Drug Information
| Drug General Information | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
D05BCF
|
|||
| Former ID |
DNC000445
|
|||
| Drug Name |
Clavulanate+Amoxicillin
|
|||
| Synonyms |
Potassium clavulanate; 61177-45-5; CLAVULANATE POTASSIUM; Amonate; BRL 14151K; UNII-Q42OMW3AT8; EINECS 262-640-9; Q42OMW3AT8; CHEBI:85264; potassium (2R,3Z,5R)-3-(2-hydroxyethylidene)-7-oxo-4-oxa-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylate; Potassium (Z)-(2R,5R)-3-(2-hydroxyethylidene)-7-oxo-4-oxa-1-azabicyclo(3.2.0)heptane-2-carboxylate; Potassium clavulanate with microcrystalline cellulose; 4-Oxa-1-azabicyclo(3.2.0)heptane-2-carboxylic acid, 3-(2-hydroxyethylidene)-7-oxo-, monopotassium salt, (2R-(2alpha,3Z,5alpha))-
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||
| Indication | Infectious disease [ICD-11: 1A00-CA43.1; ICD-9: 001-139] | Investigative | [1] | |
| Company |
GlaxoSmithKline
|
|||
| Structure |
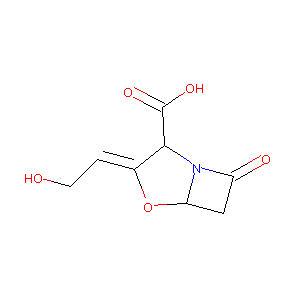 |
Download2D MOL |
||
| Formula |
C8H8KNO5
|
|||
| Canonical SMILES |
C1C2N(C1=O)C(C(=CCO)O2)C(=O)[O-].[K+]
|
|||
| InChI |
1S/C8H9NO5.K/c10-2-1-4-7(8(12)13)9-5(11)3-6(9)14-4;/h1,6-7,10H,2-3H2,(H,12,13);/q;+1/p-1/b4-1-;/t6-,7-;/m1./s1
|
|||
| InChIKey |
ABVRVIZBZKUTMK-JSYANWSFSA-M
|
|||
| CAS Number |
CAS 61177-45-5
|
|||
| PubChem Compound ID | ||||
| ChEBI ID |
CHEBI:85264
|
|||
| Interaction between the Drug and Microbe | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Abundace of Studied Microbe(s) Regulated by Drug | ||||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Bacteroidales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Odoribacter splanchnicus
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[2] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Decrease | |||
| Experiment Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | The abundance of Odoribacter splanchnicus was decreased by Clavulanate potassium (adjusted p-values: 3.34E-04). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Parabacteroides
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Increase | |||
| Experimental Species | Human | Experimental Sample | Faeces | |
| Disease or Condition | Healthy | |||
| Description | The abundance of Parabacteroides was increased by Combination of amoxicillin and clavulanate. | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Bifidobacteriales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Bifidobacterium
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[4] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Decrease | |||
| Experimental Species | Human | Experimental Sample | Faeces | |
| Disease or Condition | Healthy | |||
| Description | The abundance of Bifidobacterium was decreased by Combination of amoxicillin and clavulanate. | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Enterobacterales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Enterobacter
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Increase | |||
| Experimental Species | Human | Experimental Sample | Faeces | |
| Disease or Condition | Healthy | |||
| Description | The abundance of Enterobacter was increased by Combination of amoxicillin and clavulanate. | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Enterobacteriaceae
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[5] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Increase | |||
| Experimental Species | Human | Experimental Sample | Faeces | |
| Disease or Condition | Healthy | |||
| Description | The abundance of Enterobacteriaceae was increased by Combination of amoxicillin and clavulanate. | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Escherichia
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Increase | |||
| Experimental Species | Human | Experimental Sample | Faeces | |
| Disease or Condition | Healthy | |||
| Description | The abundance of Escherichia was increased by Combination of amoxicillin and clavulanate. | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Klebsiella
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[5] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Increase | |||
| Experimental Species | Human | Experimental Sample | Faeces | |
| Disease or Condition | Healthy | |||
| Description | The abundance of Klebsiella was increased by Combination of amoxicillin and clavulanate. | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Erysipelotrichales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Catenibacterium
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Decrease | |||
| Experimental Species | Human | Experimental Sample | Faeces | |
| Disease or Condition | Healthy | |||
| Description | The abundance of Catenibacterium was decreased by Combination of amoxicillin and clavulanate. | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Eubacteriales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Coprococcus
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Increase | |||
| Experimental Species | Human | Experimental Sample | Faeces | |
| Disease or Condition | Healthy | |||
| Description | The abundance of Coprococcus was increased by Combination of amoxicillin and clavulanate. | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Roseburia
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[3] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Decrease | |||
| Experimental Species | Human | Experimental Sample | Faeces | |
| Disease or Condition | Healthy | |||
| Description | The abundance of Roseburia was decreased by Combination of amoxicillin and clavulanate. | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Ruminococcus
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[4] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | No significant change | |||
| Experimental Species | Human | Experimental Sample | Faeces | |
| Disease or Condition | Healthy | |||
| Description | The abundance of Ruminococcus was not significantly changed by Combination of amoxicillin and clavulanate. | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Ruminococcus bromii
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[2] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Decrease | |||
| Experiment Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | The abundance of Ruminococcus bromii was decreased by Clavulanate potassium (adjusted p-values: 8.07E-03). | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Lactobacillales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Enterococcus
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[6] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Increase | |||
| Experimental Species | Human | Experimental Sample | Faeces | |
| Disease or Condition | Healthy | |||
| Description | The abundance of Enterococcus was increased by Combination of amoxicillin and clavulanate. | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Lactobacillus
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[6] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Decrease | |||
| Experimental Species | Human | Experimental Sample | Faeces | |
| Disease or Condition | Healthy | |||
| Description | The abundance of Lactobacillus was decreased by Combination of amoxicillin and clavulanate. | |||
| Target and Pathway | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target(s) | Staphylococcus Beta-lactamase (Stap-coc blaZ) | Target Info | Inhibitor | [1] |
| References | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Emerging therapies for the treatment and prevention of otitis media. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2006 May;11(2):251-64. | |||
| REF 2 | Extensive impact of non-antibiotic drugs on human gut bacteria. Nature. 2018 Mar 29;555(7698):623-628. | |||
| REF 3 | Prospective randomized controlled study on the effects of Saccharomyces boulardii CNCM I-745 and amoxicillin-clavulanate or the combination on the gut microbiota of healthy volunteers. Gut Microbes. 2017 Jan 2;8(1):17-32. | |||
| REF 4 | Long-term changes in human colonic Bifidobacterium populations induced by a 5-day oral amoxicillin-clavulanic acid treatment. PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e50257. | |||
| REF 5 | The influence of flucloxacillin and amoxicillin with clavulanic acid on the aerobic flora of the alimentary tract. Infection. 1987 Jul-Aug;15(4):241-4. | |||
| REF 6 | Ecological effects of linezolid versus amoxicillin/clavulanic acid on the normal intestinal microflora. Scand J Infect Dis. 2001;33(12):899-903. | |||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

