Drug Information
| Drug General Information | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
D09ZIS
|
|||
| Former ID |
DAP000500
|
|||
| Drug Name |
Zonisamide
|
|||
| Synonyms |
Exceglan; Excegram; Excegran; Tremode; Trerief; Zonegran; Zonisamida; Zonisamidum; Elan brand of zonisamide; Zonisamida [Spanish]; Zonisamide monosodium; Zonisamidum [Latin]; AD 810; PD 110843; SPR_2; AD-810; AD-810N; E-2090; Excegran (TN); PD-110843; Zonegran (TN); Zonegran, Zonisamide; Zonisamide (ZNS); Zonisamide (JAN/USAN/INN); Zonisamide [USAN:BAN:INN:JAN]; 1,2-Benzisoxazole-3-methanesulfonamide; 1,2-benzoxazol-3-ylmethanesulfonamide; 1-(1,2-Benzoxazol-3-Yl)methanesulfonamide; 1-(1,2-benzisoxazol-3-yl)methanesulfonamide; 3-(Sulfamoylmethyl)-1,2-benzisoxazole; 3-sulfamoylmethyl-1,2-benzisoxazole
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||
| Indication | Epilepsy [ICD-11: 8A60-8A68] | Approved | [1], [2] | |
| Therapeutic Class |
Analgesics
|
|||
| Company |
Eisai
|
|||
| Structure |
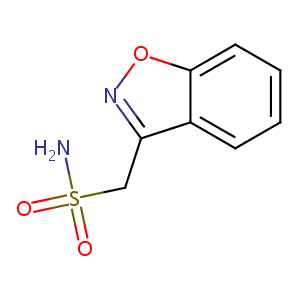 |
Download2D MOL |
||
| Formula |
C8H8N2O3S
|
|||
| Canonical SMILES |
C1=CC=C2C(=C1)C(=NO2)CS(=O)(=O)N
|
|||
| InChI |
1S/C8H8N2O3S/c9-14(11,12)5-7-6-3-1-2-4-8(6)13-10-7/h1-4H,5H2,(H2,9,11,12)
|
|||
| InChIKey |
UBQNRHZMVUUOMG-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|||
| CAS Number |
CAS 68291-97-4
|
|||
| PubChem Compound ID | ||||
| PubChem Substance ID |
9707, 5375171, 7847604, 8153515, 11528623, 12012838, 12016186, 15220241, 29215225, 29224771, 46505278, 46511458, 49666067, 50086000, 50109845, 57322921, 74524371, 81093137, 85174242, 85788213, 87322638, 92308963, 92714085, 92729687, 93166866, 93167201, 99437155, 103147645, 103200464, 103911541, 104170135, 104310103, 105859475, 117532844, 117843348, 118048699, 121362594, 124757254, 124801297, 125164058, 125324718, 125356086, 126629668, 126655670, 126670159, 129345232, 130010354, 131323538, 131377323, 134337793
|
|||
| ADReCS Drug ID | BADD_D02396 | |||
| SuperDrug ATC ID |
N03AX15
|
|||
| SuperDrug CAS ID |
cas=068291974
|
|||
| Interaction between the Drug and Microbe | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Metabolism of Drug Affected by Studied Microbe(s) | ||||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Bacteroidales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides vulgatus
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Metabolic Reaction | Reduction | |||
| Description | Zonisamide can be metabolized by Bacteroides vulgatus through reduction. | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Bifidobacteriales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Bifidobacterium bifidum
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Metabolic Reaction | Reduction | |||
| Description | Zonisamide can be metabolized by Bifidobacterium bifidum through reduction. | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Enterobacterales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Escherichia coli
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Metabolic Reaction | Reduction | |||
| Description | Zonisamide can be metabolized by Escherichia coli through reduction. | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Salmonella enterica ser. Typhimurium
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Metabolic Reaction | Reduction | |||
| Description | Zonisamide can be metabolized by Salmonella enterica ser. Typhimurium through reduction. | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Eubacteriales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Clostridium
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[4] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Resulting Metabolite | 2-sulphamoylacetylphenol | |||
| Description | Zonisamide can be metabolized to 2-Sulphamoylacetylphenol by Clostridium. | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Clostridium sporogenes
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Microbial Enzyme | Zonisamide reductase | |||
| Metabolic Reaction | Benzisoxazole ring reduction | |||
| Resulting Metabolite | 2-sulphamoylacetylphenol | |||
| Metabolic Effect | Increase activity | |||
| Description | Zonisamide can be metabolized to 2-sulphamoylacetylphenol by the zonisamide reductase of Clostridium sporogenes through benzisoxazole ring reduction, which results in the increase of the drug's activity. | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Lactobacillales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Enterococcus faecalis
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Metabolic Reaction | Reduction | |||
| Description | Zonisamide can be metabolized by Enterococcus faecalis through reduction. | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Lactobacillus rhamnosus
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Metabolic Reaction | Reduction | |||
| Description | Zonisamide can be metabolized by Lactobacillus rhamnosus through reduction. | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Pseudomonadales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Pseudomonas fluorescens
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Metabolic Reaction | Reduction | |||
| Description | Zonisamide can be metabolized by Pseudomonas fluorescens through reduction. | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Gut microbiota | ||||
| Studied Microbe: Gut microbiota unspecific | [5], [6] | |||
| Metabolic Reaction | O-N reduction and ring fission | |||
| Resulting Metabolite | 2-sulphamoylacetylphenol | |||
| Metabolic Effect | Decrease activity | |||
| Description | Zonisamide can be metabolized to 2-sulphamoylacetylphenol by gut microbiota through O-N reduction and ring fission, which results in the decrease of the drug's activity. | |||
| Target and Pathway | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target(s) | Sodium channel unspecific (NaC) | Target Info | Blocker | [7] |
| KEGG Pathway | Dopaminergic synapse | |||
| Reactome | Interaction between L1 and Ankyrins | |||
| References | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7047). | |||
| REF 2 | Use of second-generation antiepileptic drugs in the pediatric population. Paediatr Drugs. 2008;10(4):217-54. | |||
| REF 3 | Gut microbiota modulates drug pharmacokinetics. Drug Metab Rev. 2018 Aug;50(3):357-368. | |||
| REF 4 | Effects of Gut Microbiota on Drug Metabolism and Guidance for Rational Drug Use Under Hypoxic Conditions at High Altitudes. Curr Drug Metab. 2019;20(2):155-165. | |||
| REF 5 | Gut Microbiota-Mediated Drug-Antibiotic Interactions. Drug Metab Dispos. 2015 Oct;43(10):1581-9. | |||
| REF 6 | Gut Pharmacomicrobiomics: the tip of an iceberg of complex interactions between drugs and gut-associated microbes. Gut Pathog. 2012 Nov 30;4(1):16. | |||
| REF 7 | Antiepileptic drugs and relapse after epilepsy surgery. Epileptic Disord. 2008 Sep;10(3):193-8. | |||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

