Drug Information
| Drug General Information | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
D0M9DC
|
|||
| Former ID |
DAP000622
|
|||
| Drug Name |
Oxaprozin
|
|||
| Synonyms |
Actirin; Alvo; Danoprox; Daypro; Dayrun; Deflam; Oxaprozina; Oxaprozine; Oxaprozinum; Voir; Xopane; Apotex brand of oxaprozin; CSC brand of oxaprozin; Pfizer brand of oxaprozin; Rhoxalpharma brand of oxaprozin; TRB brand of oxaprozin; Lyl)propenoic acid; NCI310839; O 9637; WY 21743; Apo-Oxaprozin; Daypro (TN); Duraprox (TN); Oxaprozina [INN-Spanish]; Oxaprozine [INN-French]; Oxaprozinum [INN-Latin]; Rhoxal-oxaprozin; WY-21743; WY-21,743; Oxaprozin (JP15/USAN/INN); Oxaprozin [USAN:BAN:INN:JAN]; Beta-(4,5-Diphenyloxazol-2-yl)propionic acid; 3-(4, 5-Diphenyl-2-oxazo; 3-(4,5-Diphenyl-1,3-oxazol-2-yl)propanoic acid; 3-(4,5-Diphenyl-2-oxazolyl)propenoic acid; 4, 5-Diphenyl-2-oxazolepropionic acid; 4,5-Diphenyl-2-oxazolepropanoic acid; 4,5-Diphenyl-2-oxazolepropionic acid
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||
| Indication | Rheumatoid arthritis [ICD-11: FA20] | Approved | [1] | |
| Therapeutic Class |
Antiinflammatory Agents
|
|||
| Company |
Gd Searle Llc
|
|||
| Structure |
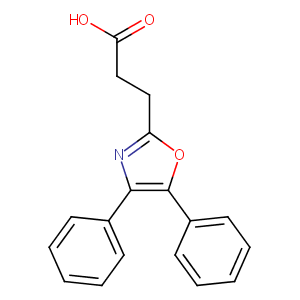 |
Download2D MOL |
||
| Formula |
C18H15NO3
|
|||
| Canonical SMILES |
C1=CC=C(C=C1)C2=C(OC(=N2)CCC(=O)O)C3=CC=CC=C3
|
|||
| InChI |
1S/C18H15NO3/c20-16(21)12-11-15-19-17(13-7-3-1-4-8-13)18(22-15)14-9-5-2-6-10-14/h1-10H,11-12H2,(H,20,21)
|
|||
| InChIKey |
OFPXSFXSNFPTHF-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|||
| CAS Number |
CAS 21256-18-8
|
|||
| PubChem Compound ID | ||||
| PubChem Substance ID |
9561, 224921, 455291, 3159337, 4254158, 7434787, 7847529, 7980214, 8141108, 8152831, 10320082, 11110656, 11110657, 11372015, 11374860, 11387071, 11407074, 11458222, 11460192, 11467088, 11468208, 11485388, 11486676, 11489512, 11490893, 11493045, 12013314, 14922602, 17405502, 24278617, 26534590, 26612863, 26652602, 26680054, 26719634, 26747622, 26747623, 29223703, 46386783, 46506429, 47216866, 47365302, 47515409, 47589083, 47810846, 47959863, 48185086, 49681726, 49699271, 50001218
|
|||
| ChEBI ID |
CHEBI:7822
|
|||
| ADReCS Drug ID | BADD_D01635 | |||
| SuperDrug ATC ID |
M01AE12
|
|||
| SuperDrug CAS ID |
cas=021256188
|
|||
| Interaction between the Drug and Microbe | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Metabolism of Drug Affected by Studied Microbe(s) | ||||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Bacteroidales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides dorei DSM 17855
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[2] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Oxaprozin can be metabolized by Bacteroides dorei DSM 17855 (log2FC = -0.616; p = 0.003). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides fragilis ATCC43859
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[2] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Oxaprozin can be metabolized by Bacteroides fragilis ATCC43859 (log2FC = -0.759; p = 0.002). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides fragilis HMW 610
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[2] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Oxaprozin can be metabolized by Bacteroides fragilis HMW 610 (log2FC = -0.694; p = 0.001). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides fragilis HMW 615
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[2] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Oxaprozin can be metabolized by Bacteroides fragilis HMW 615 (log2FC = -0.663; p = 0.012). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides fragilis NCTC 9343
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[2] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Oxaprozin can be metabolized by Bacteroides fragilis NCTC 9343 (log2FC = -0.496; p = 0.017). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides fragilis str. 3986 T(B)9
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[2] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Oxaprozin can be metabolized by Bacteroides fragilis str. 3986 T(B)9 (log2FC = -0.594; p = 0.005). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides fragilis str. DS-208
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[2] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Oxaprozin can be metabolized by Bacteroides fragilis str. DS-208 (log2FC = -0.621; p = 0.017). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides intestinalis DSM 17393
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[2] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Oxaprozin can be metabolized by Bacteroides intestinalis DSM 17393 (log2FC = -0.323; p = 0.047). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides ovatus ATCC 8483
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[2] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Oxaprozin can be metabolized by Bacteroides ovatus ATCC 8483 (log2FC = -0.395; p = 0.005). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides stercoris ATCC 43183
