Resistance mutation info of drug
| Drug General Information | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID | D00STL | ||||||||||||||
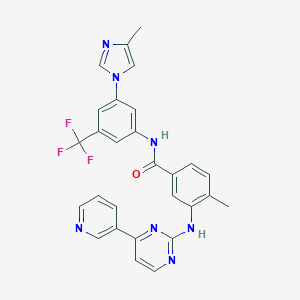
| Drug Name | Nilotinib | ||||||||||||||
| Synonyms | NIL; Nilotinibum; Tasigna (Novartis); Nilotinib (INN/USAN); Nilotinib, AMN107, Tasigna; Tasigna, AMN-107, Nilotinib; L-1-yl)-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]benzamide; Benzamide, 4-methyl-N-[3-(4-methyl-1H-imidazol-1-yl)-5-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-3-[[4-(3-pyridinyl)-2-pyrimidinyl]amino]-(9CI); 4-Methyl-3-[[4-(3-pyridinyl)-2-pyrimidinyl]amino]-N-[5-(4-methyl-1H-imidazo; 4-Methyl-N-(3-(4-methylimidazol-1-yl)-5-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-3-((4-pyridin-3-ylpyrimidin-2-yl)amino)benzamide; 4-Methyl-N-[3-(4-methylimidazol-1-yl)-5-trifluoromethylphenyl]-3-[[4-(pyridin-3-yl)pyrimidin-2-yl]amino]benzamide; 4-methyl-N-[3-(4-methylimidazol-1-yl)-5-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-3-[(4-pyridin-3-ylpyrimidin-2-yl)amino]benzamide; Nilotinib (BCR-ABL inhibitor 2nd gen) | ||||||||||||||
| Drug Type | Small molecular drug | ||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class | Anticancer Agents | ||||||||||||||
| Company | Novartis AG | ||||||||||||||
| Structure |
|
||||||||||||||
| Drug Resistance Mutations | |||||||||||||||
| Target Name | Tyrosine-protein kinase ABL1(ABL1) | Target Info | |||||||||||||
| Gene Name | ABL1 | ||||||||||||||
| Uniprot ID | ABL1_HUMAN | ||||||||||||||
| Species | Homo sapiens | ||||||||||||||
| Reference Sequence |
MLEICLKLVGCKSKKGLSSSSSCYLEEALQRPVASDFEPQGLSEAARWNSKENLLAGPSE NDPNLFVALYDFVASGDNTLSITKGEKLRVLGYNHNGEWCEAQTKNGQGWVPSNYITPVN SLEKHSWYHGPVSRNAAEYLLSSGINGSFLVRESESSPGQRSISLRYEGRVYHYRINTAS DGKLYVSSESRFNTLAELVHHHSTVADGLITTLHYPAPKRNKPTVYGVSPNYDKWEMERT DITMKHKLGGGQYGEVYEGVWKKYSLTVAVKTLKEDTMEVEEFLKEAAVMKEIKHPNLVQ LLGVCTREPPFYIITEFMTYGNLLDYLRECNRQEVNAVVLLYMATQISSAMEYLEKKNFI HRDLAARNCLVGENHLVKVADFGLSRLMTGDTYTAHAGAKFPIKWTAPESLAYNKFSIKS DVWAFGVLLWEIATYGMSPYPGIDLSQVYELLEKDYRMERPEGCPEKVYELMRACWQWNP SDRPSFAEIHQAFETMFQESSISDEVEKELGKQGVRGAVSTLLQAPELPTKTRTSRRAAE HRDTTDVPEMPHSKGQGESDPLDHEPAVSPLLPRKERGPPEGGLNEDERLLPKDKKTNLF SALIKKKKKTAPTPPKRSSSFREMDGQPERRGAGEEEGRDISNGALAFTPLDTADPAKSP KPSNGAGVPNGALRESGGSGFRSPHLWKKSSTLTSSRLATGEEEGGGSSSKRFLRSCSAS CVPHGAKDTEWRSVTLPRDLQSTGRQFDSSTFGGHKSEKPALPRKRAGENRSDQVTRGTV TPPPRLVKKNEEAADEVFKDIMESSPGSSPPNLTPKPLRRQVTVAPASGLPHKEEAGKGS ALGTPAAAEPVTPTSKAGSGAPGGTSKGPAEESRVRRHKHSSESPGRDKGKLSRLKPAPP PPPAASAGKAGGKPSQSPSQEAAGEAVLGAKTKATSLVDAVNSDAAKPSQPGEGLKKPVL PATPKPQSAKPSGTPISPAPVPSTLPSASSALAGDQPSSTAFIPLISTRVSLRKTRQPPE RIASGAITKGVVLDSTEALCLAISRNSEQMASHSAVLEAGKNLYTFCVSYVDSIQQMRNK FAFREAINKLENNLRELQICPATAGSGPAATQDFSKLLSSVKEISDIVQR [Homo sap iens] |
||||||||||||||
| Targeted Disease | Leukemia | ||||||||||||||
| Drug Resistance Mutations |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
