Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T04741
(Former ID: TTDR00945)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Phosphoribosylaminoimidazolecarboxamide formyltransferase (ATIC)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
PURH; OK/SW-cl.86; Bifunctional purine biosynthesis protein PURH
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
ATIC
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Literature-reported target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 1 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||||
| Function |
Bifunctional enzyme that catalyzes 2 steps in purine biosynthesis.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Methyltransferase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| Sequence |
MAPGQLALFSVSDKTGLVEFARNLTALGLNLVASGGTAKALRDAGLAVRDVSELTGFPEM
LGGRVKTLHPAVHAGILARNIPEDNADMARLDFNLIRVVACNLYPFVKTVASPGVTVEEA VEQIDIGGVTLLRAAAKNHARVTVVCEPEDYVVVSTEMQSSESKDTSLETRRQLALKAFT HTAQYDEAISDYFRKQYSKGVSQMPLRYGMNPHQTPAQLYTLQPKLPITVLNGAPGFINL CDALNAWQLVKELKEALGIPAAASFKHVSPAGAAVGIPLSEDEAKVCMVYDLYKTLTPIS AAYARARGADRMSSFGDFVALSDVCDVPTAKIISREVSDGIIAPGYEEEALTILSKKKNG NYCVLQMDQSYKPDENEVRTLFGLHLSQKRNNGVVDKSLFSNVVTKNKDLPESALRDLIV ATIAVKYTQSNSVCYAKNGQVIGIGAGQQSRIHCTRLAGDKANYWWLRHHPQVLSMKFKT GVKRAEISNAIDQYVTGTIGEDEDLIKWKALFEEVPELLTEAEKKEWVEKLTEVSISSDA FFPFRDNVDRAKRSGVAYIAAPSGSAADKVVIEACDELGIILAHTNLRLFHH Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: Xanthosine-5'-monophosphate | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal Structure of human ATIC in complex with XMP | PDB:1PKX | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 1.90 Å | Mutation | No | [3] |
| PDB Sequence |
PGQLALFSVS
