Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T02469
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate 5-kinase (PIP5K3)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Type III PIP kinase; Phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate 5-kinase type III; PIPkin-III; PIKfyve; FYVE finger-containing phosphoinositide kinase
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
PIKFYVE
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Clinical trial target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 2 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Malignant haematopoietic neoplasm [ICD-11: 2B33] | |||||
| 2 | Mature B-cell leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A82] | |||||
| Function |
The PI(3,5)P2 regulatory complex regulates both the synthesis and turnover of phosphatidylinositol 3,5-bisphosphate (PtdIns(3,5)P2). Catalyzes the phosphorylation of phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate on the fifth hydroxyl of the myo-inositol ring, to form phosphatidylinositol 3,5-bisphosphate. Required for endocytic-vacuolar pathway and nuclear migration. Plays a role in the biogenesis of endosome carrier vesicles (ECV)/ multivesicular bodies (MVB) transport intermediates from early endosomes.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 2.7.1.150
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MATDDKTSPTLDSANDLPRSPTSPSHLTHFKPLTPDQDEPPFKSAYSSFVNLFRFNKERA
EGGQGEQQPLSGSWTSPQLPSRTQSVRSPTPYKKQLNEELQRRSSALDTRRKAEPTFGGH DPRTAVQLRSLSTVLKRLKEIMEGKSQDSDLKQYWMPDSQCKECYDCSEKFTTFRRRHHC RLCGQIFCSRCCNQEIPGKFMGYTGDLRACTYCRKIALSYAHSTDSNSIGEDLNALSDSA CSVSVLDPSEPRTPVGSRKASRNIFLEDDLAWQSLIHPDSSNTPLSTRLVSVQEDAGKSP ARNRSASITNLSLDRSGSPMVPSYETSVSPQANRTYVRTETTEDERKILLDSVQLKDLWK KICHHSSGMEFQDHRYWLRTHPNCIVGKELVNWLIRNGHIATRAQAIAIGQAMVDGRWLD CVSHHDQLFRDEYALYRPLQSTEFSETPSPDSDSVNSVEGHSEPSWFKDIKFDDSDTEQI AEEGDDNLANSASPSKRTSVSSFQSTVDSDSAASISLNVELDNVNFHIKKPSKYPHVPPH PADQKEYLISDTGGQQLSISDAFIKESLFNRRVEEKSKELPFTPLGWHHNNLELLREENG EKQAMERLLSANHNHMMALLQQLLHSDSLSSSWRDIIVSLVCQVVQTVRPDVKNQDDDMD IRQFVHIKKIPGGKKFDSVVVNGFVCTKNIAHKKMSSCIKNPKILLLKCSIEYLYREETK FTCIDPIVLQEREFLKNYVQRIVDVRPTLVLVEKTVSRIAQDMLLEHGITLVINVKSQVL ERISRMTQGDLVMSMDQLLTKPHLGTCHKFYMQIFQLPNEQTKTLMFFEGCPQHLGCTIK LRGGSDYELARVKEILIFMICVAYHSQLEISFLMDEFAMPPTLMQNPSFHSLIEGRGHEG AVQEQYGGGSIPWDPDIPPESLPCDDSSLLELRIVFEKGEQENKNLPQAVASVKHQEHST TACPAGLPCAFFAPVPESLLPLPVDDQQDALGSEQPETLQQTVVLQDPKSQIRAFRDPLQ DDTGLYVTEEVTSSEDKRKTYSLAFKQELKDVILCISPVITFREPFLLTEKGMRCSTRDY FAEQVYWSPLLNKEFKEMENRRKKQLLRDLSGLQGMNGSIQAKSIQVLPSHELVSTRIAE HLGDSQSLGRMLADYRARGGRIQPKNSDPFAHSKDASSTSSGQSGSKNEGDEERGLILSD