Drug Information
| Drug General Information | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
D0OF2J
|
|||
| Former ID |
DIB018858
|
|||
| Drug Name |
anti-BrP-LPA
|
|||
| Synonyms |
CHEMBL3621356; anti-BrP-LPA; GTPL6987; BDBM50187696; [(1S,3S)-1-bromo-4-hexadecanoyloxy-3-hydroxybutyl]phosphonic acid; Hexadecanoic acid (2S,4S)-2-hydroxy-4-bromo-4-(dihydroxyphosphinyl)butyl ester
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||
| Indication | Discovery agent [ICD-11: N.A.] | Investigative | [1] | |
| Structure |
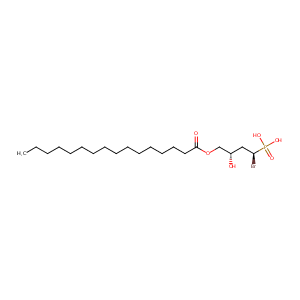 |
Download2D MOL
|
||
| Formula |
C20H40BrO6P
|
|||
| Canonical SMILES |
CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(=O)OCC(CC(P(=O)(O)O)Br)O
|
|||
| InChI |
1S/C20H40BrO6P/c1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15-20(23)27-17-18(22)16-19(21)28(24,25)26/h18-19,22H,2-17H2,1H3,(H2,24,25,26)/t18-,19+/m0/s1
|
|||
| InChIKey |
HLVKVWDSLLFMSX-RBUKOAKNSA-N
|
|||
| PubChem Compound ID | ||||
| PubChem Substance ID | ||||
| Target and Pathway | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target(s) | Lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1 (LPAR1) | Target Info | Antagonist | [2] |
| KEGG Pathway | Rap1 signaling pathway | |||
| Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction | ||||
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | ||||
| Gap junction | ||||
| Pathways in cancer | ||||
| NetPath Pathway | TGF_beta_Receptor Signaling Pathway | |||
| Pathway Interaction Database | LPA receptor mediated events | |||
| Reactome | G alpha (q) signalling events | |||
| G alpha (i) signalling events | ||||
| Lysosphingolipid and LPA receptors | ||||
| WikiPathways | Myometrial Relaxation and Contraction Pathways | |||
| Gastrin-CREB signalling pathway via PKC and MAPK | ||||
| Small Ligand GPCRs | ||||
| GPCR ligand binding | ||||
| GPCR downstream signaling | ||||
| References | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 6987). | |||
| REF 2 | Dual activity lysophosphatidic acid receptor pan-antagonist/autotaxin inhibitor reduces breast cancer cell migration in vitro and causes tumor regression in vivo. Cancer Res. 2009 Jul 1;69(13):5441-9. | |||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

