Drug Information
| Drug General Information | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
D0BA9U
|
|||
| Former ID |
DAP001207
|
|||
| Drug Name |
Levonorgestrel
|
|||
| Synonyms |
norgestrel; 797-63-7; D-Norgestrel; (-)-Norgestrel; Microval; Levonova; Postinor; Mirena; Ovrette; Neogest; Jadelle; Plan B; NORPLANT; Norplant 2; Microlution; Follistrel; Trivora; Monovar; Triciclor; Microgyn; Ovranette; Triagynon; Microlut; Nordet; Trigoa; 18-Methylnorethisterone; Levonorgestrelum; Microgynon CD; Microgest ED; Norplant II; Ovral-Lo; Logynon ED; Levlen ED; Trinordiol 28; Trinordiol 21; Microgynon 28; Microgynon 21; d(-)-Norgestrel; Neogynon 21; Monofeme 28; Nordette 28; Minivlar 30; Stediril 30; Nordette 21; Trifeme; Capronor; DNorgestrel; Levlen; Levonelle; Methylnorethindrone; Microluton; NorLevo; Norgeston; Norgestrel; Norgestrelum; Preven; Tetragynon; LD norgestrel [French]; Ld norgestrel; Levonorgestrel implants; Norgestrel [Progestins]; Norplant System in Plastic Container; Triquilar ED; Microgynon 30 ED; SH 70850; SH 850; Trifeme 28; Triphasil 21; Triphasil 28; Wy 3707; Alpha-Norgestrel; Component of Lo/ovral; Dl-Norgestrel; FH 122-A; LO/Ovral; Levonorgestrelum [INN-Latin]; Levora-21; Levora-28; Mirena (TN); Norgestrelum [INN-Latin]; Norplant (TN); Norplant-2; Ovoplex 30-150; Ovrette (TN); Postinor-2; Rigevidon 21+7; SOH-075; Tri-Levlen 21; Wy-3707; Wy-5104; E-Gen-C; Levonorgestrel [USAN:INN:BAN]; D(-)-Norgestrel; Levonorgestrel (JAN/USP/INN); Norgestrel (JP15/USP/INN); Norgestrel [USAN:BAN:INN:JAN]; Norgestrel [USAN:INN:BAN:JAN]; D-(-)-Norgestrel; Levonelle, D-Norgestrel, Levonova, Levonorgestrel; Norgestrel-(-)-D; Dl-13-beta-Ethyl-17-alpha-ethynyl-19-nortestosterone; 13-BETA-ETHYL-17-ALPHA-ETHYNYL-17-BETA-HYDROXYGON-4-EN-3-ONE; 13-Ehyl-17alpha-ethynyl-17-hydroxygon-4-en-3-one; 13-Ethyl-17-alpha-ethynyl-17-beta-hydroxy-4-gonen-3-one; 13-Ethyl-17-alpha-ethynylgon-4-en-17-beta-ol-3-one; 13-Ethyl-17alpha-ethynylgon-4-en-17beta-ol-3-one; 13-beta-Ethyl-17alpha-ethynyl-17beta-hydroxygon-4-en-3-one; 13beta-Ethyl-17alpha-ethynyl-17beta-hydroxygon-4-en-3-one; 17-Ethynyl-18-methyl-19-nortestosterone; 17-alpha-Ethynyl-13-ethyl-19-nortestosterone; 17alpha-Ethynyl-13-ethyl-19-nortestosterone; 17alpha-Ethynyl-13beta-ethyl-3-oxo-4-estren-17beta-ol; 17alpha-Ethynyl-17-hydroxy-18-methylestr-4-en-3-one; 17alpha-Ethynyl-18-homo-19-nor-testosterone; 17alpha-Ethynyl-18-homo-19-nortestosterone; 17alpha-ethynyl-17beta-hydroxy-18a-homoestr-4-en-3-one; 18,19-Dinor-4-pregnen-20-yn-3-one; 18-Methyl-17-alpha-ethynyl-19-nortestosterone; 72-HOURS
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||
| Indication | Contraception [ICD-11: QA21] | Approved | [1], [2] | |
| Therapeutic Class |
Contraceptive Agents
|
|||
| Structure |
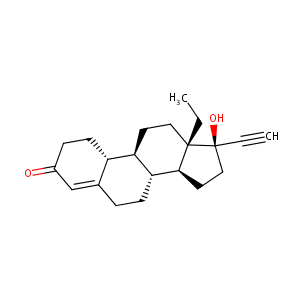 |
Download2D MOL |
||
| Formula |
C21H28O2
|
|||
| Canonical SMILES |
CCC12CCC3C(C1CCC2(C#C)O)CCC4=CC(=O)CCC34
|
|||
| InChI |
1S/C21H28O2/c1-3-20-11-9-17-16-8-6-15(22)13-14(16)5-7-18(17)19(20)10-12-21(20,23)4-2/h2,13,16-19,23H,3,5-12H2,1H3/t16-,17+,18+,19-,20-,21-/m0/s1
|
|||
| InChIKey |
WWYNJERNGUHSAO-XUDSTZEESA-N
|
|||
| CAS Number |
CAS 797-63-7
|
|||
| PubChem Compound ID | ||||
| PubChem Substance ID |
10349, 10353, 7848013, 7848017, 7889451, 8159864, 10321210, 11466801, 11467921, 11486521, 11532896, 14801049, 14923455, 24702331, 24897561, 26719646, 29215264, 29281281, 46386677, 46508082, 46509177, 47275737, 47499732, 48094724, 48318626, 49698635, 49963134, 49963135, 50109848, 53787534, 53789027, 56352919, 56422866, 57654445, 71821473, 76968564, 81093159, 85787473, 91147155, 92125812, 92308478, 92309282, 93167212, 103469384, 103913690, 104253340, 104330879, 117622363, 121363483, 124658858
|
|||
| ChEBI ID |
CHEBI:6443
|
|||
| ADReCS Drug ID | BADD_D01281 | |||
| SuperDrug ATC ID |
G03AC03; G03AD01
|
|||
| SuperDrug CAS ID |
cas=000797637
|
|||
| Interaction between the Drug and Microbe | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Metabolism of Drug Affected by Studied Microbe(s) | ||||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Bacteroidales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides caccae ATCC 43185
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Levonorgestrel can be metabolized by Bacteroides caccae ATCC 43185 (log2FC = -0.556; p = 0.026). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides cellulosilyticus DSM 14838
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Levonorgestrel can be metabolized by Bacteroides cellulosilyticus DSM 14838 (log2FC = -0.571; p = 0.002). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides dorei DSM 17855
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Levonorgestrel can be metabolized by Bacteroides dorei DSM 17855 (log2FC = -3.565; p = 0.007). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides fragilis ATCC43859
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Levonorgestrel can be metabolized by Bacteroides fragilis ATCC43859 (log2FC = -0.769; p = 0.009). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides fragilis HMW 610
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Levonorgestrel can be metabolized by Bacteroides fragilis HMW 610 (log2FC = -0.846; p = 0.014). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides fragilis HMW 615