12 DKTGLVEFAR22 NLTALGLNLV32 ASGGTAKALR42 DAGLAVRDVS52 ELTGFPEMLG 62 GRVKTLHPAV72 HAGILARNIP82 EDNADMARLD92 FNLIRVVACN102 LYPFVKTVAS 112 PGVTVEEAVE122 QIDIGGVTLL132 RAAAKNHARV142 TVVCEPEDYV152 VVSTEMQSSE 162 SKDTSLETRR172 QLALKAFTHT182 AQYDEAISDY192 FRKQYSKGVS202 QMPLRYGMNP 212 HQTPAQLYTL222 QPKLPITVLN232 GAPGFINLCD242 ALNAWQLVKE252 LKEALGIPAA 262 ASFKHVSPAG272 AAVGIPLSED282 EAKVCMVYDL292 YKTLTPISAA302 YARARGADRM 312 SSFGDFVALS322 DVCDVPTAKI332 ISREVSDGII342 APGYEEEALT352 ILSKKKNGNY 362 CVLQMDQSYK372 PDENEVRTLF382 GLHLSQKRNN392 GVVDKSLFSN402 VVTKNKDLPE 412 SALRDLIVAT422 IAVKYTQSNS432 VCYAKNGQVI442 GIGAGQQSRI452 HCTRLAGDKA 462 NYWWLRHHPQ472 VLSMKFKTGV482 AEISNAIDQY494 VTGTIGEDED504 LIKWKALFEE 514 VPELLTEAEK524 KEWVEKLTEV534 SISSDAFFPF544 RDNVDRAKRS554 GVAYIAAPSG 564 SAADKVVIEA574 CDELGIILAH584 TNLRLFHH
|
|||||
|
|
SER10
3.081
VAL11
3.657
SER12
2.959
LYS14
2.887
SER34
2.656
GLY35
3.839
GLY36
3.080
THR37
2.730
ALA38
4.741
GLU59
4.590
GLY63
3.847
ARG64
2.775
VAL65
3.750
|
|||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Ligand Name: N-[(S)-(4-{[(2-Amino-4-hydroxyquinazolin-6-YL)(dihydroxy)-lambda~4~-sulfanyl]amino}phenyl)(hydroxy)methyl]-L-glutamic acid | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal Structure of Human ATIC in complex with folate-based inhibitor BW1540U88UD | PDB:1P4R | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.55 Å | Mutation | No | [4] |
| PDB Sequence |
GQLALFSVSD
13 KTGLVEFARN23 LTALGLNLVA33 SGGTAKALRD43 AGLAVRDVSE53 LTGFPEMLGG 63 RVKTLHPAVH73 AGILARNIPE83 DNADMARLDF93 NLIRVVACNL103 YPFVKTVASP 113 GVTVEEAVEQ123 IDIGGVTLLR133 AAAKNHARVT143 VVCEPEDYVV153 VSTEMQSSES 163 KDTSLETRRQ173 LALKAFTHTA183 QYDEAISDYF193 RKQYSKGVSQ203 MPLRYGMNPH 213 QTPAQLYTLQ223 PKLPITVLNG233 APGFINLCDA243 LNAWQLVKEL253 KEALGIPAAA 263 SFKHVSPAGA273 AVGIPLSEDE283 AKVCMVYDLY293 KTLTPISAAY303 ARARGADRMS 313 SFGDFVALSD323 VCDVPTAKII333 SREVSDGIIA343 PGYEEEALTI353 LSKKKNGNYC 363 VLQMDQSYKP373 DENEVRTLFG383 LHLSQKRNNG393 VVDKSLFSNV403 VTKNKDLPES 413 ALRDLIVATI423 AVKYTQSNSV433 CYAKNGQVIG443 IGAGQQSRIH453 CTRLAGDKAN 463 YWWLRHHPQV473 LSMKFKTGVK483 RAEISNAIDQ493 YVTGTIGEDE503 DLIKWKALFE 513 EVPELLTEAE523 KKEWVEKLTE533 VSISSDAFFP543 FRDNVDRAKR553 SGVAYIAAPS 563 GSAADKVVIE573 ACDELGIILA583 HTNLRLFHH