AVWSTKVDCLNPINHQRLCVLFSSSSAQSSNAPSACVSPWIVTMEFYGKNDLTLGIFLER YCFRPSYQCPSMFCDTPMVHHIRRFVHGQGCVQIILKELDSPVPGYQHTILTYSWCRICK QVTPVVALSNESWSMSFAKYLELRFYGHQYTRRANAEPCGHSIHHDYHQYFSYNQMVASF SYSPIRLLEVCVPLPKIFIKRQAPLKVSLLQDLKDFFQKVSQVYVAIDERLASLKTDTFS KTREEKMEDIFAQKEMEEGEFKNWIEKMQARLMSSSVDTPQQLQSVFESLIAKKQSLCEV LQAWNNRLQDLFQQEKGRKRPSVPPSPGRLRQGEESKISAMDASPRNISPGLQNGEKEDR FLTTLSSQSSTSSTHLQLPTPPEVMSEQSVGGPPELDTASSSEDVFDGHLLGSTDSQVKE KSTMKAIFANLLPGNSYNPIPFPFDPDKHYLMYEHERVPIAVCEKEPSSIIAFALSCKEY RNALEELSKATQWNSAEEGLPTNSTSDSRPKSSSPIRLPEMSGGQTNRTTETEPQPTKKA SGMLSFFRGTAGKSPDLSSQKRETLRGADSAYYQVGQTGKEGTENQGVEPQDEVDGGDTQ KKQLINPHVELQFSDANAKFYCRLYYAGEFHKMREVILDSSEEDFIRSLSHSSPWQARGG KSGAAFYATEDDRFILKQMPRLEVQSFLDFAPHYFNYITNAVQQKRPTALAKILGVYRIG YKNSQNNTEKKLDLLVMENLFYGRKMAQVFDLKGSLRNRNVKTDTGKESCDVVLLDENLL KMVRDNPLYIRSHSKAVLRTSIHSDSHFLSSHLIIDYSLLVGRDDTSNELVVGIIDYIRT FTWDKKLEMVVKSTGILGGQGKMPTVVSPELYRTRFCEAMDKYFLMVPDHWTGLGLNC Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 2 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Apilimod dimesylate | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Non-hodgkin lymphoma | [1] | |
| 2 | LAM-002 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Non-hodgkin lymphoma | [2] | |
