Target expression details
| Target's General Information | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID | T18477 | ||||
| Target Name | Heat shock protein 90 alpha (HSP90A) | ||||
| Synonyms | Renal carcinoma antigen NY-REN-38; Lipopolysaccharide-associated protein 2; LPS-associated protein 2; LAP-2; Heat shock protein HSP 90-alpha; Heat shock 86 kDa; HSPCA; HSPC1; HSP90A; HSP86; HSP 86 | ||||
| Target Type | Successful | ||||
| Gene Name | HSP90AA1 | ||||
| Biochemical Class | Heat shock protein | ||||
| UniProt ID | HS90A_HUMAN||HS90B_HUMAN | ||||
| Target's Expression Profile in Disease Related Tissue between Patients and Normal People | |||||
| Disease | Myeloma | ||||
| Example drug | Tanespimycin | Discontinued in Phase 3 | [1], [2], [3], [4] | ||
| Tissue | Bone marrow | ||||
| Level of differential expression between the patients in the disease section of the tissue and the tissues of healthy individual |
Fold-change: 1.3 Z-score: 4.35 P-value: 5.98E-06 |
||||
|
Target gene expression profiles of the patients in the disease section of the tissue
Target gene expression profiles in the tissue of healthy individual

|
|||||
| Disease | Melanoma | ||||
| Example drug | Tanespimycin | Phase 2 | [1], [2], [3], [4] | ||
| Tissue | Skin | ||||
| Level of differential expression between the patients in the disease section of the tissue and the tissues of healthy individual |
Fold-change: 0.44 Z-score: 0.71 P-value: 1.54E-02 |
||||
|
Target gene expression profiles of the patients in the disease section of the tissue
Target gene expression profiles in the tissue of healthy individual
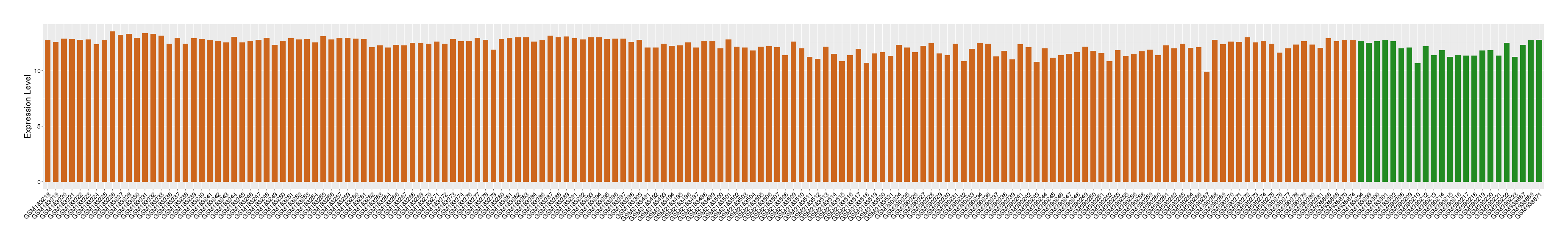
|
|||||
| Disease | Ovarian cancer | ||||
| Example drug | Alvespimycin hydrochloride | Phase 1 | [5], [3], [4] | ||
| Tissue | Ovarian tissue | ||||
| Level of differential expression between the patients in the disease section of the tissue and the tissues of healthy individual |
Fold-change: 0.18 Z-score: 0.48 P-value: 3.96E-01 |
||||
| Level of differential expression between the patients in the disease section of the tissue section of the tissue adjacent to the disease section |
Fold-change: -0.05 Z-score: -0.09 P-value: 8.65E-01 |
||||
|
Target gene expression profiles of the patients in the disease section of the tissue
Target gene expression profiles of the patients in the normal section of the tissue adjacent to the disease section
Target gene expression profiles in the tissue of healthy individual

|
|||||
| Disease | Lung cancer | ||||
| Tissue | Lung tissue | ||||
| Level of differential expression between the patients in the disease section of the tissue and the tissues of healthy individual |
Fold-change: 0.15 Z-score: 0.6 P-value: 4.65E-03 |
||||
| Level of differential expression between the patients in the disease section of the tissue section of the tissue adjacent to the disease section |
Fold-change: 0.3 Z-score: 1.07 P-value: 1.61E-10 |
||||
|
Target gene expression profiles of the patients in the disease section of the tissue
Target gene expression profiles of the patients in the normal section of the tissue adjacent to the disease section
Target gene expression profiles in the tissue of healthy individual

|
|||||
| Target's Expression Profile across Various Tissues of Healthy Individual | |||||
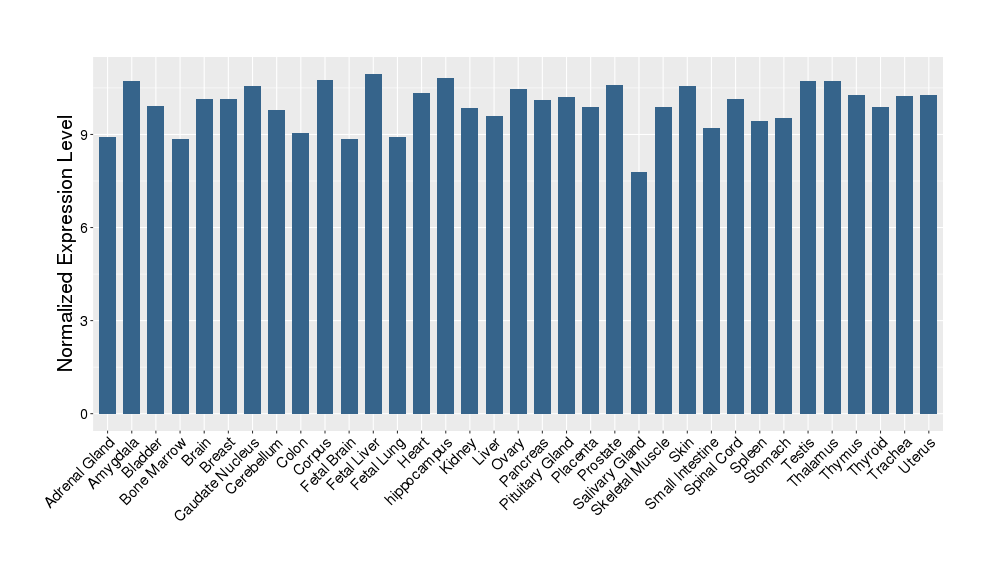
|
|||||
| References | |||||
| REF 1 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7751). | ||||
| REF 2 | Emerging therapies for multiple myeloma. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2009 Mar;14(1):99-127. | ||||
| REF 3 | Interpreting expression profiles of cancers by genome-wide survey of breadth of expression in normal tissues. Genomics 2005 Aug;86(2):127-41. | ||||
| REF 4 | NCBI GEO: archive for functional genomics data sets--update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Jan;41(Database issue):D991-5. | ||||
| REF 5 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT00089271) 17-DMAG in Treating Patients With Metastatic or Unresectable Solid Tumors or Lymphomas. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | ||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