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purine metabolism | hsa00230 | Affiliated Target |
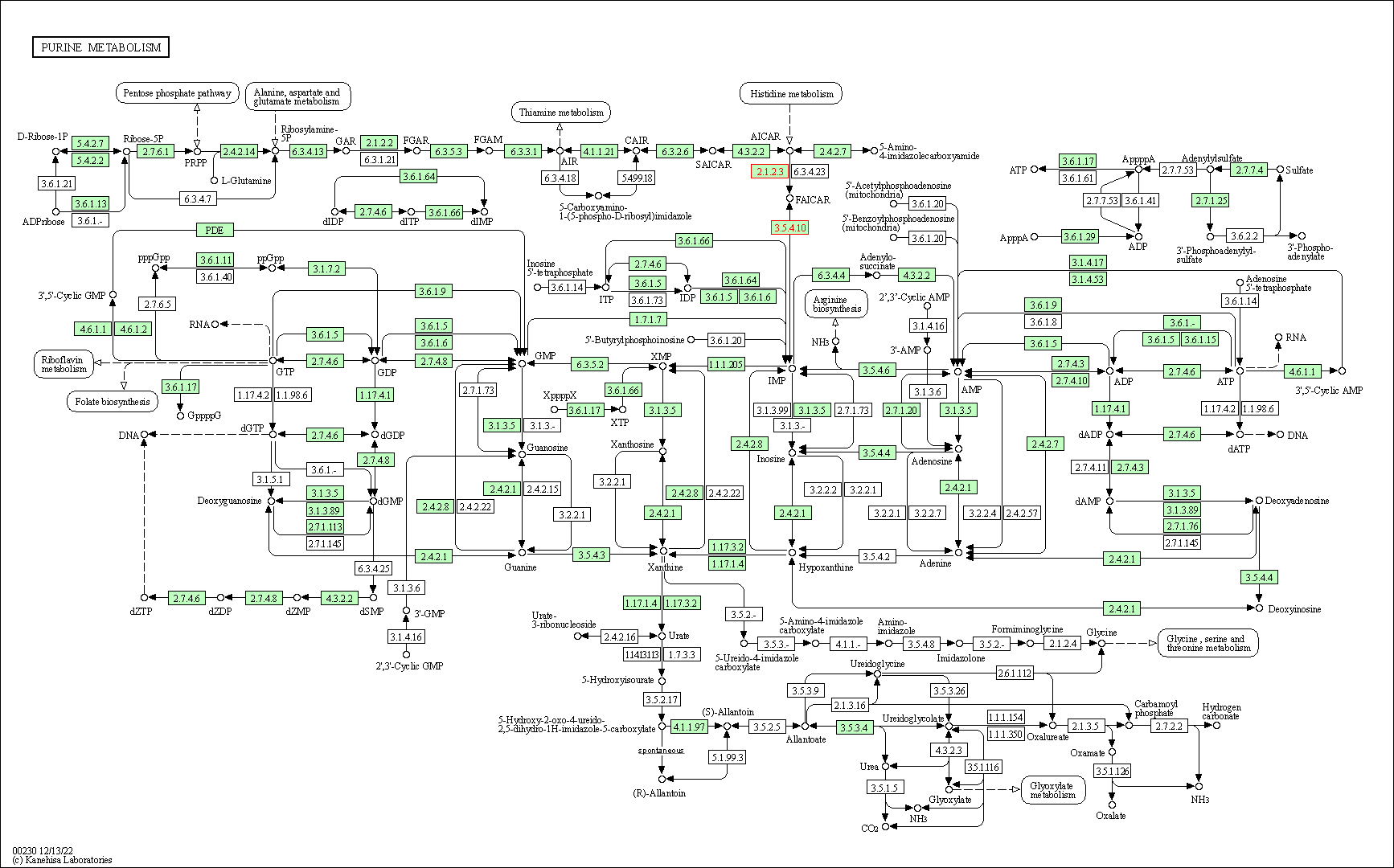
|
| Class: Metabolism => Nucleotide metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| One carbon pool by folate | hsa00670 | Affiliated Target |
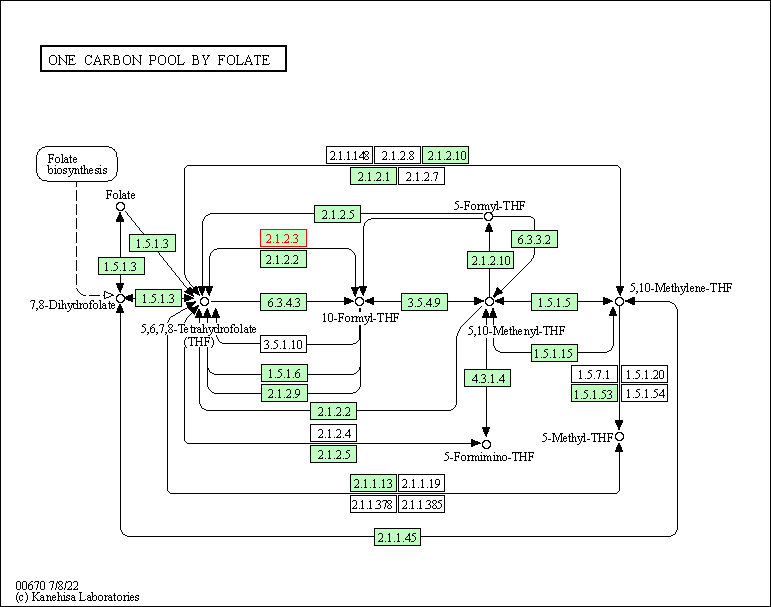
|
| Class: Metabolism => Metabolism of cofactors and vitamins | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Degree | 22 | Degree centrality | 2.36E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 8.18E-04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 1.80E-01 | Radiality | 1.30E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 2.64E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 1.22E+01 | Topological coefficient | 1.55E-01 | Eccentricity | 11 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Virtual screening of human 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribonucleotide transformylase against the NCI diversity set by use of AutoDock to identif... J Med Chem. 2004 Dec 30;47(27):6681-90. | |||||
| REF 2 | Structure-based design, synthesis, evaluation, and crystal structures of transition state analogue inhibitors of inosine monophosphate cyclohydrolase. J Biol Chem. 2007 Apr 27;282(17):13033-46. | |||||
| REF 3 | Structural insights into the human and avian IMP cyclohydrolase mechanism via crystal structures with the bound XMP inhibitor. Biochemistry. 2004 Feb 10;43(5):1171-83. | |||||
| REF 4 | Crystal structures of human bifunctional enzyme aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribonucleotide transformylase/IMP cyclohydrolase in complex with potent sulfonyl-containing antifolates. J Biol Chem. 2004 Apr 23;279(17):18034-45. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

