Drug Information
| Drug General Information | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
D8NY3J
|
|||
| Drug Name |
Guanfacine
|
|||
| Synonyms |
GUANFACINE; 29110-47-2; Estulic; Guanfacinum [INN-Latin]; Guanfacina [INN-Spanish]; Guanfacinum; Guanfacina; N-(diaminomethylidene)-2-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)acetamide; Benzeneacetamide, N-(aminoiminomethyl)-2,6-dichloro-; N-amidino-2-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)acetamide; UNII-30OMY4G3MK; EINECS 249-442-8; 30OMY4G3MK; N-carbamimidoyl-2-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)acetamide; NSC-759121; CHEBI:5558; DTXSID9046944; Guanfacine (INN); NSC 759121; GUANFACINE [INN]; Guanfacinum (INN-Latin); Guanfacina (INN-Spanish); Guanfacine [INN:BAN]; NCGC00015469-05; CAS-29110-48-3; Estulic (TN); Tenex (Salt/Mix); Estulic (Salt/Mix); Tocris-1030; GUANFACINE [MI]; Prestwick0_000339; Prestwick1_000339; Prestwick2_000339; Prestwick3_000339; Lopac-G-1043; GUANFACINE [VANDF]; CHEMBL862; GUANFACINE [WHO-DD]; LON 798 (Salt/Mix); Lopac0_000519; SCHEMBL35094; BSPBio_000377; GTPL522; RASPBERRYKETONEGLUCOSIDE; SPBio_002298; BPBio1_000415; DTXCID7026944; BDBM81984; C02AC02; BCP09647; NSC_3519; Guanfacine hydrochloride (Salt/Mix); HY-17416A; (2,6-dichlorophenylacetyl)-guanidine; [(2,6-dichlorophenyl)acetyl]guanidine; AKOS030255657; AKOS030526130; CCG-204609; DB01018; SDCCGSBI-0050502.P002; MRF-0000019; NCGC00015469-01; NCGC00015469-02; NCGC00015469-03; NCGC00015469-04; NCGC00015469-06; NCGC00015469-07; NCGC00024950-01; NCGC00024950-02; NCGC00024950-03; CAS_29110-47-2; FT-0669067; FT-0669068; C07037; D08031; EN300-243924; AB01563079_01; A902647; A918619; L000286; L013430; J-017394; Q5613599; BRD-K32830106-003-03-0; BRD-K32830106-003-11-3; N-(Diaminomethyliden)-2-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)acetamid; [(2,6-Dichlorophenyl)acetyl]guanidine hydrochloride;Guanfacine HCl
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| Drug Type |
Small molecule
|
|||
| Indication | Alzheimer disease [ICD-11: 8A20; ICD-10: G30, G30.9; ICD-9: 331] | Phase 3 | [1] | |
| Company |
Imperial College London, UK National Institute of Health Research
|
|||
| Structure |
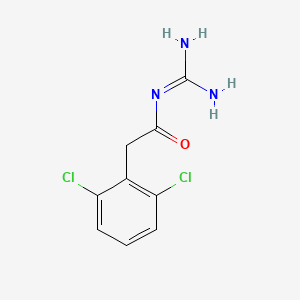 |
Download2D MOL |
||
| Formula |
C9H9Cl2N3O
|
|||
| Canonical SMILES |
C1=CC(=C(C(=C1)Cl)CC(=O)N=C(N)N)Cl
|
|||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C9H9Cl2N3O/c10-6-2-1-3-7(11)5(6)4-8(15)14-9(12)13/h1-3H,4H2,(H4,12,13,14,15)
|
|||
| InChIKey |
INJOMKTZOLKMBF-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|||
| PubChem Compound ID | ||||
| Target and Pathway | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target(s) | Adrenergic receptor alpha-2A (ADRA2A) | Target Info | Agonist | [2] |
| KEGG Pathway | cGMP-PKG signaling pathway | |||
| Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction | ||||
| Panther Pathway | Alpha adrenergic receptor signaling pathway | |||
| Reactome | Adrenoceptors | |||
| Adrenaline signalling through Alpha-2 adrenergic receptor | ||||
| Adrenaline,noradrenaline inhibits insulin secretion | ||||
| G alpha (i) signalling events | ||||
| G alpha (z) signalling events | ||||
| Surfactant metabolism | ||||
| WikiPathways | Monoamine GPCRs | |||
| GPCRs, Class A Rhodopsin-like | ||||
| Platelet Aggregation (Plug Formation) | ||||
| Integration of energy metabolism | ||||
| GPCR ligand binding | ||||
| GPCR downstream signaling | ||||
| References | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT03116126) Randomised Clinical Trial of Noradrenergic Add-on Therapy With Extended-Release Guanfacine in Alzheimer's Disease. U.S.National Institutes of Health. | |||
| REF 2 | Scientific rationale for the use of alpha2A-adrenoceptor agonists in treating neuroinflammatory cognitive disorders. Mol Psychiatry. 2023 Apr 7:1-13. | |||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

