Drug Information
| Drug General Information | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
D0U5QK
|
|||
| Former ID |
DAP000776
|
|||
| Drug Name |
Acetaminophen
|
|||
| Synonyms |
acetaminophen; 4-Acetamidophenol; Paracetamol; 103-90-2; Tylenol; N-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)acetamide; APAP; Acetaminofen; Panadol; Datril; p-Hydroxyacetanilide; N-Acetyl-p-aminophenol; p-Acetamidophenol; Algotropyl; Naprinol; Lonarid; 4'-Hydroxyacetanilide; Multin; Acenol; Acamol; Anelix; p-Acetaminophenol; Liquagesic; Acetagesic; Gelocatil; Servigesic; Acetalgin; Abensanil; Pyrinazine; Injectapap; Clixodyne; Valgesic; Tussapap; Finimal; Paracet; Homoolan; Febrolin; Febrilix; Febridol; Dymadon; Anaflon; Apamide; Valadol; Tralgon; Tabalgin; Lestemp; Alvedon; Abenol; Abrol; Abrolet; Acephen; Acertol; Acetaco; Acetamol; Acetavance; Acetofen; Actamin; Actimol; Afebrin; Afebryl; Aferadol; Algesidal; Algina; Algomol; Alpiny; Alpinyl; Amadil; Aminofen; Analter; Anapap; Andox; Anhiba; Antidol; Anuphen; Apacet; Apadon; Apitrelal; Arfen; Arthralgen; Asetam; Asomal; Aspac; Asplin; Atasol; Atralidon; Babikan; Bacetamol; Banesin; Benmyo; Biocetamol; Cadafen; Calapol; Calmanticold; Calonal; Calpol; Capital; Captin; Causalon; Cefalex; Cetadol; Codabrol; Codalgin; Codapane; Codicet; Codisal; Codoliprane; Cofamol; Conacetol; Cosutone; Cuponol; Curadon; Curpol; Custodial; Dafalgan; Darocet; Darvocet; Daygrip; Deminofen; Democyl; Demogripal; Desfebre; Dhamol; Dimindol; Dirox; Disprol; Dolcor; Dolefin; Dolegrippin; Dolgesic; Doliprane; Dolko; Dolofugin; Doloreduct; Dolorfug; Dolorstop; Dolotec; Dolprone; Dorocoff; Dresan; Dristancito; Duaneo; Dularin; Duorol; Duracetamol; Durapan; Dypap; Ecosetol; Elixodyne; Empracet; Enelfa; Eneril; Excipain; Exdol; Fanalgic; Farmadol; Febranine; Febrectal; Febrectol; Febrex; Febricet; Febrin; Febrinol; Fendon; Fensum; Fepanil; Fevor; Finiweh; Fluparmol; Geluprane; Genapap; Genebs; Grippostad; Gynospasmine; Hedex; Ildamol; Inalgex; Infadrops; Janupap; Kataprin; Korum; Labamol; Lekadol; Lemgrip; Lemsip; Liqiprine; Lupocet; Lyteca; Magnidol; Malgis; Malidens; Maxadol; Medocodene; Mexalen; Minafen; Minoset; Miralgin; Momentum; NEBS; Napafen; Nealgyl; NeoCitran; Neodol; Neodolito; Neopap; Neotrend; Neuridon; NilnOcen; Nina; Nobedon; Nodolex; Noral; Ofirmev; Oltyl; Oralgan; Ortensan; Oxycocet; Paceco; Pacemo; Pacemol; Pacet; Pacimol; Paedialgon; Paedol; Painex; Paldesic; Pamol; Panacete; Panadeine; Panadiene; Panaleve; Panamax; Panasorb; Panasorbe; Panets; Panex; Panodil; Panofen; Pantalgin; Paracemol; Paracenol; Paracetamole; Paracetamolo; Paracetanol; Paracetol; Paracin; Paracod; Paracodol; Parador; Paradrops; Parakapton; Parake; Paralen; Paralief; Paralink; Paralyoc; Paramol; Paramolan; Paranox; Parapan; Parasedol; Parasin; Paraspen; Parcetol; Parelan; Parmol; Parogal; Paroma; Pasolind; Pediapirin; Pediatrix; Pedric; Perfalgan; Phendon; Phenipirin; Phogoglandin; Pinex; Piramin; Pirinasol; Plicet; Polmofen; Predimol; Predualito; Prodol; Prompt; Prontina; Puernol; Pulmofen; Pyrigesic; Pyromed; Redutemp; Reliv; Remedol; Rivalgyl; Robigesic; Rounox; RubieMol; Rubophen; Rupemol; Salzone; Sanicet; Sanicopyrine; Scanol; Scentalgyl; Schmerzex; Sedalito; Semolacin; Seskamol; Setakop; Setamol; Setol; Sifenol; Sinaspril; Sinedol; Sinmol; Stanback; Stopain; Sunetheton; Supofen; Suppap; TYL; Tachiprina; Tapanol; Tapar; Tazamol; Temlo; Tempanal; Tempra; Termacet; Termalgin; Termalgine; Termofren; Tiffy; Titralgan; Treuphadol; Tricoton; Tylex; Tylol; Tymol; Upsanol; Utragin; Valorin; Veralgina; Vermidon; Verpol; Vips; Viruflu; Vivimed; Volpan; Zatinol; Zolben; Aceta Elixir; Actifed Plus; Aspirin free anacin; Bayer Select; D oliprane; Dymadon Co; Fortalidon P; Gattaphen T; Gripin Bebe; Helon N; Influbene N; Jin Gang; Lonarid Mono; Lyteca Syrup; Malex N; Panadeine Co; Panale ve; Pasolind N; Spalt N; Supadol mono; Toximer P; Treupel N; Treupel mon; Ty lenol; Tylex CD; Anacin 3; A-Per; Accu-Tap; Ultracet
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||
