Drug Information
| Drug General Information | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
D00KRE
|
|||
| Former ID |
DIB011348
|
|||
| Drug Name |
Olsalazine
|
|||
| Synonyms |
Azodisal; Dipentum; Olsalazine sodium; Di-mesalazine
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||
| Indication | Ulcerative colitis [ICD-11: DD71; ICD-9: 556] | Approved | [1] | |
| Company |
Pharmacia & Upjohn AB
|
|||
| Structure |
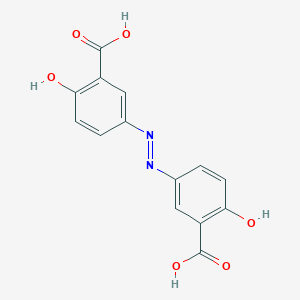 |
Download2D MOL |
||
| Formula |
C14H10N2O6
|
|||
| Canonical SMILES |
C1=CC(=C(C=C1N=NC2=CC(=C(C=C2)O)C(=O)O)C(=O)O)O
|
|||
| InChI |
1S/C14H10N2O6/c17-11-3-1-7(5-9(11)13(19)20)15-16-8-2-4-12(18)10(6-8)14(21)22/h1-6,17-18H,(H,19,20)(H,21,22)
|
|||
| InChIKey |
QQBDLJCYGRGAKP-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|||
| CAS Number |
CAS 15722-48-2
|
|||
| PubChem Compound ID | ||||
| ChEBI ID |
CHEBI:7770
|
|||
| ADReCS Drug ID | BADD_D01607 ; BADD_D01608 | |||
| Interaction between the Drug and Microbe | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Metabolism of Drug Affected by Studied Microbe(s) | ||||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Eubacteriales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Clostridium
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[2] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Microbial Enzyme | Azoreductase | |||
| Metabolic Reaction | Reduction | |||
| Resulting Metabolite | 5-aminosalicylic acid | |||
| Metabolic Effect | Increase activity; Increase toxicity | |||
| Description | Olsalazine can be metabolized to 5-aminosalicylic acid by the azoreductase of Clostridium through reduction, which results in the increase of drug's activity and toxicity. | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Eubacterium
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[2] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Microbial Enzyme | Azoreductase | |||
| Metabolic Reaction | Reduction | |||
| Resulting Metabolite | 5-aminosalicylic acid | |||
| Metabolic Effect | Increase activity; Increase toxicity | |||
| Description | Olsalazine can be metabolized to 5-aminosalicylic acid by the azoreductase of Eubacterium through reduction, which results in the increase of drug's activity and toxicity. | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Gut microbiota | ||||
| Studied Microbe: Gut microbiota unspecific | [3], [4], [5], [6] | |||
| Metabolic Reaction | Azo bond reduction | |||
| Resulting Metabolite | 5-aminosalicylic acid | |||
| Metabolic Effect | Increase activity; Increase side effect (anorexia | |||
| Description | Olsalazine can be metabolized to 5-aminosalicylic acid by gut microbiota through azo bond reduction, which results in the increase of drug's activity and side effect (anorexia, nausea). | |||
| Target and Pathway | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target(s) | Oxidoreductase unspecific (OR) | Target Info | Modulator | [7], [8] |
| References | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT00004288) Phase II Pilot Study of Olsalazine for Ankylosing Spondylitis. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||
| REF 2 | Gut microbiota modulates drug pharmacokinetics. Drug Metab Rev. 2018 Aug;50(3):357-368. | |||
| REF 3 | The influence of gut microbiota on drug metabolism and toxicity. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2016;12(1):31-40. | |||
| REF 4 | Irinotecan in the treatment of colorectal cancer: clinical overview. J Clin Oncol. 2001 Mar 1;19(5):1501-18. | |||
| REF 5 | Cometabolism of microbes and host: implications for drug metabolism and drug-induced toxicity. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2013 Nov;94(5):574-81. | |||
| REF 6 | Human gut microbiota plays a role in the metabolism of drugs. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2016 Sep;160(3):317-26. | |||
| REF 7 | Reaction mechanism of azoreductases suggests convergent evolution with quinone oxidoreductases. Protein Cell. 2010 Aug;1(8):780-90. | |||
| REF 8 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. 2015 | |||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