| Target Name | UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1-1 (UGT1A1) | Target Info | |||||||||||||
| Gene Name | UGT1A1 | ||||||||||||||
| Uniprot ID | UD11_HUMAN | ||||||||||||||
| Species | Homo sapiens | ||||||||||||||
| Reference Sequence |
MAVESQGGRPLVLGLLLCVLGPVVSHAGKILLIPVDGSHWLSMLGAIQQLQQRGHEIVVL APDASLYIRDGAFYTLKTYPVPFQREDVKESFVSLGHNVFENDSFLQRVIKTYKKIKKDS AMLLSGCSHLLHNKELMASLAESSFDVMLTDPFLPCSPIVAQYLSLPTVFFLHALPCSLE FEATQCPNPFSYVPRPLSSHSDHMTFLQRVKNMLIAFSQNFLCDVVYSPYATLASEFLQR EVTVQDLLSSASVWLFRSDFVKDYPRPIMPNMVFVGGINCLHQNPLSQEFEAYINASGEH GIVVFSLGSMVSEIPEKKAMAIADALGKIPQTVLWRYTGTRPSNLANNTILVKWLPQNDL LGHPMTRAFITHAGSHGVYESICNGVPMVMMPLFGDQMDNAKRMETKGAGVTLNVLEMTS EDLENALKAVINDKSYKENIMRLSSLHKDRPVEPLDLAVFWVEFVMRHKGAPHLRPAAHD LTWYQYHSLDVIGFLLAVVLTVAFITFKCCAYGYRKCLGKKGRVKKAHKSKTH [Homo sapiens] |
||||||||||||||
| Targeted Disease | Leukemia | ||||||||||||||
| Drug Resistance Mutations |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
| References | |||||||||||||||
| REF 1 | BCR-ABL kinase domain mutation analysis in chronic myeloid leukemia patients treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors: recommendations from an expert panel on behalf of European LeukemiaNet. Blood. 2011 Aug 4;118(5):1208-15. | ||||||||||||||
| REF 2 | Role of treatment in the appearance and selection of BCR-ABL1 kinase domain mutations. Mol Diagn Ther. 2012 Aug 1;16(4):251-9. | ||||||||||||||
| REF 3 | Results of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for chronic myelogenous leukemia patients who failed tyrosine kinase inhibitors after developing BCR-ABL1 kinase domain mutations. Blood. 2011 Mar 31;117(13):3641-7. | ||||||||||||||
| REF 4 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. | ||||||||||||||
| REF 5 | Analysis of mutations in the BCR-ABL1 kinase domain, using direct sequencing: detection of the T315I mutation in bone marrow CD34+ cells of a patient with chronic myelogenous leukemia 6 months prior to its emergence in peripheral blood. Mol Diagn Ther. 2012 Jun 1;16(3):163-6. | ||||||||||||||
| REF 6 | Sequential development of mutant clones in an imatinib resistant chronic myeloid leukaemia patient following sequential treatment with multiple tyrosine kinase inhibitors: an emerging problem Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2009 Jun;64(1):195-7. | ||||||||||||||
| REF 7 | Outcome of patients with chronic myeloid leukemia with multiple ABL1 kinase domain mutations receiving tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy. Haematologica. 2011 Jun;96(6):918-21. | ||||||||||||||
| REF 8 | Three novel patient-derived BCR/ABL mutants show different sensitivity to second and third generation tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Am J Hematol. 2012 Nov;87(11):E125-8. | ||||||||||||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