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[2] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Oxaprozin can be metabolized by Bacteroides stercoris ATCC 43183 (log2FC = -0.386; p = 0.01). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron 3731
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[2] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Oxaprozin can be metabolized by Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron 3731 (log2FC = -0.556; p = 0.009). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron 7330
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[2] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Oxaprozin can be metabolized by Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron 7330 (log2FC = -0.565; p = 0.0). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron VPI-5482
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[2] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Oxaprozin can be metabolized by Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron VPI-5482 (log2FC = -0.617; p = 0.045). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides uniformis ATCC 8492
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[2] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Oxaprozin can be metabolized by Bacteroides uniformis ATCC 8492 (log2FC = -0.794; p = 0.006). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides vulgatus ATCC 8482
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[2] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Oxaprozin can be metabolized by Bacteroides vulgatus ATCC 8482 (log2FC = -0.536; p = 0.028). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides xylanisolvens DSM18836
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[2] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Oxaprozin can be metabolized by Bacteroides xylanisolvens DSM18836 (log2FC = -0.686; p = 0.001). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Odoribacter splanchnicus
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[2] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Oxaprozin can be metabolized by Odoribacter splanchnicus (log2FC = -0.6; p = 0.002). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Parabacteroides distasonis ATCC 8503
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[2] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Oxaprozin can be metabolized by Parabacteroides distasonis ATCC 8503 (log2FC = -0.432; p = 0.047). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Pretovella copri DSM 18205
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[2] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Oxaprozin can be metabolized by Pretovella copri DSM 18205 (log2FC = -0.322; p = 0.01). | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Bifidobacteriales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Bifidobacterium ruminantium
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[2] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Oxaprozin can be metabolized by Bifidobacterium ruminantium (log2FC = -0.469; p = 0.01). | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Eubacteriales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Blautia hansenii DSM20583
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[2] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Oxaprozin can be metabolized by Blautia hansenii DSM20583 (log2FC = -0.458; p = 0.011). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Clostridium sp.
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[2] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Oxaprozin can be metabolized by Clostridium sp. (log2FC = -0.408; p = 0.014). | |||
| The Abundace of Studied Microbe(s) Regulated by Drug | ||||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Eubacteriales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Coprococcus comes
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Decrease | |||
| Experiment Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | The abundance of Coprococcus comes was decreased by Oxaprozin (adjusted p-values: 5.36E-03). | |||
| Target and Pathway | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target(s) | Prostaglandin G/H synthase (COX) | Target Info | Inhibitor | [4] |
| References | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. 2015 | |||
| REF 2 | Mapping human microbiome drug metabolism by gut bacteria and their genes. Nature. 2019 Jun;570(7762):462-467. | |||
| REF 3 | Extensive impact of non-antibiotic drugs on human gut bacteria. Nature. 2018 Mar 29;555(7698):623-628. | |||
| REF 4 | The aryl propionic acid R-flurbiprofen selectively induces p75NTR-dependent decreased survival of prostate tumor cells. Cancer Res. 2007 Apr 1;67(7):3254-62. | |||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

