Drug Information
| Drug General Information | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
D0E2OU
|
|||
| Former ID |
DAP001288
|
|||
| Drug Name |
Quinupristin
|
|||
| Synonyms |
Quinupristina; Quinupristine; Quinupristinum; SYB; RP 57669; Quinupristin [USAN:INN]; Quinupristina [INN-Spanish]; Quinupristine [INN-French]; Quinupristinum [INN-Latin]; RP-57669; Synercid (TN); Quinupristin (JAN/USAN/INN); 4-[4-(DIMETHYLAMINO)-N-METHYL-L-PHENYLALANINE]-5-[(2S,5R)-5-[[[(3S)-1-AZABICYCLO-[2.2.2]OCT-3-YL]THIO]METHYL]-4-OXO-2-PIPERIDINECARBOXYLIC ACID]VIRGINIAMYCIN; 5delta-(3-quinuclidinyl)thiomethylpristinamycin IA
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||
| Indication | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z; ICD-10: A00-B99] | Approved | [1] | |
| Therapeutic Class |
Antibiotics
|
|||
| Structure |
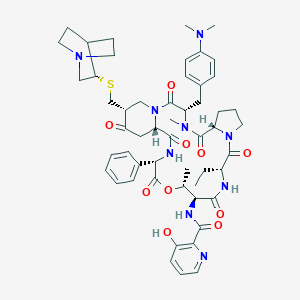 |
Download2D MOL
|
||
| Formula |
C53H67N9O10S
|
|||
| Canonical SMILES |
CCC1C(=O)N2CCCC2C(=O)N(C(C(=O)N3CC(C(=O)CC3C(=O)NC(C(=O)OC(C(C(=O)N1)NC(=O)C4=C(C=CC=N4)O)C)C5=CC=CC=C5)CSC6CN7CCC6CC7)CC8=CC=C(C=C8)N(C)C)C
|
|||
| InChI |
1S/C53H67N9O10S/c1-6-37-50(68)61-23-11-14-38(61)51(69)59(5)40(26-32-16-18-36(19-17-32)58(3)4)52(70)62-28-35(30-73-43-29-60-24-20-33(43)21-25-60)42(64)27-39(62)47(65)57-45(34-12-8-7-9-13-34)53(71)72-31(2)44(48(66)55-37)56-49(67)46-41(63)15-10-22-54-46/h7-10,12-13,15-19,22,31,33,35,37-40,43-45,63H,6,11,14,20-21,23-30H2,1-5H3,(H,55,66)(H,56,67)(H,57,65)/t31-,35+,37-,38+,39+,40+,43-,44+,45+/m1/s1
|
|||
| InChIKey |
WTHRRGMBUAHGNI-LCYNINFDSA-N
|
|||
| CAS Number |
CAS 120138-50-3
|
|||
| PubChem Compound ID | ||||
| PubChem Substance ID | ||||
| SuperDrug ATC ID |
J01FG02
|
|||
| SuperDrug CAS ID |
cas=126602899
|
|||
| Interaction between the Drug and Microbe | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Abundace of Studied Microbe(s) Regulated by Drug | ||||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Enterobacterales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Enterobacter
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[2] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Increase | |||
| Experimental Species | Human | Experimental Sample | Faeces | |
| Disease or Condition | Healthy | |||
| Description | The abundance of Enterobacter was increased by Combination of quinupristin and dalfopristin. | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Enterobacteriaceae
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[2] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Increase | |||
| Experimental Species | Human | Experimental Sample | Faeces | |
| Disease or Condition | Healthy | |||
| Description | The abundance of Enterobacteriaceae was increased by Combination of quinupristin and dalfopristin (p < 0.01). | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Eubacteriales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Clostridium difficile
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[2] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Decrease | |||
| Experimental Species | Human | Experimental Sample | Faeces | |
| Disease or Condition | Healthy | |||
| Description | The abundance of Clostridium difficile was decreased by Combination of quinupristin and dalfopristin. | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Pseudomonadales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Pseudomonas
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[2] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | No significant change | |||
| Experimental Species | Human | Experimental Sample | Faeces | |
| Disease or Condition | Healthy | |||
| Description | The abundance of Pseudomonas was not significantly changed by Combination of quinupristin and dalfopristin. | |||
| Target and Pathway | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target(s) | Bacterial Integral membrane LmrP (Bact lmrP) | Target Info | Modulator | [3] |
| References | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Natural products as sources of new drugs over the last 25 years. J Nat Prod. 2007 Mar;70(3):461-77. | |||
| REF 2 | Impact of quinupristin/dalfopristin (RP59500) on the faecal microflora in healthy volunteers. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2002 Jan;49(1):135-9. | |||
| REF 3 | The lactococcal secondary multidrug transporter LmrP confers resistance to lincosamides, macrolides, streptogramins and tetracyclines. Microbiology. 2001 Oct;147(Pt 10):2873-80. | |||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

