Drug Information
| Drug General Information | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
D00XPB
|
|||
| Former ID |
DIB019179
|
|||
| Drug Name |
PMID22533316C1
|
|||
| Synonyms |
GTPL6709
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||
| Indication | Discovery agent [ICD-11: N.A.] | Investigative | [1], [2] | |
| Structure |
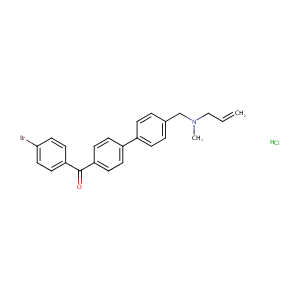 |
Download2D MOL
|
||
| Formula |
C24H23BrClNO
|
|||
| Canonical SMILES |
CN(CC=C)CC1=CC=C(C=C1)C2=CC=C(C=C2)C(=O)C3=CC=C(C=C3)Br.Cl
|
|||
| InChI |
1S/C24H22BrNO.ClH/c1-3-16-26(2)17-18-4-6-19(7-5-18)20-8-10-21(11-9-20)24(27)22-12-14-23(25)15-13-22;/h3-15H,1,16-17H2,2H3;1H
|
|||
| InChIKey |
MCMDJJBPNGLKKM-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|||
| PubChem Compound ID | ||||
| PubChem Substance ID | ||||
| Target and Pathway | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target(s) | Lanosterol synthase (LSS) | Target Info | Inhibitor | [1] |
| BioCyc | Cholesterol biosynthesis II (via 24,25-dihydrolanosterol) | |||
| Cholesterol biosynthesis III (via desmosterol) | ||||
| Cholesterol biosynthesis I | ||||
| Superpathway of cholesterol biosynthesis | ||||
| Lanosterol biosynthesis | ||||
| KEGG Pathway | Steroid biosynthesis | |||
| Metabolic pathways | ||||
| Biosynthesis of antibiotics | ||||
| Panther Pathway | Cholesterol biosynthesis | |||
| Pathwhiz Pathway | Steroid Biosynthesis | |||
| Reactome | Cholesterol biosynthesis | |||
| Activation of gene expression by SREBF (SREBP) | ||||
| WikiPathways | Activation of Gene Expression by SREBP (SREBF) | |||
| SREBP signalling | ||||
| Cholesterol Biosynthesis | ||||
| Cholesterol biosynthesis | ||||
| References | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Cytotoxic effects of combination of oxidosqualene cyclase inhibitors with atorvastatin in human cancer cells. J Med Chem. 2012 Jun 14;55(11):4990-5002. | |||
| REF 2 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 6709). | |||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

