Drug Information
| Drug General Information | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
D0SV6C
|
|||
| Former ID |
DNC010199
|
|||
| Drug Name |
PRONTOCIL
|
|||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||
| Indication | Discovery agent [ICD-11: N.A.] | Investigative | [1] | |
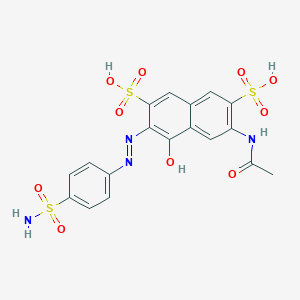
| Structure |
 |
Download2D MOL |
||
| Formula |
C18H16N4O10S3
|
|||
| Canonical SMILES |
CC(=O)NC1=C(C=C2C=C(C(=C(C2=C1)O)N=NC3=CC=C(C=C3)S(=O)(=O)N)S(=O)(=O)O)S(=O)(=O)O
|
|||
| InChI |
1S/C18H16N4O10S3/c1-9(23)20-14-8-13-10(6-15(14)34(27,28)29)7-16(35(30,31)32)17(18(13)24)22-21-11-2-4-12(5-3-11)33(19,25)26/h2-8,24H,1H3,(H,20,23)(H2,19,25,26)(H,27,28,29)(H,30,31,32)
|
|||
| InChIKey |
RALNLQYPLYWQRT-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|||
| CAS Number |
CAS 132-38-7
|
|||
| PubChem Compound ID | ||||
| Interaction between the Drug and Microbe | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Metabolism of Drug Affected by Studied Microbe(s) | ||||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Gut microbiota | ||||
| Studied Microbe: Gut microbiota unspecific | [2], [3], [4] | |||
| Microbial Enzyme | Azoreductase | |||
| Metabolic Reaction | Azo bond reduction | |||
| Resulting Metabolite | Sulfanilamide | |||
| Metabolic Effect | Increase activity; Increase toxicity | |||
| Description | Neoprontosil can be metabolized to Sulfanilamide by the azoreductase of gut microbiota through azo bond reduction, which results in the increase of drug's activity and toxicity. | |||
| Target and Pathway | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target(s) | Carbonic anhydrase (CA) | Target Info | Inhibitor | [1] |
| Carbonic anhydrase II (CA-II) | Target Info | Inhibitor | [5] | |
| KEGG Pathway | Nitrogen metabolism | |||
| Proximal tubule bicarbonate reclamation | ||||
| Collecting duct acid secretion | ||||
| Gastric acid secretion | ||||
| Pancreatic secretion | ||||
| Bile secretion | ||||
| NetPath Pathway | IL4 Signaling Pathway | |||
| EGFR1 Signaling Pathway | ||||
| Reactome | Erythrocytes take up carbon dioxide and release oxygen | |||
| Erythrocytes take up oxygen and release carbon dioxide | ||||
| Reversible hydration of carbon dioxide | ||||
| WikiPathways | Reversible Hydration of Carbon Dioxide | |||
| Uptake of Carbon Dioxide and Release of Oxygen by Erythrocytes | ||||
| Uptake of Oxygen and Release of Carbon Dioxide by Erythrocytes | ||||
| References | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: cloning, characterization, and inhibition studies of the cytosolic isozyme III with sulfonamides. Bioorg Med Chem. 2007 Dec 1;15(23):7229-36. | |||
| REF 2 | Human gut microbiota plays a role in the metabolism of drugs. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2016 Sep;160(3):317-26. | |||
| REF 3 | Gut microbiota modulation of chemotherapy efficacy and toxicity. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017 Jun;14(6):356-365. | |||
| REF 4 | The metabolic effect of gut microbiota on drugs. Drug Metab Rev. 2020 Feb;52(1):139-156. | |||
| REF 5 | Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Inhibition of the Rv1284 and Rv3273 beta-carbonic anhydrases from Mycobacterium tuberculosis with diazenylbenzenesul... Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2009 Sep 1;19(17):4929-32. | |||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