| Preclinical Drug(s) | [+] 1 Preclinical Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | YM-201636 | Drug Info | Preclinical | Discovery agent | [3] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 1 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Inhibitor | [+] 3 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Apilimod dimesylate | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 2 | LAM-002 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 3 | YM-201636 | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inositol phosphate metabolism | hsa00562 | Affiliated Target |
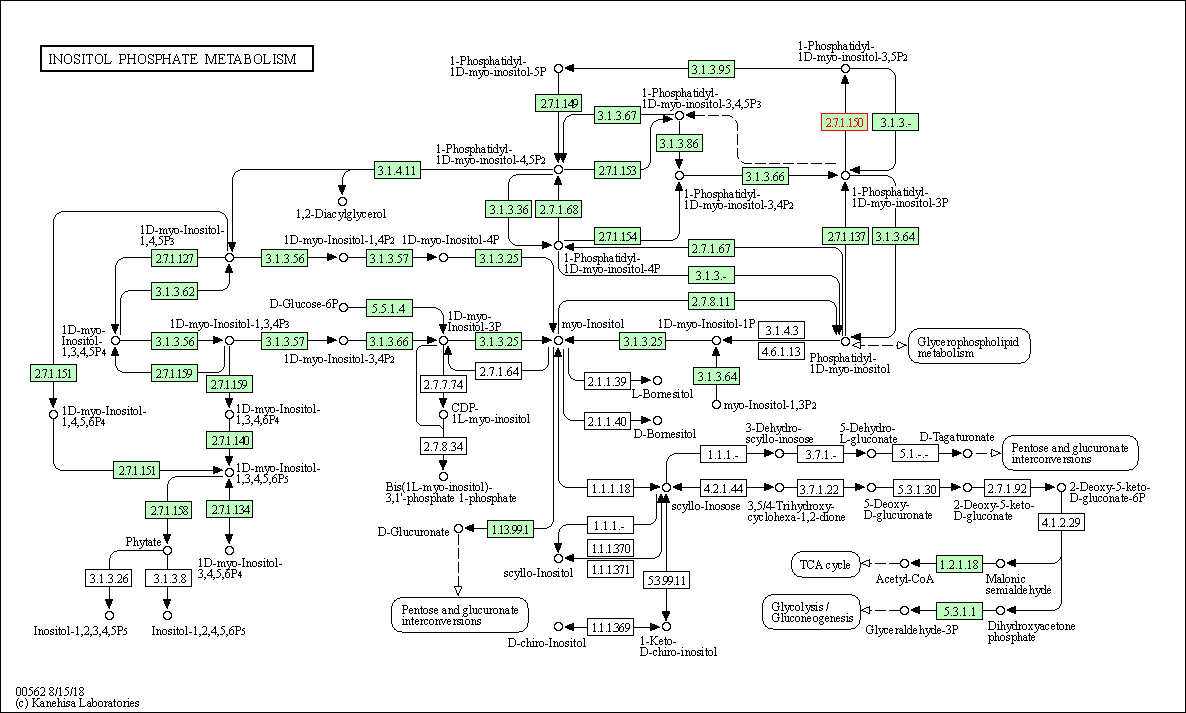
|
| Class: Metabolism => Carbohydrate metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Phosphatidylinositol signaling system | hsa04070 | Affiliated Target |
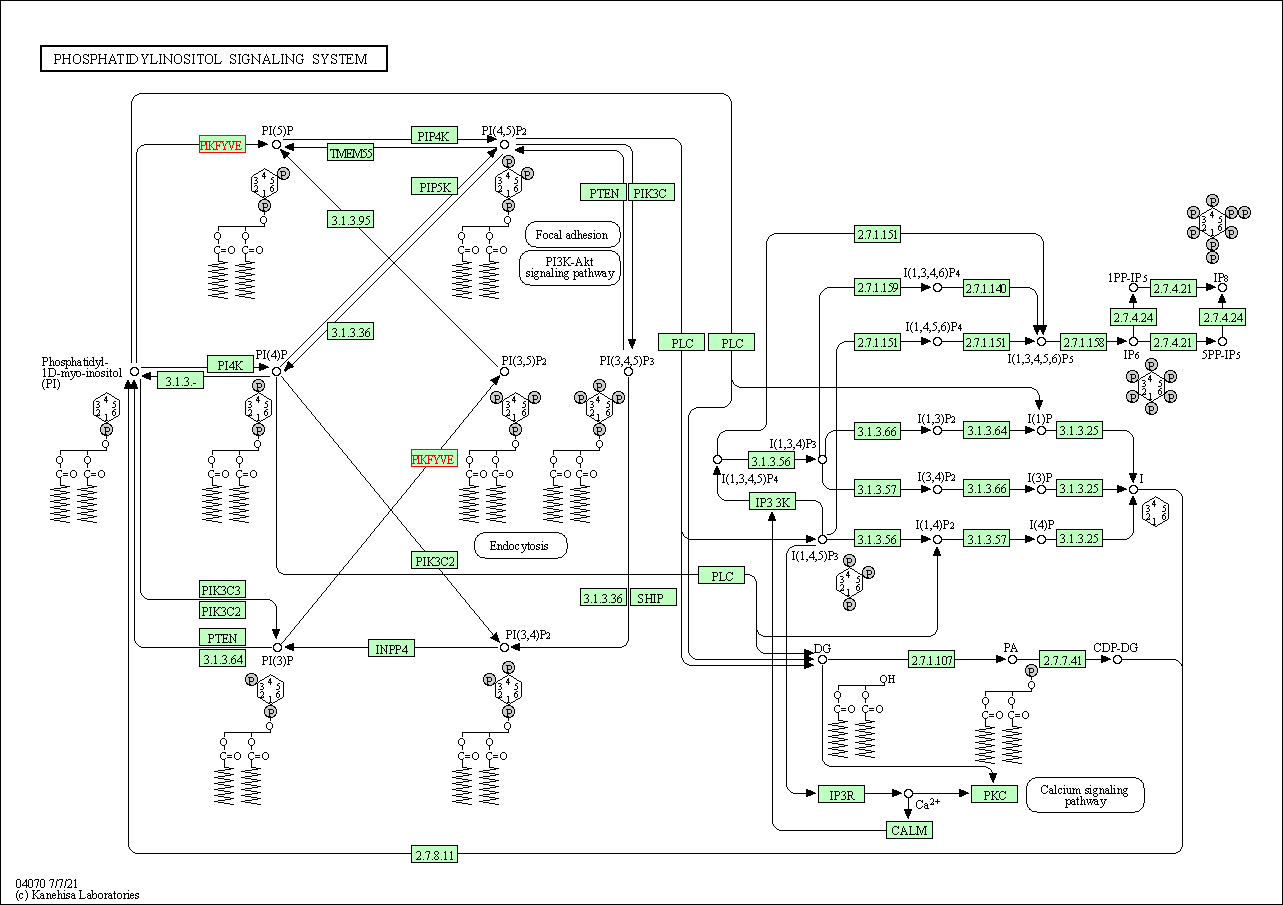
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Phagosome | hsa04145 | Affiliated Target |
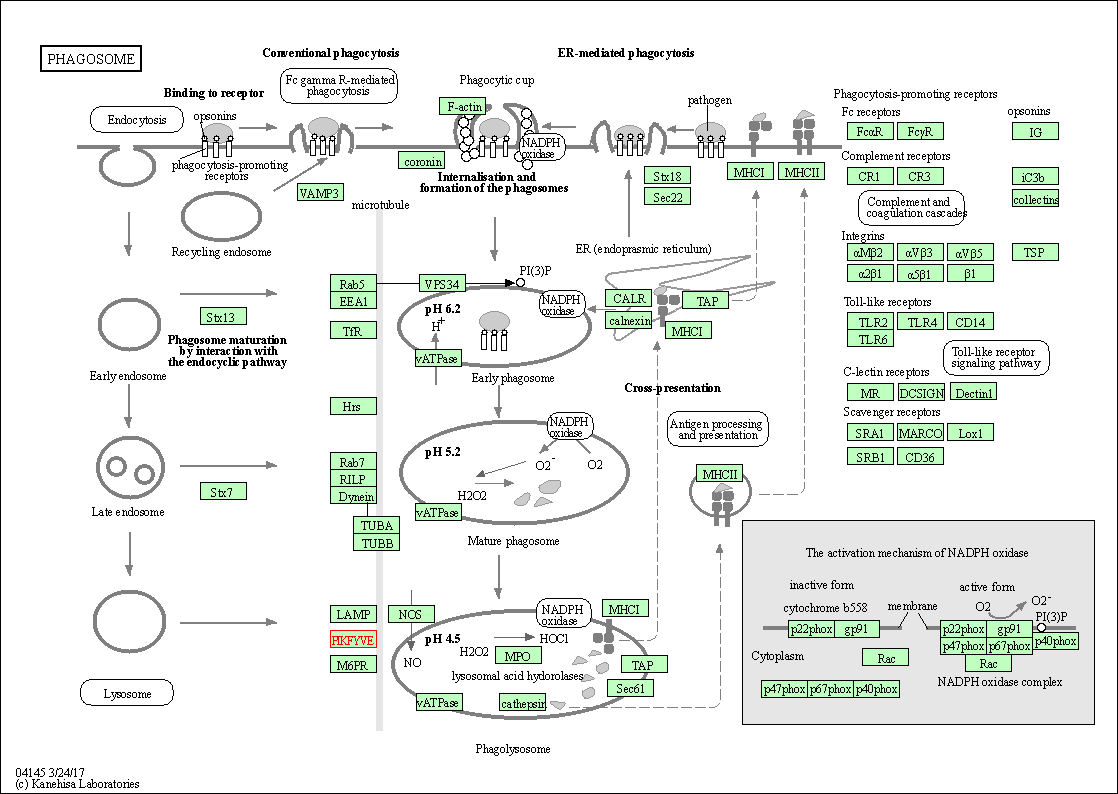
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Transport and catabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Regulation of actin cytoskeleton | hsa04810 | Affiliated Target |
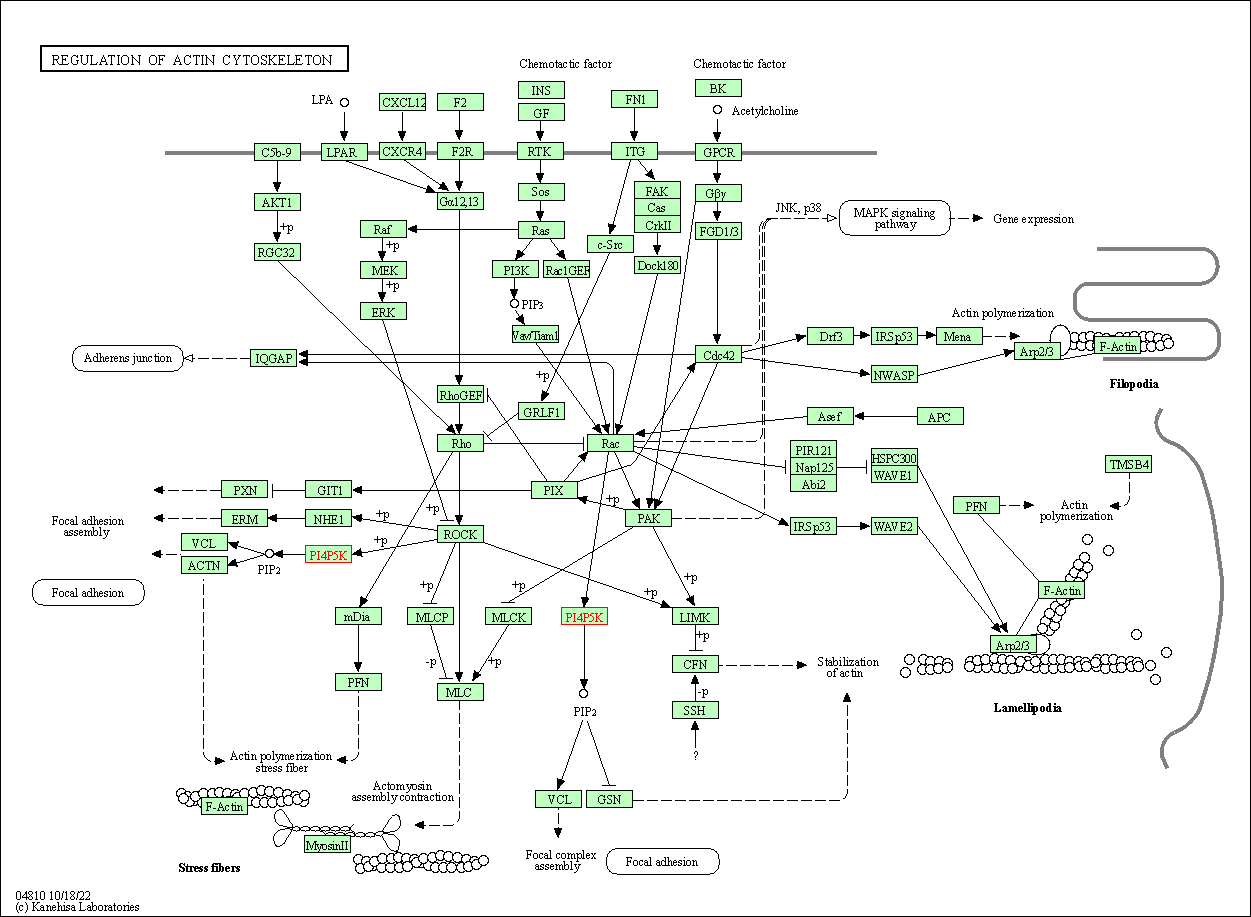
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell motility | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Degree | 14 | Degree centrality | 1.50E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 1.14E-03 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 1.86E-01 | Radiality | 1.31E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 1.43E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 8.79E+00 | Topological coefficient | 1.37E-01 | Eccentricity | 13 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KEGG Pathway | [+] 5 KEGG Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Inositol phosphate metabolism | |||||
| 2 | Metabolic pathways | |||||
| 3 | Phosphatidylinositol signaling system | |||||
| 4 | Phagosome | |||||
| 5 | Regulation of actin cytoskeleton | |||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 2 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT02594384) A Phase I Dose Escalation Study of the Safety and Pharmacokinetics of LAM-002A In Patients With Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma (LAM-002A/NHL) (LAM-002A/NHL). U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 3 | Lysosomes as a therapeutic target. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2019 Dec;18(12):923-948. | |||||
| REF 4 | PIKfyve negatively regulates exocytosis in neurosecretory cells. J Biol Chem. 2008 Feb 1;283(5):2804-13. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