| Indication | Pain [ICD-11: MG30-MG3Z] | Approved | [1], [2], [3] | |
| Therapeutic Class |
Analgesics
|
|||
| Company |
Beximco Pharma
|
|||
| Structure |
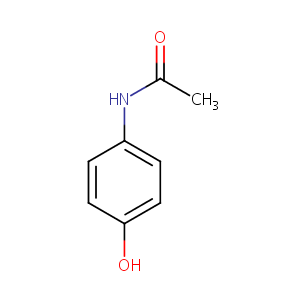 |
Download2D MOL |
||
| Formula |
C8H9NO2
|
|||
| Canonical SMILES |
CC(=O)NC1=CC=C(C=C1)O
|
|||
| InChI |
1S/C8H9NO2/c1-6(10)9-7-2-4-8(11)5-3-7/h2-5,11H,1H3,(H,9,10)
|
|||
| InChIKey |
RZVAJINKPMORJF-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|||
| CAS Number |
CAS 103-90-2
|
|||
| PubChem Compound ID | ||||
| PubChem Substance ID |
9023, 70391, 408305, 609360, 3131814, 4266416, 5199969, 7847284, 7890920, 7978634, 8149184, 8151363, 10321115, 10502811, 11112253, 11114188, 11335835, 11361074, 11362770, 11365332, 11367894, 11371386, 11373699, 11376056, 11462046, 11466896, 11468016, 11483746, 11486572, 11487901, 11490099, 11491955, 11493830, 11532417, 15321628, 17390068, 17436465, 22388563, 24714721, 24715004, 24890717, 24890930, 24891173, 24891200, 26512241, 26611588, 26679279, 26697092, 26747171, 26752236
|
|||
| ChEBI ID |
CHEBI:46195
|
|||
| ADReCS Drug ID | BADD_D00023 | |||
| SuperDrug ATC ID |
N02BE01
|
|||
| SuperDrug CAS ID |
cas=000103902
|
|||
| Interaction between the Drug and Microbe | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Metabolism of Drug Affected by Studied Microbe(s) | ||||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Eubacteriales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Clostridioides difficile
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[4], [5] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Metabolic Reaction | O-sulfation and C-S cleavage | |||
| Resulting Metabolite | Acetaminophen sulfate; glucuronide | |||
| Metabolic Effect | Decrease activity; Increase toxicity | |||
| Description | Acetaminophen can be metabolized to Acetaminophen sulfate and glucuronide by Clostridioides difficile through O-sulfation and C-S cleavage, which results in the decrease of drug's activity and the increase of the drug's toxicity. | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Clostridium
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[6] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Resulting Metabolite | P-cresol | |||
| Description | Acetaminophen can be metabolized to P-cresol by Clostridium. | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Gut microbiota | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Actinobacteria
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[7] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Resulting Metabolite | P-cresol | |||
| Metabolic Effect | Increase toxicity | |||
| Description | Acetaminophen can be metabolized to P-cresol by Actinobacteria, which results in the increase of the drug's toxicity. | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroidetes
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[7] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Resulting Metabolite | P-cresol | |||
| Metabolic Effect | Increase toxicity | |||
| Description | Acetaminophen can be metabolized to P-cresol by Bacteroidetes, which results in the increase of the drug's toxicity. | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Fusobacteria
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[7] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Resulting Metabolite | P-cresol | |||
| Metabolic Effect | Increase toxicity | |||
| Description | Acetaminophen can be metabolized to P-cresol by Fusobacteria, which results in the increase of the drug's toxicity. | |||
| Studied Microbe: Gut microbiota unspecific | [8], [9] | |||
| Resulting Metabolite | N-acetyl p-benzoquuinone imine | |||
| Metabolic Effect | Increase toxicity | |||
| Description | Acetaminophen can be metabolized to N-acetyl p-benzoquuinone imine by gut microbiota, which results in the increase of the drug's toxicity. | |||
| The Abundace of Studied Microbe(s) Regulated by Drug | ||||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Bifidobacteriales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Bifidobacterium dentium