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Levonorgestrel can be metabolized by Bacteroides fragilis HMW 615 (log2FC = -0.658; p = 0.046). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides fragilis NCTC 9343
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Levonorgestrel can be metabolized by Bacteroides fragilis NCTC 9343 (log2FC = -0.952; p = 0.003). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides fragilis str. 3397 T10
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Levonorgestrel can be metabolized by Bacteroides fragilis str. 3397 T10 (log2FC = -0.674; p = 0.034). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides fragilis str. 3986 T(B)9
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Levonorgestrel can be metabolized by Bacteroides fragilis str. 3986 T(B)9 (log2FC = -0.682; p = 0.003). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides fragilis str. DS-208
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Levonorgestrel can be metabolized by Bacteroides fragilis str. DS-208 (log2FC = -0.645; p = 0.002). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron 3731
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Levonorgestrel can be metabolized by Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron 3731 (log2FC = -0.684; p = 0.008). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron 7330
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Levonorgestrel can be metabolized by Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron 7330 (log2FC = -0.648; p = 0.018). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides uniformis ATCC 8492
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Levonorgestrel can be metabolized by Bacteroides uniformis ATCC 8492 (log2FC = -0.69; p = 0.019). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides vulgatus ATCC 8482
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Levonorgestrel can be metabolized by Bacteroides vulgatus ATCC 8482 (log2FC = -2.148; p = 0.003). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides WH2
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Levonorgestrel can be metabolized by Bacteroides WH2 (log2FC = -0.477; p = 0.01). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides xylanisolvens DSM18836
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Levonorgestrel can be metabolized by Bacteroides xylanisolvens DSM18836 (log2FC = -0.823; p = 0.002). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Odoribacter splanchnicus
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Levonorgestrel can be metabolized by Odoribacter splanchnicus (log2FC = -0.53; p = 0.022). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Parabacteroides johnsonii DSM 18315
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Levonorgestrel can be metabolized by Parabacteroides johnsonii DSM 18315 (log2FC = -0.847; p = 0.032). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Parabacteroides merdae ATCC 43184
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Levonorgestrel can be metabolized by Parabacteroides merdae ATCC 43184 (log2FC = -0.814; p = 0.047). | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Erysipelotrichales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Eubacterium biforme DSM 3989
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Levonorgestrel can be metabolized by Eubacterium biforme DSM 3989 (log2FC = -7.605; p = 0.006). | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Eubacteriales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Clostridium sp.
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Levonorgestrel can be metabolized by Clostridium sp. (log2FC = -0.485; p = 0.005). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Ruminococcus gnavus ATCC 29149
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Levonorgestrel can be metabolized by Ruminococcus gnavus ATCC 29149 (log2FC = -1.579; p = 0.003). | |||
| Target and Pathway | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target(s) | Progesterone receptor (PGR) | Target Info | Binder | [4], [5] |
| KEGG Pathway | Oocyte meiosis | |||
| Progesterone-mediated oocyte maturation | ||||
| Pathway Interaction Database | Cellular roles of Anthrax toxin | |||
| Reactome | Nuclear signaling by ERBB4 | |||
| Nuclear Receptor transcription pathway | ||||
| WikiPathways | Ovarian Infertility Genes | |||
| Signaling by ERBB4 | ||||
| Nuclear Receptors | ||||
| References | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 2881). | |||
| REF 2 | Natural products as sources of new drugs over the last 25 years. J Nat Prod. 2007 Mar;70(3):461-77. | |||
| REF 3 | Mapping human microbiome drug metabolism by gut bacteria and their genes. Nature. 2019 Jun;570(7762):462-467. | |||
| REF 4 | Met909 plays a key role in the activation of the progesterone receptor and also in the high potency of 13-ethyl progestins. Mol Pharmacol. 2009 Jun;75(6):1317-24. | |||
| REF 5 | Toll-like receptor-4-mediated macrophage activation is differentially regulated by progesterone via the glucocorticoid and progesterone receptors. Immunology. 2008 Sep;125(1):59-69. | |||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

