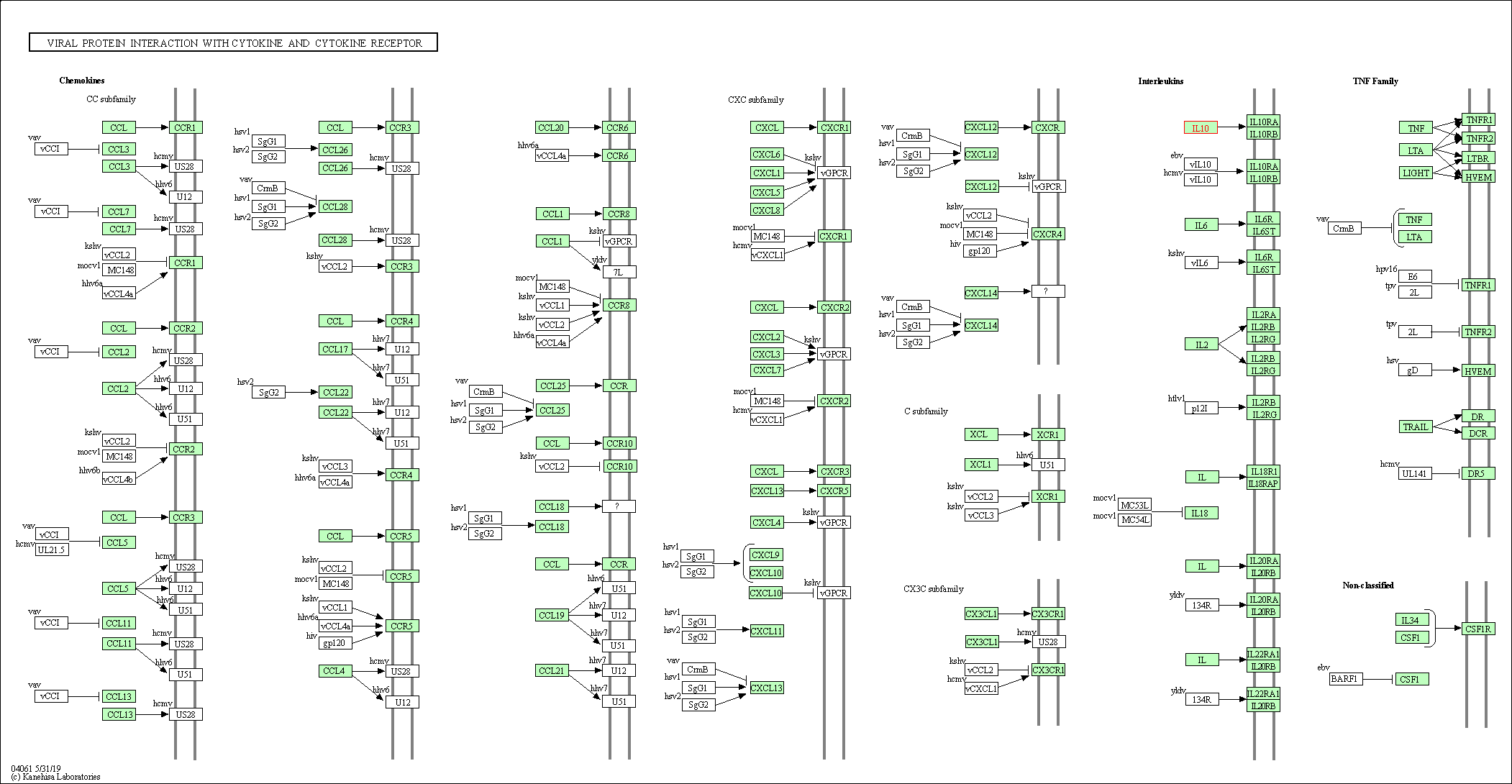
| Viral protein interaction with cytokine and cytokine receptor | hsa04061 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signaling molecules and interaction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
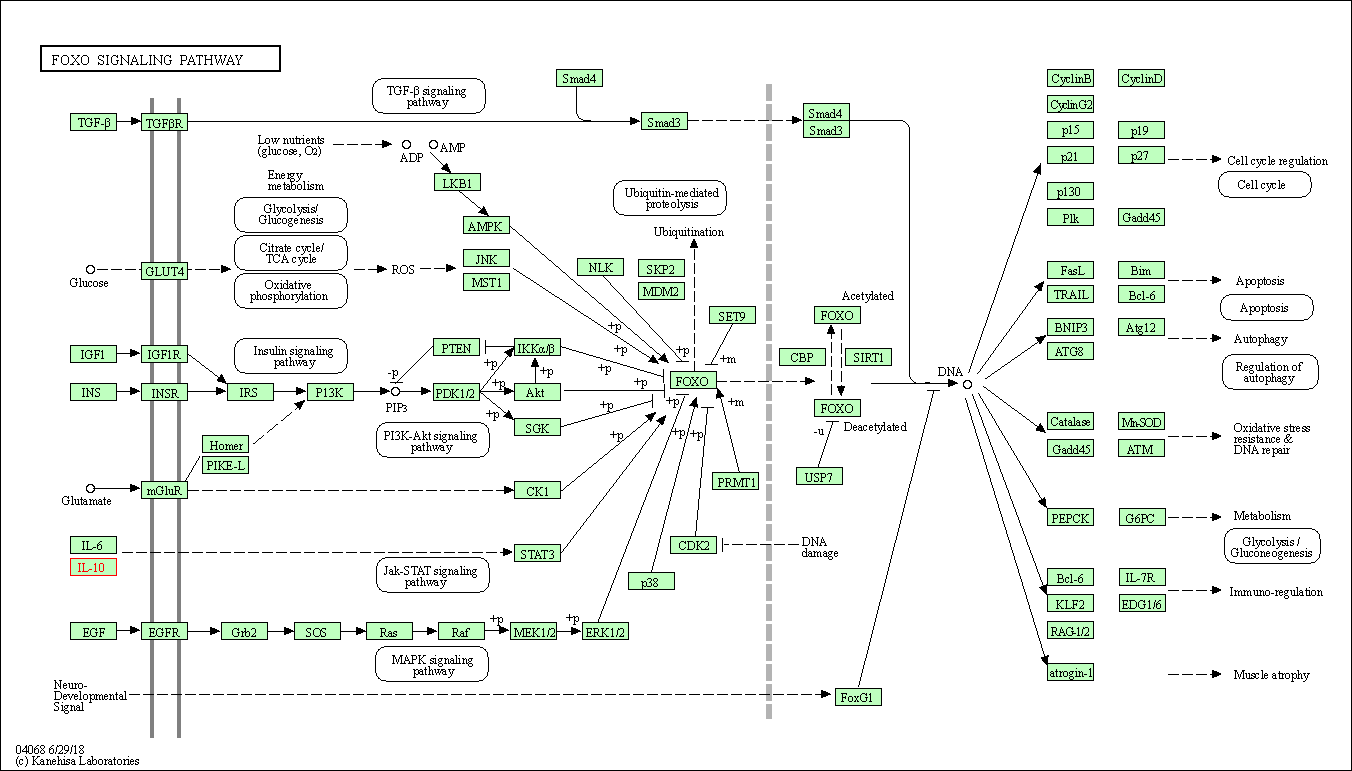
| FoxO signaling pathway | hsa04068 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
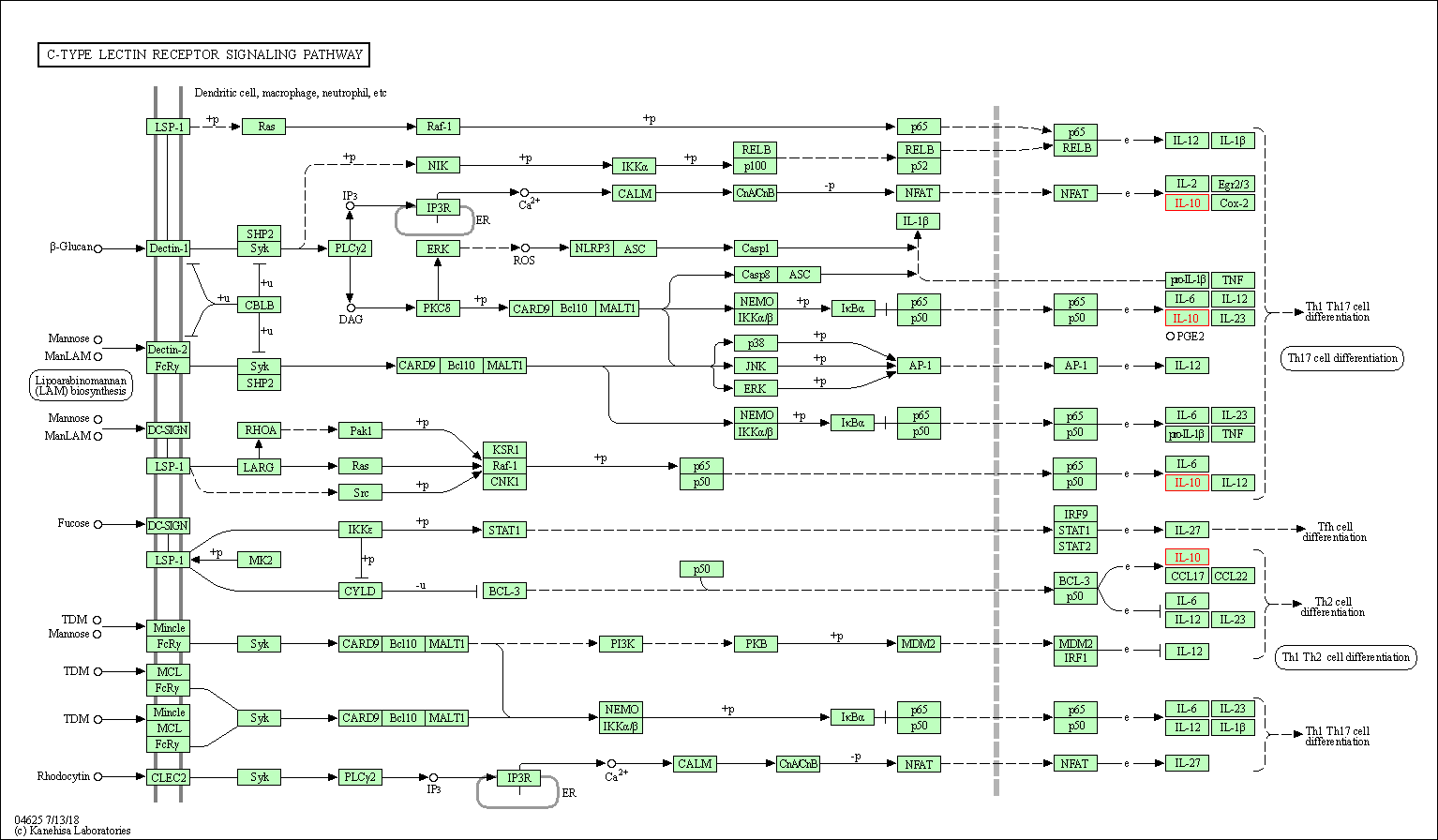
| C-type lectin receptor signaling pathway | hsa04625 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