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[10], [11] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Increase | |||
| Experimental Species | Human | Experimental Sample | Faeces | |
| Disease or Condition | Constipation and cystitis | |||
| Description | The abundance of Bifidobacterium dentium was increased by Paracetamol. | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Burkholderiales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Oxalobacteraceae
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[11], [12] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Decrease | |||
| Experimental Species | Human | Experimental Sample | Faeces | |
| Disease or Condition | Constipation | |||
| Description | The abundance of Oxalobacteraceae was decreased by Paracetamol. | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Eubacteriales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Christensenellaceae
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[11], [12] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Decrease | |||
| Experimental Species | Human | Experimental Sample | Faeces | |
| Disease or Condition | Constipation | |||
| Description | The abundance of Christensenellaceae was decreased by Paracetamol. | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Dehalobacteriaceae
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[11], [12] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Decrease | |||
| Experimental Species | Human | Experimental Sample | Faeces | |
| Disease or Condition | Constipation | |||
| Description | The abundance of Dehalobacteriaceae was decreased by Paracetamol. | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Dorea
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[10], [11] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Decrease | |||
| Experimental Species | Human | Experimental Sample | Faeces | |
| Disease or Condition | Constipation and cystitis | |||
| Description | The abundance of Dorea was decreased by Paracetamol. | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Eubacteriaceae
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[11], [12] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Increase | |||
| Experimental Species | Human | Experimental Sample | Faeces | |
| Disease or Condition | Constipation | |||
| Description | The abundance of Eubacteriaceae was increased by Paracetamol. | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Lachnospiraceae
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[10], [11] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Decrease | |||
| Experimental Species | Human | Experimental Sample | Faeces | |
| Disease or Condition | Constipation and cystitis | |||
| Description | The abundance of Lachnospiraceae was decreased by Paracetamol. | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Peptostreptococcaceae
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[11], [12] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Increase | |||
| Experimental Species | Human | Experimental Sample | Faeces | |
| Disease or Condition | Constipation | |||
| Description | The abundance of Peptostreptococcaceae was increased by Paracetamol. | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Lactobacillales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Streptococcaceae
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[11], [12] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Increase | |||
| Experimental Species | Human | Experimental Sample | Faeces | |
| Disease or Condition | Constipation | |||
| Description | The abundance of Streptococcaceae was increased by Paracetamol. | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Streptococcus salivarius
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[10], [11] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Increase | |||
| Experimental Species | Human | Experimental Sample | Faeces | |