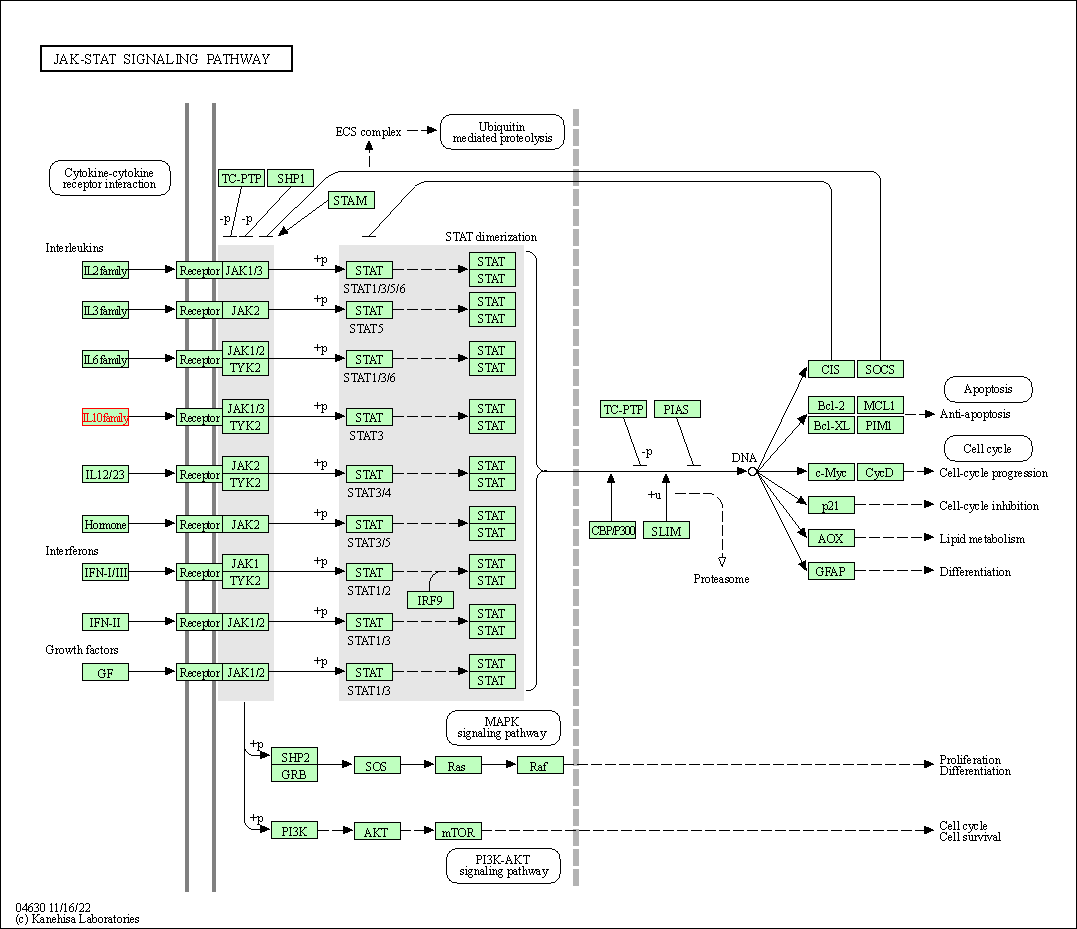
| JAK-STAT signaling pathway | hsa04630 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
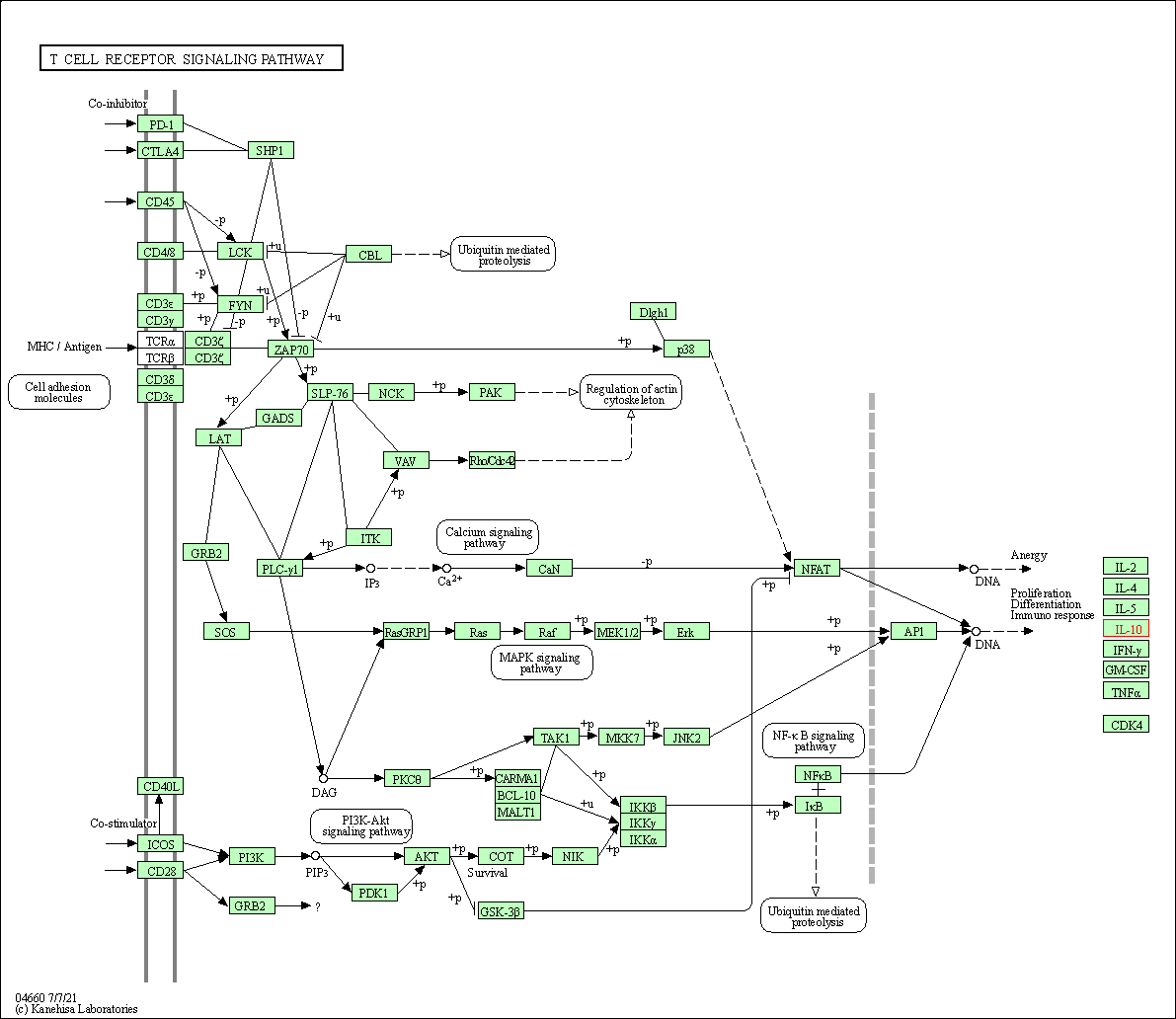
| T cell receptor signaling pathway | hsa04660 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
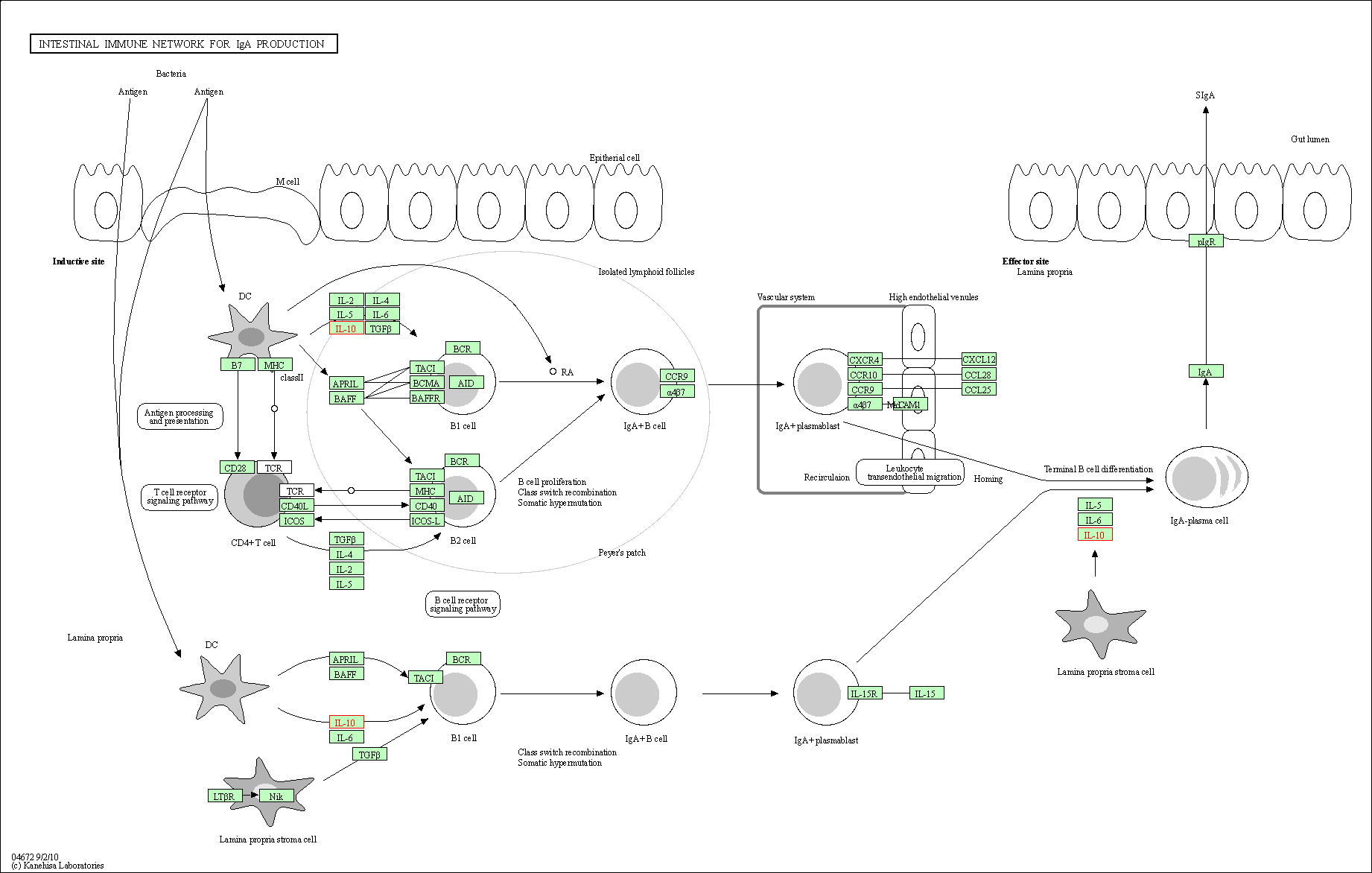
| Intestinal immune network for IgA production | hsa04672 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 55 | Degree centrality | 5.91E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 2.40E-03 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.40E-01 | Radiality | 1.42E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 1.70E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 2.37E+01 | Topological coefficient | 4.86E-02 | Eccentricity | 11 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Expression Profile (TEP) |
||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Preclinical characterization of DEKAVIL (F8-IL10), a novel clinical-stage immunocytokine which inhibits the progression of collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2009;11(5):R142. | |||||
| REF 2 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 3 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 4 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT02270632) A Randomized, Placebo-controlled Phase II Clinical Trial to Evaluate the Safety and Efficacy of F8IL10 Dekavil) in Patients With Active RA Receiving MTX. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 5 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT00984646) Investigation Into the Scar Reduction Potential of Prevascar (Interleukin-10). U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 6 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04124042) A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Assessment of the Tolerability and Efficacy of XT-150 for the Treatment of Moderate to Severe Pain Due to Osteoarthritis of the Knee. U.S.National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 7 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT03751007) A Study to Assess the Safety and Tolerability of Different Doses of AG019 Administered Alone or in Combination With Teplizumab in Participants With Recently Diagnosed Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (T1D). U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 8 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of ARMO BioSciences. | |||||
| REF 9 | Ilodecakin. Schering-Plough Corp. IDrugs. 1999 Oct;2(10):1045-58. | |||||
| REF 10 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of Xalud Therapeutics | |||||
| REF 11 | Emerging drugs for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2006 May;11(2):275-91. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