| Disease or Condition | Constipation and cystitis | |||
| Description | The abundance of Streptococcus salivarius was increased by Paracetamol. | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Micrococcales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Micrococcaceae
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[11], [12] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Increase | |||
| Experimental Species | Human | Experimental Sample | Faeces | |
| Disease or Condition | Constipation | |||
| Description | The abundance of Micrococcaceae was increased by Paracetamol. | |||
| Target and Pathway | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target(s) | Norepinephrine transporter (NET) | Target Info | Inhibitor | [13] |
| Prostaglandin G/H synthase (COX) | Target Info | Inhibitor | [14], [15], [16] | |
| Serotonin transporter (SERT) | Target Info | Inhibitor | [13] | |
| KEGG Pathway | Serotonergic synapse | |||
| NetPath Pathway | TCR Signaling Pathway | |||
| Panther Pathway | Adrenaline and noradrenaline biosynthesis | |||
| 5HT1 type receptor mediated signaling pathway | ||||
| 5HT2 type receptor mediated signaling pathway | ||||
| 5HT3 type receptor mediated signaling pathway | ||||
| 5HT4 type receptor mediated signaling pathway | ||||
| Reactome | Na+/Cl- dependent neurotransmitter transporters | |||
| WikiPathways | Monoamine Transport | |||
| NRF2 pathway | ||||
| Transport of glucose and other sugars, bile salts and organic acids, metal ions and amine compounds | ||||
| SIDS Susceptibility Pathways | ||||
| Synaptic Vesicle Pathway | ||||
| Serotonin Transporter Activity | ||||
| References | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | The Diversion of Ultram, Ultracet, and generic tramadol HCL. J Addict Dis. 2006;25(2):53-8. | |||
| REF 2 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 5239). | |||
| REF 3 | FDA Approved Drug Products from FDA Official Website. 2009. Application Number: (NDA) 018337. | |||
| REF 4 | The influence of gut microbiota on drug metabolism and toxicity. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2016;12(1):31-40. | |||
| REF 5 | Gut microbiota: what is its place in pharmacology?. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2019 Oct;12(10):921-930. | |||
| REF 6 | Effects of Gut Microbiota on Drug Metabolism and Guidance for Rational Drug Use Under Hypoxic Conditions at High Altitudes. Curr Drug Metab. 2019;20(2):155-165. | |||
| REF 7 | The microbial pharmacists within us: a metagenomic view of xenobiotic metabolism. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2016 Apr;14(5):273-87. | |||
| REF 8 | Pharmacometabonomic identification of a significant host-microbiome metabolic interaction affecting human drug metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Aug 25;106(34):14728-33. | |||
| REF 9 | Gut Microbiome and Response to Cardiovascular Drugs. Circ Genom Precis Med. 2019 Sep;12(9):421-429. | |||
| REF 10 | Impact of commonly used drugs on the composition and metabolic function of the gut microbiota. Nat Commun. 2020 Jan 17;11(1):362. | |||
| REF 11 | Interaction between drugs and the gut microbiome. Gut. 2020 Aug;69(8):1510-1519. | |||
| REF 12 | Gut microbiota associations with common diseases and prescription medications in a population-based cohort. Nat Commun. 2018 Jul 9;9(1):2655. | |||
| REF 13 | Augmentation effect of combination therapy of aripiprazole and antidepressants on forced swimming test in mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2009 Sep;206(1):97-107. | |||
| REF 14 | Mechanism of action of paracetamol. Am J Ther. 2005 Jan-Feb;12(1):46-55. | |||
| REF 15 | COX-3: just another COX or the solitary elusive target of paracetamol Lancet. 2003 Mar 22;361(9362):981-2. | |||
| REF 16 | COX-3, a cyclooxygenase-1 variant inhibited by acetaminophen and other analgesic/antipyretic drugs: cloning, structure, and expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Oct 15;99(21):13926-31. | |||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

